Yijie Jin
LoPA: Scaling dLLM Inference via Lookahead Parallel Decoding
Dec 22, 2025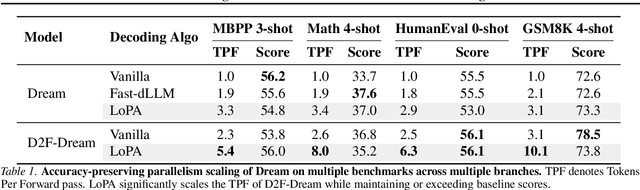
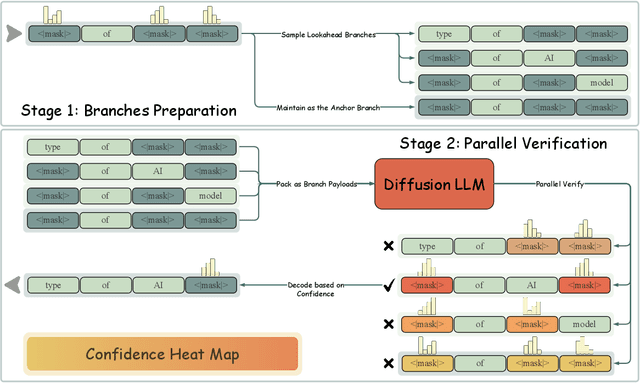
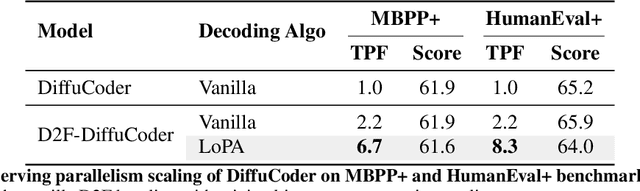
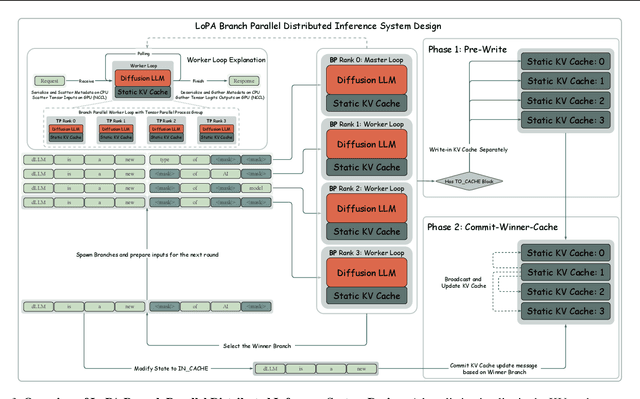
Abstract:Diffusion Large Language Models (dLLMs) have demonstrated significant potential for high-speed inference. However, current confidence-driven decoding strategies are constrained by limited parallelism, typically achieving only 1--3 tokens per forward pass (TPF). In this work, we identify that the degree of parallelism during dLLM inference is highly sensitive to the Token Filling Order (TFO). Then, we introduce Lookahead PArallel Decoding LoPA, a training-free, plug-and-play algorithm, to identify a superior TFO and hence accelerate inference. LoPA concurrently explores distinct candidate TFOs via parallel branches, and selects the one with the highest potential for future parallelism based on branch confidence. We apply LoPA to the state-of-the-art D2F model and observe a substantial enhancement in decoding efficiency. Notably, LoPA increases the TPF of D2F-Dream to 10.1 on the GSM8K while maintaining performance superior to the Dream baseline. Furthermore, to facilitate this unprecedented degree of parallelism, we develop a specialized multi-device inference system featuring Branch Parallelism (BP), which achieves a single-sample throughput of 1073.9 tokens per second under multi-GPU deployment. The code is available at https://github.com/zhijie-group/LoPA.
Multimodal Transformers are Hierarchical Modal-wise Heterogeneous Graphs
May 02, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Sentiment Analysis (MSA) is a rapidly developing field that integrates multimodal information to recognize sentiments, and existing models have made significant progress in this area. The central challenge in MSA is multimodal fusion, which is predominantly addressed by Multimodal Transformers (MulTs). Although act as the paradigm, MulTs suffer from efficiency concerns. In this work, from the perspective of efficiency optimization, we propose and prove that MulTs are hierarchical modal-wise heterogeneous graphs (HMHGs), and we introduce the graph-structured representation pattern of MulTs. Based on this pattern, we propose an Interlaced Mask (IM) mechanism to design the Graph-Structured and Interlaced-Masked Multimodal Transformer (GsiT). It is formally equivalent to MulTs which achieves an efficient weight-sharing mechanism without information disorder through IM, enabling All-Modal-In-One fusion with only 1/3 of the parameters of pure MulTs. A Triton kernel called Decomposition is implemented to ensure avoiding additional computational overhead. Moreover, it achieves significantly higher performance than traditional MulTs. To further validate the effectiveness of GsiT itself and the HMHG concept, we integrate them into multiple state-of-the-art models and demonstrate notable performance improvements and parameter reduction on widely used MSA datasets.
GSIFN: A Graph-Structured and Interlaced-Masked Multimodal Transformer Based Fusion Network for Multimodal Sentiment Analysis
Aug 27, 2024Abstract:Multimodal Sentiment Analysis (MSA) leverages multiple modals to analyze sentiments. Typically, advanced fusion methods and representation learning-based methods are designed to tackle it. Our proposed GSIFN solves two key problems to be solved in MSA: (i) In multimodal fusion, the decoupling of modal combinations and tremendous parameter redundancy in existing fusion methods, which lead to poor fusion performance and efficiency. (ii) The trade-off between representation capability and computation overhead of the unimodal feature extractors and enhancers. GSIFN incorporates two main components to solve these problems: (i) Graph-Structured and Interlaced-Masked Multimodal Transformer. It adopts the Interlaced Mask mechanism to construct robust multimodal graph embedding, achieve all-modal-in-one Transformer-based fusion, and greatly reduce the computation overhead. (ii) A self-supervised learning framework with low computation overhead and high performance, which utilizes a parallelized LSTM with matrix memory to enhance non-verbal modal feature for unimodal label generation. Evaluated on the MSA datasets CMU-MOSI, CMU-MOSEI, and CH-SIMS, GSIFN demonstrates superior performance with significantly lower computation overhead compared with state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge