Lan Wang
Double Fairness Policy Learning: Integrating Action Fairness and Outcome Fairness in Decision-making
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Fairness is a central pillar of trustworthy machine learning, especially in domains where accuracy- or profit-driven optimization is insufficient. While most fairness research focuses on supervised learning, fairness in policy learning remains less explored. Because policy learning is interventional, it induces two distinct fairness targets: action fairness (equitable action assignments) and outcome fairness (equitable downstream consequences). Crucially, equalizing actions does not generally equalize outcomes when groups face different constraints or respond differently to the same action. We propose a novel double fairness learning (DFL) framework that explicitly manages the trade-off among three objectives: action fairness, outcome fairness, and value maximization. We integrate fairness directly into a multi-objective optimization problem for policy learning and employ a lexicographic weighted Tchebyshev method that recovers Pareto solutions beyond convex settings, with theoretical guarantees on the regret bounds. Our framework is flexible and accommodates various commonly used fairness notions. Extensive simulations demonstrate improved performance relative to competing methods. In applications to a motor third-party liability insurance dataset and an entrepreneurship training dataset, DFL substantially improves both action and outcome fairness while incurring only a modest reduction in overall value.
Causally-Grounded Dual-Path Attention Intervention for Object Hallucination Mitigation in LVLMs
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Object hallucination remains a critical challenge in Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs), where models generate content inconsistent with visual inputs. Existing language-decoder based mitigation approaches often regulate visual or textual attention independently, overlooking their interaction as two key causal factors. To address this, we propose Owl (Bi-mOdal attention reWeighting for Layer-wise hallucination mitigation), a causally-grounded framework that models hallucination process via a structural causal graph, treating decomposed visual and textual attentions as mediators. We introduce VTACR (Visual-to-Textual Attention Contribution Ratio), a novel metric that quantifies the modality contribution imbalance during decoding. Our analysis reveals that hallucinations frequently occur in low-VTACR scenarios, where textual priors dominate and visual grounding is weakened. To mitigate this, we design a fine-grained attention intervention mechanism that dynamically adjusts token- and layer-wise attention guided by VTACR signals. Finally, we propose a dual-path contrastive decoding strategy: one path emphasizes visually grounded predictions, while the other amplifies hallucinated ones -- letting visual truth shine and hallucination collapse. Experimental results on the POPE and CHAIR benchmarks show that Owl achieves significant hallucination reduction, setting a new SOTA in faithfulness while preserving vision-language understanding capability. Our code is available at https://github.com/CikZ2023/OWL
Ming-Omni: A Unified Multimodal Model for Perception and Generation
Jun 11, 2025


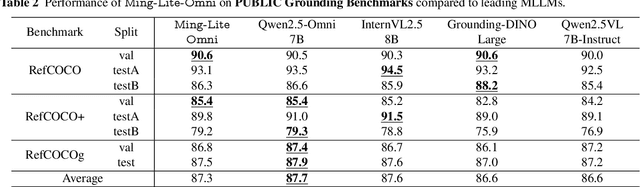
Abstract:We propose Ming-Omni, a unified multimodal model capable of processing images, text, audio, and video, while demonstrating strong proficiency in both speech and image generation. Ming-Omni employs dedicated encoders to extract tokens from different modalities, which are then processed by Ling, an MoE architecture equipped with newly proposed modality-specific routers. This design enables a single model to efficiently process and fuse multimodal inputs within a unified framework, thereby facilitating diverse tasks without requiring separate models, task-specific fine-tuning, or structural redesign. Importantly, Ming-Omni extends beyond conventional multimodal models by supporting audio and image generation. This is achieved through the integration of an advanced audio decoder for natural-sounding speech and Ming-Lite-Uni for high-quality image generation, which also allow the model to engage in context-aware chatting, perform text-to-speech conversion, and conduct versatile image editing. Our experimental results showcase Ming-Omni offers a powerful solution for unified perception and generation across all modalities. Notably, our proposed Ming-Omni is the first open-source model we are aware of to match GPT-4o in modality support, and we release all code and model weights to encourage further research and development in the community.
Multimodal Transformers are Hierarchical Modal-wise Heterogeneous Graphs
May 02, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Sentiment Analysis (MSA) is a rapidly developing field that integrates multimodal information to recognize sentiments, and existing models have made significant progress in this area. The central challenge in MSA is multimodal fusion, which is predominantly addressed by Multimodal Transformers (MulTs). Although act as the paradigm, MulTs suffer from efficiency concerns. In this work, from the perspective of efficiency optimization, we propose and prove that MulTs are hierarchical modal-wise heterogeneous graphs (HMHGs), and we introduce the graph-structured representation pattern of MulTs. Based on this pattern, we propose an Interlaced Mask (IM) mechanism to design the Graph-Structured and Interlaced-Masked Multimodal Transformer (GsiT). It is formally equivalent to MulTs which achieves an efficient weight-sharing mechanism without information disorder through IM, enabling All-Modal-In-One fusion with only 1/3 of the parameters of pure MulTs. A Triton kernel called Decomposition is implemented to ensure avoiding additional computational overhead. Moreover, it achieves significantly higher performance than traditional MulTs. To further validate the effectiveness of GsiT itself and the HMHG concept, we integrate them into multiple state-of-the-art models and demonstrate notable performance improvements and parameter reduction on widely used MSA datasets.
Dynamic QoS Prediction via a Non-Negative Tensor Snowflake Factorization
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Dynamic quality of service (QoS) data exhibit rich temporal patterns in user-service interactions, which are crucial for a comprehensive understanding of user behavior and service conditions in Web service. As the number of users and services increases, there is a large amount of unobserved QoS data, which significantly affects users'choice of services. To predict unobserved QoS data, we propose a Non-negative Snowflake Factorization of tensors model. This method designs a snowflake core tensor to enhance the model's learning capability. Additionally, it employs a single latent factor-based, nonnegative multiplication update on tensor (SLF-NMUT) for parameter learning. Empirical results demonstrate that the proposed model more accurately learns dynamic user-service interaction patterns, thereby yielding improved predictions for missing QoS data.
Water Quality Data Imputation via A Fast Latent Factorization of Tensors with PID-based Optimizer
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:Water quality data can supply a substantial decision support for water resources utilization and pollution prevention. However, there are numerous missing values in water quality data due to inescapable factors like sensor failure, thereby leading to biased result for hydrological analysis and failing to support environmental governance decision accurately. A Latent Factorization of Tensors (LFT) with Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) proves to be an efficient imputation method. However, a standard SGD-based LFT model commonly surfers from the slow convergence that impairs its efficiency. To tackle this issue, this paper proposes a Fast Latent Factorization of Tensors (FLFT) model. It constructs an adjusted instance error into SGD via leveraging a nonlinear PID controller to incorporates the past, current and future information of prediction error for improving convergence rate. Comparing with state-of-art models in real world datasets, the results of experiment indicate that the FLFT model achieves a better convergence rate and higher accuracy.
IV-tuning: Parameter-Efficient Transfer Learning for Infrared-Visible Tasks
Dec 21, 2024Abstract:Infrared-visible (IR-VIS) tasks, such as semantic segmentation and object detection, greatly benefit from the advantage of combining infrared and visible modalities. To inherit the general representations of the Vision Foundation Models (VFMs), task-specific dual-branch networks are designed and fully fine-tuned on downstream datasets. Although effective, this manner lacks generality and is sub-optimal due to the scarcity of downstream infrared-visible datasets and limited transferability. In this paper, we propose a novel and general fine-tuning approach, namely "IV-tuning", to parameter-efficiently harness VFMs for various infrared-visible downstream tasks. At its core, IV-tuning freezes pre-trained visible-based VFMs and integrates modal-specific prompts with adapters within the backbone, bridging the gap between VFMs and downstream infrared-visible tasks while simultaneously learning the complementarity between different modalities. By fine-tuning approximately 3% of the backbone parameters, IV-tuning outperforms full fine-tuning across various baselines in infrared-visible semantic segmentation and object detection, as well as previous state-of-the-art methods. Extensive experiments across various settings demonstrate that IV-tuning achieves superior performance with fewer training parameters, providing a good alternative to full fine-tuning and a novel method of extending visible-based models for infrared-visible tasks. The code is available at https://github.com/Yummy198913/IV-tuning.
Ranking of Large Language Model with Nonparametric Prompts
Dec 07, 2024
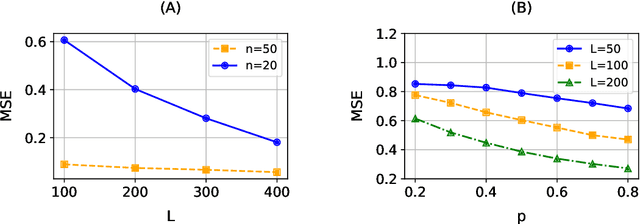
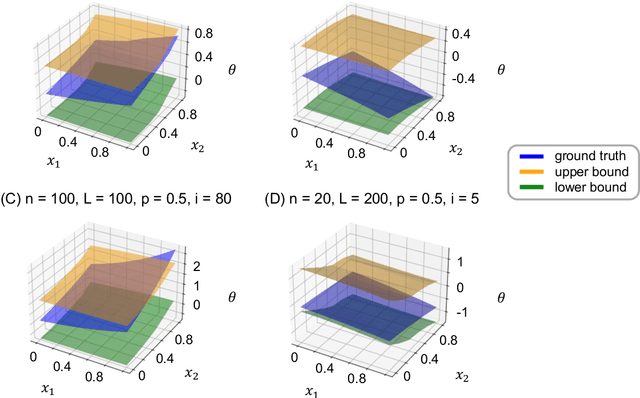
Abstract:We consider the inference for the ranking of large language models (LLMs). Alignment arises as a big challenge to mitigate hallucinations in the use of LLMs. Ranking LLMs has been shown as a well-performing tool to improve alignment based on the best-of-$N$ policy. In this paper, we propose a new inferential framework for testing hypotheses and constructing confidence intervals of the ranking of language models. We consider the widely adopted Bradley-Terry-Luce (BTL) model, where each item is assigned a positive preference score that determines its pairwise comparisons' outcomes. We further extend it into the contextual setting, where the score of each model varies with the prompt. We show the convergence rate of our estimator. By extending the current Gaussian multiplier bootstrap theory to accommodate the supremum of not identically distributed empirical processes, we construct the confidence interval for ranking and propose a valid testing procedure. We also introduce the confidence diagram as a global ranking property. We conduct numerical experiments to assess the performance of our method.
OmniCreator: Self-Supervised Unified Generation with Universal Editing
Dec 03, 2024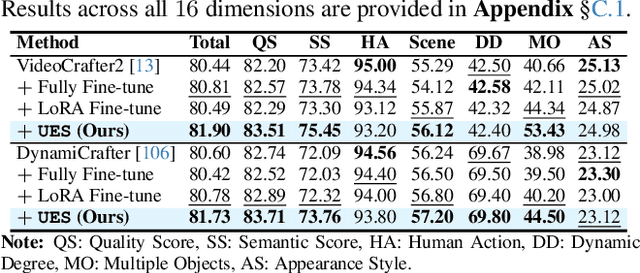
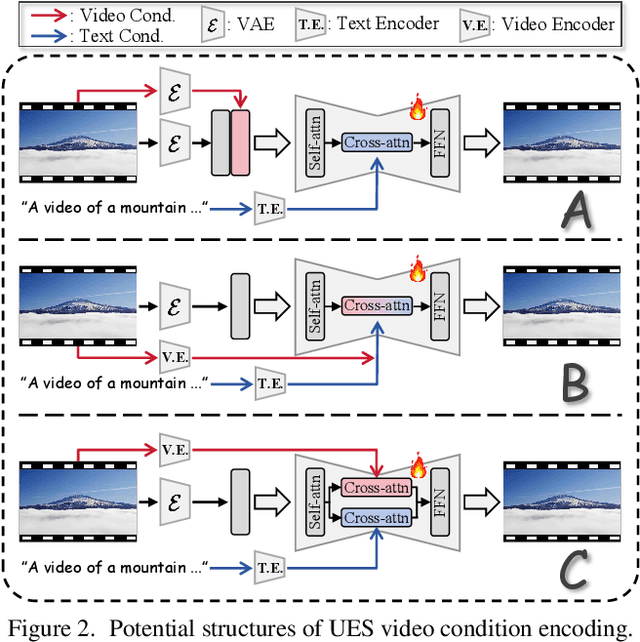
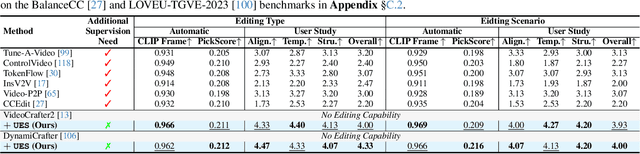
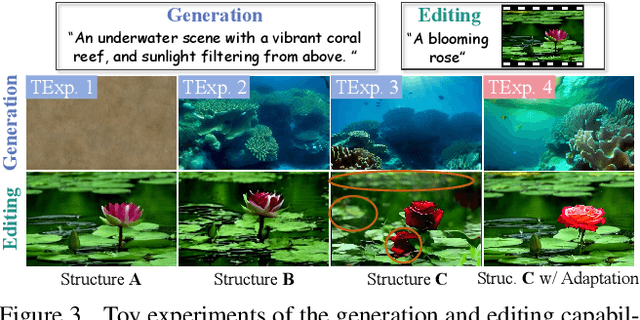
Abstract:We introduce OmniCreator, a novel framework that can conduct text-prompted unified (image+video) generation as well as editing all in one place. OmniCreator acquires generative and universal editing capabilities in a self-supervised manner, taking original text-video pairs as conditions while utilizing the same video as a denoising target to learn the semantic correspondence between video and text. During inference, when presented with a text prompt and a video, OmniCreator is capable of generating a target that is faithful to both, achieving a universal editing effect that is unconstrained as opposed to existing editing work that primarily focuses on certain editing types or relies on additional controls (e.g., structural conditions, attention features, or DDIM inversion). On the other hand, when presented with a text prompt only, OmniCreator becomes generative, producing high-quality video as a result of the semantic correspondence learned. Importantly, we found that the same capabilities extend to images as is, making OmniCreator a truly unified framework. Further, due to the lack of existing generative video editing benchmarks, we introduce the OmniBench-99 dataset, designed to evaluate the performance of generative video editing models comprehensively. Extensive experiments demonstrate that OmniCreator exhibits substantial superiority over all other models.
SEAL: Semantic Attention Learning for Long Video Representation
Dec 02, 2024Abstract:Long video understanding presents challenges due to the inherent high computational complexity and redundant temporal information. An effective representation for long videos must process such redundancy efficiently while preserving essential contents for downstream tasks. This paper introduces SEmantic Attention Learning (SEAL), a novel unified representation for long videos. To reduce computational complexity, long videos are decomposed into three distinct types of semantic entities: scenes, objects, and actions, allowing models to operate on a handful of entities rather than a large number of frames or pixels. To further address redundancy, we propose an attention learning module that balances token relevance with diversity formulated as a subset selection optimization problem. Our representation is versatile, enabling applications across various long video understanding tasks. Extensive experiments show that SEAL significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in video question answering and temporal grounding tasks and benchmarks including LVBench, MovieChat-1K, and Ego4D.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge