Qian Dong
GLM-5: from Vibe Coding to Agentic Engineering
Feb 17, 2026Abstract:We present GLM-5, a next-generation foundation model designed to transition the paradigm of vibe coding to agentic engineering. Building upon the agentic, reasoning, and coding (ARC) capabilities of its predecessor, GLM-5 adopts DSA to significantly reduce training and inference costs while maintaining long-context fidelity. To advance model alignment and autonomy, we implement a new asynchronous reinforcement learning infrastructure that drastically improves post-training efficiency by decoupling generation from training. Furthermore, we propose novel asynchronous agent RL algorithms that further improve RL quality, enabling the model to learn from complex, long-horizon interactions more effectively. Through these innovations, GLM-5 achieves state-of-the-art performance on major open benchmarks. Most critically, GLM-5 demonstrates unprecedented capability in real-world coding tasks, surpassing previous baselines in handling end-to-end software engineering challenges. Code, models, and more information are available at https://github.com/zai-org/GLM-5.
LegalOne: A Family of Foundation Models for Reliable Legal Reasoning
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:While Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive general capabilities, their direct application in the legal domain is often hindered by a lack of precise domain knowledge and complexity of performing rigorous multi-step judicial reasoning. To address this gap, we present LegalOne, a family of foundational models specifically tailored for the Chinese legal domain. LegalOne is developed through a comprehensive three-phase pipeline designed to master legal reasoning. First, during mid-training phase, we propose Plasticity-Adjusted Sampling (PAS) to address the challenge of domain adaptation. This perplexity-based scheduler strikes a balance between the acquisition of new knowledge and the retention of original capabilities, effectively establishing a robust legal foundation. Second, during supervised fine-tuning, we employ Legal Agentic CoT Distillation (LEAD) to distill explicit reasoning from raw legal texts. Unlike naive distillation, LEAD utilizes an agentic workflow to convert complex judicial processes into structured reasoning trajectories, thereby enforcing factual grounding and logical rigor. Finally, we implement a Curriculum Reinforcement Learning (RL) strategy. Through a progressive reinforcement process spanning memorization, understanding, and reasoning, LegalOne evolves from simple pattern matching to autonomous and reliable legal reasoning. Experimental results demonstrate that LegalOne achieves state-of-the-art performance across a wide range of legal tasks, surpassing general-purpose LLMs with vastly larger parameter counts through enhanced knowledge density and efficiency. We publicly release the LegalOne weights and the LegalKit evaluation framework to advance the field of Legal AI, paving the way for deploying trustworthy and interpretable foundation models in high-stakes judicial applications.
LangPrecip: Language-Aware Multimodal Precipitation Nowcasting
Dec 26, 2025Abstract:Short-term precipitation nowcasting is an inherently uncertain and under-constrained spatiotemporal forecasting problem, especially for rapidly evolving and extreme weather events. Existing generative approaches rely primarily on visual conditioning, leaving future motion weakly constrained and ambiguous. We propose a language-aware multimodal nowcasting framework(LangPrecip) that treats meteorological text as a semantic motion constraint on precipitation evolution. By formulating nowcasting as a semantically constrained trajectory generation problem under the Rectified Flow paradigm, our method enables efficient and physically consistent integration of textual and radar information in latent space.We further introduce LangPrecip-160k, a large-scale multimodal dataset with 160k paired radar sequences and motion descriptions. Experiments on Swedish and MRMS datasets show consistent improvements over state-of-the-art methods, achieving over 60 \% and 19\% gains in heavy-rainfall CSI at an 80-minute lead time.
GLM-4.5: Agentic, Reasoning, and Coding (ARC) Foundation Models
Aug 08, 2025Abstract:We present GLM-4.5, an open-source Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) large language model with 355B total parameters and 32B activated parameters, featuring a hybrid reasoning method that supports both thinking and direct response modes. Through multi-stage training on 23T tokens and comprehensive post-training with expert model iteration and reinforcement learning, GLM-4.5 achieves strong performance across agentic, reasoning, and coding (ARC) tasks, scoring 70.1% on TAU-Bench, 91.0% on AIME 24, and 64.2% on SWE-bench Verified. With much fewer parameters than several competitors, GLM-4.5 ranks 3rd overall among all evaluated models and 2nd on agentic benchmarks. We release both GLM-4.5 (355B parameters) and a compact version, GLM-4.5-Air (106B parameters), to advance research in reasoning and agentic AI systems. Code, models, and more information are available at https://github.com/zai-org/GLM-4.5.
AdapSCA-PSO: An Adaptive Localization Algorithm with AI-Based Hybrid SCA-PSO for IoT WSNs
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:The accurate localization of sensor nodes is a fundamental requirement for the practical application of the Internet of Things (IoT). To enable robust localization across diverse environments, this paper proposes a hybrid meta-heuristic localization algorithm. Specifically, the algorithm integrates the Sine Cosine Algorithm (SCA), which is effective in global search, with Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), which excels at local search. An adaptive switching module is introduced to dynamically select between the two algorithms. Furthermore, the initialization, fitness evaluation, and parameter settings of the algorithm have been specifically redesigned and optimized to address the characteristics of the node localization problem. Simulation results across varying numbers of sensor nodes demonstrate that, compared to standalone PSO and the unoptimized SCAPSO algorithm, the proposed method significantly reduces the number of required iterations and achieves an average localization error reduction of 84.97%.
Dynamic and Parametric Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Jun 07, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has become a foundational paradigm for equipping large language models (LLMs) with external knowledge, playing a critical role in information retrieval and knowledge-intensive applications. However, conventional RAG systems typically adopt a static retrieve-then-generate pipeline and rely on in-context knowledge injection, which can be suboptimal for complex tasks that require multihop reasoning, adaptive information access, and deeper integration of external knowledge. Motivated by these limitations, the research community has moved beyond static retrieval and in-context knowledge injection. Among the emerging directions, this tutorial delves into two rapidly growing and complementary research areas on RAG: Dynamic RAG and Parametric RAG. Dynamic RAG adaptively determines when and what to retrieve during the LLM's generation process, enabling real-time adaptation to the LLM's evolving information needs. Parametric RAG rethinks how retrieved knowledge should be injected into LLMs, transitioning from input-level to parameter-level knowledge injection for enhanced efficiency and effectiveness. This tutorial offers a comprehensive overview of recent advances in these emerging research areas. It also shares theoretical foundations and practical insights to support and inspire further research in RAG.
LLMs-as-Judges: A Comprehensive Survey on LLM-based Evaluation Methods
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:The rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs) has driven their expanding application across various fields. One of the most promising applications is their role as evaluators based on natural language responses, referred to as ''LLMs-as-judges''. This framework has attracted growing attention from both academia and industry due to their excellent effectiveness, ability to generalize across tasks, and interpretability in the form of natural language. This paper presents a comprehensive survey of the LLMs-as-judges paradigm from five key perspectives: Functionality, Methodology, Applications, Meta-evaluation, and Limitations. We begin by providing a systematic definition of LLMs-as-Judges and introduce their functionality (Why use LLM judges?). Then we address methodology to construct an evaluation system with LLMs (How to use LLM judges?). Additionally, we investigate the potential domains for their application (Where to use LLM judges?) and discuss methods for evaluating them in various contexts (How to evaluate LLM judges?). Finally, we provide a detailed analysis of the limitations of LLM judges and discuss potential future directions. Through a structured and comprehensive analysis, we aim aims to provide insights on the development and application of LLMs-as-judges in both research and practice. We will continue to maintain the relevant resource list at https://github.com/CSHaitao/Awesome-LLMs-as-Judges.
CalibraEval: Calibrating Prediction Distribution to Mitigate Selection Bias in LLMs-as-Judges
Oct 20, 2024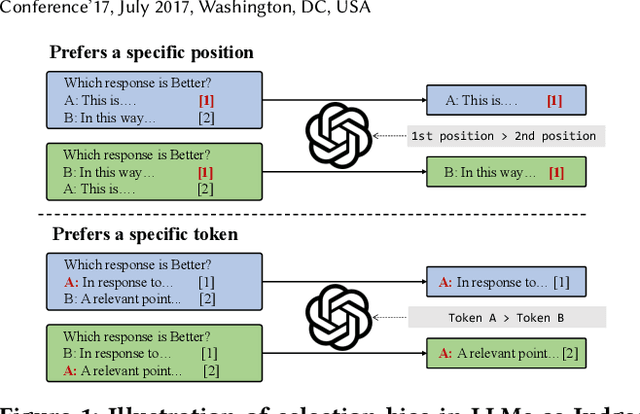
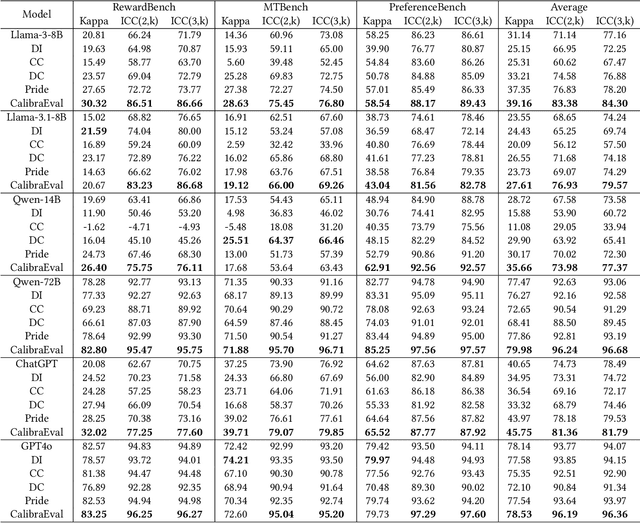
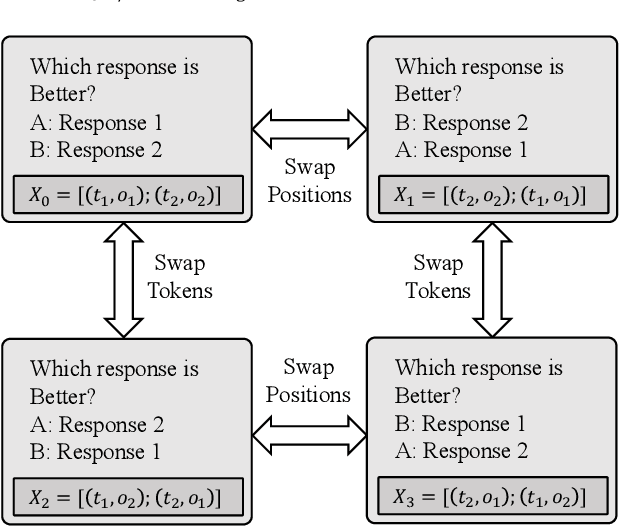
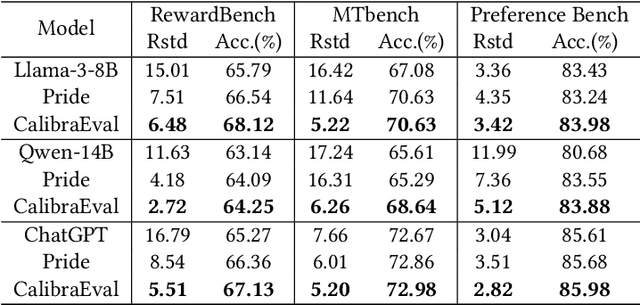
Abstract:The use of large language models (LLMs) as automated evaluation tools to assess the quality of generated natural language, known as LLMs-as-Judges, has demonstrated promising capabilities and is rapidly gaining widespread attention. However, when applied to pairwise comparisons of candidate responses, LLM-based evaluators often exhibit selection bias. Specifically, their judgments may become inconsistent when the option positions or ID tokens are swapped, compromising the effectiveness and fairness of the evaluation result. To address this challenge, we introduce CalibraEval, a novel label-free method for mitigating selection bias during inference. Specifically, CalibraEval reformulates debiasing as an optimization task aimed at adjusting observed prediction distributions to align with unbiased prediction distributions. To solve this optimization problem, we propose a non-parametric order-preserving algorithm (NOA). This algorithm leverages the partial order relationships between model prediction distributions, thereby eliminating the need for explicit labels and precise mathematical function modeling.Empirical evaluations of LLMs in multiple representative benchmarks demonstrate that CalibraEval effectively mitigates selection bias and improves performance compared to existing debiasing methods. This work marks a step toward building more robust and unbiased automated evaluation frameworks, paving the way for improved reliability in AI-driven assessments
BLADE: Enhancing Black-box Large Language Models with Small Domain-Specific Models
Mar 27, 2024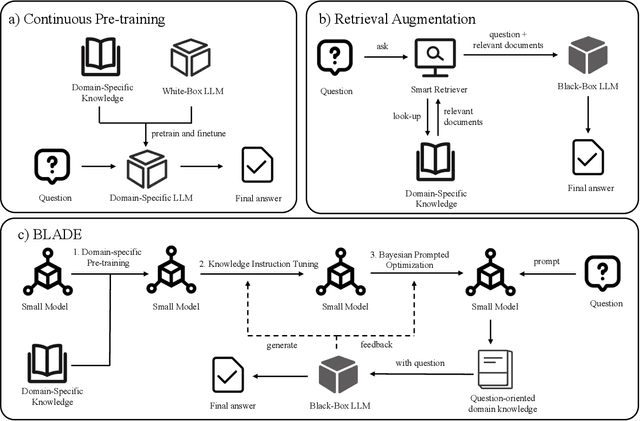
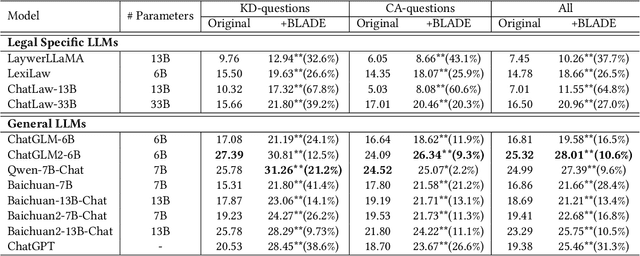
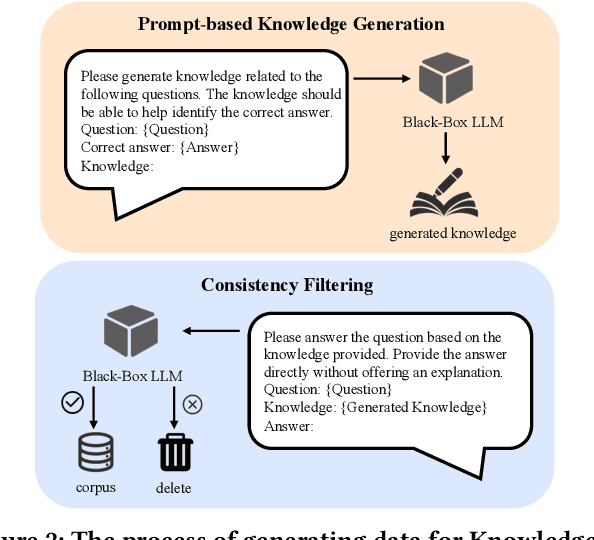
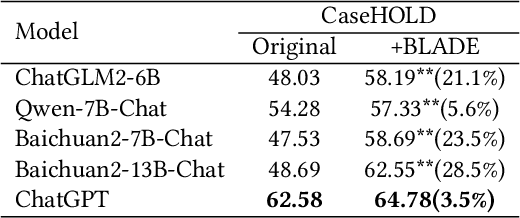
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT and GPT-4 are versatile and capable of addressing a diverse range of tasks. However, general LLMs, which are developed on open-domain data, may lack the domain-specific knowledge essential for tasks in vertical domains, such as legal, medical, etc. To address this issue, previous approaches either conduct continuous pre-training with domain-specific data or employ retrieval augmentation to support general LLMs. Unfortunately, these strategies are either cost-intensive or unreliable in practical applications. To this end, we present a novel framework named BLADE, which enhances Black-box LArge language models with small Domain-spEcific models. BLADE consists of a black-box LLM and a small domain-specific LM. The small LM preserves domain-specific knowledge and offers specialized insights, while the general LLM contributes robust language comprehension and reasoning capabilities. Specifically, our method involves three steps: 1) pre-training the small LM with domain-specific data, 2) fine-tuning this model using knowledge instruction data, and 3) joint Bayesian optimization of the general LLM and the small LM. Extensive experiments conducted on public legal and medical benchmarks reveal that BLADE significantly outperforms existing approaches. This shows the potential of BLADE as an effective and cost-efficient solution in adapting general LLMs for vertical domains.
DELTA: Pre-train a Discriminative Encoder for Legal Case Retrieval via Structural Word Alignment
Mar 27, 2024



Abstract:Recent research demonstrates the effectiveness of using pre-trained language models for legal case retrieval. Most of the existing works focus on improving the representation ability for the contextualized embedding of the [CLS] token and calculate relevance using textual semantic similarity. However, in the legal domain, textual semantic similarity does not always imply that the cases are relevant enough. Instead, relevance in legal cases primarily depends on the similarity of key facts that impact the final judgment. Without proper treatments, the discriminative ability of learned representations could be limited since legal cases are lengthy and contain numerous non-key facts. To this end, we introduce DELTA, a discriminative model designed for legal case retrieval. The basic idea involves pinpointing key facts in legal cases and pulling the contextualized embedding of the [CLS] token closer to the key facts while pushing away from the non-key facts, which can warm up the case embedding space in an unsupervised manner. To be specific, this study brings the word alignment mechanism to the contextual masked auto-encoder. First, we leverage shallow decoders to create information bottlenecks, aiming to enhance the representation ability. Second, we employ the deep decoder to enable translation between different structures, with the goal of pinpointing key facts to enhance discriminative ability. Comprehensive experiments conducted on publicly available legal benchmarks show that our approach can outperform existing state-of-the-art methods in legal case retrieval. It provides a new perspective on the in-depth understanding and processing of legal case documents.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge