Haobin Chen
Virtual Width Networks
Nov 17, 2025



Abstract:We introduce Virtual Width Networks (VWN), a framework that delivers the benefits of wider representations without incurring the quadratic cost of increasing the hidden size. VWN decouples representational width from backbone width, expanding the embedding space while keeping backbone compute nearly constant. In our large-scale experiment, an 8-times expansion accelerates optimization by over 2 times for next-token and 3 times for next-2-token prediction. The advantage amplifies over training as both the loss gap grows and the convergence-speedup ratio increases, showing that VWN is not only token-efficient but also increasingly effective with scale. Moreover, we identify an approximately log-linear scaling relation between virtual width and loss reduction, offering an initial empirical basis and motivation for exploring virtual-width scaling as a new dimension of large-model efficiency.
Seed1.5-VL Technical Report
May 11, 2025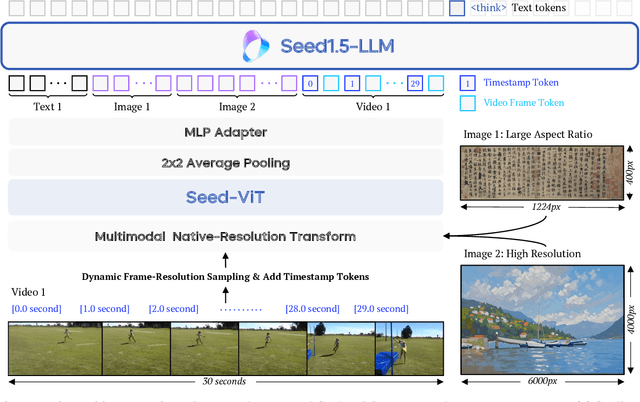

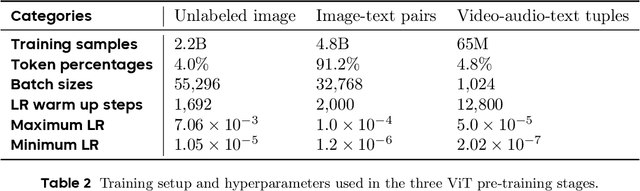
Abstract:We present Seed1.5-VL, a vision-language foundation model designed to advance general-purpose multimodal understanding and reasoning. Seed1.5-VL is composed with a 532M-parameter vision encoder and a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) LLM of 20B active parameters. Despite its relatively compact architecture, it delivers strong performance across a wide spectrum of public VLM benchmarks and internal evaluation suites, achieving the state-of-the-art performance on 38 out of 60 public benchmarks. Moreover, in agent-centric tasks such as GUI control and gameplay, Seed1.5-VL outperforms leading multimodal systems, including OpenAI CUA and Claude 3.7. Beyond visual and video understanding, it also demonstrates strong reasoning abilities, making it particularly effective for multimodal reasoning challenges such as visual puzzles. We believe these capabilities will empower broader applications across diverse tasks. In this report, we mainly provide a comprehensive review of our experiences in building Seed1.5-VL across model design, data construction, and training at various stages, hoping that this report can inspire further research. Seed1.5-VL is now accessible at https://www.volcengine.com/ (Volcano Engine Model ID: doubao-1-5-thinking-vision-pro-250428)
Research on Information Extraction of LCSTS Dataset Based on an Improved BERTSum-LSTM Model
Jun 26, 2024



Abstract:With the continuous advancement of artificial intelligence, natural language processing technology has become widely utilized in various fields. At the same time, there are many challenges in creating Chinese news summaries. First of all, the semantics of Chinese news is complex, and the amount of information is enormous. Extracting critical information from Chinese news presents a significant challenge. Second, the news summary should be concise and clear, focusing on the main content and avoiding redundancy. In addition, the particularity of the Chinese language, such as polysemy, word segmentation, etc., makes it challenging to generate Chinese news summaries. Based on the above, this paper studies the information extraction method of the LCSTS dataset based on an improved BERTSum-LSTM model. We improve the BERTSum-LSTM model to make it perform better in generating Chinese news summaries. The experimental results show that the proposed method has a good effect on creating news summaries, which is of great importance to the construction of news summaries.
Research on an Autonomous UAV Search and Rescue System Based on the Improved
Jun 01, 2024Abstract:The demand is to solve the issue of UAV (unmanned aerial vehicle) operating autonomously and implementing practical functions such as search and rescue in complex unknown environments. This paper proposes an autonomous search and rescue UAV system based on an EGO-Planner algorithm, which is improved by innovative UAV body application and takes the methods of inverse motor backstepping to enhance the overall flight efficiency of the UAV and miniaturization of the whole machine. At the same time, the system introduced the EGO-Planner planning tool, which is optimized by a bidirectional A* algorithm along with an object detection algorithm. It solves the issue of intelligent obstacle avoidance and search and rescue. Through the simulation and field verification work, and compared with traditional algorithms, this method shows more efficiency and reliability in the task. In addition, due to the existing algorithm's improved robustness, this application shows good prospection.
Self-Supervised Video Desmoking for Laparoscopic Surgery
Mar 17, 2024Abstract:Due to the difficulty of collecting real paired data, most existing desmoking methods train the models by synthesizing smoke, generalizing poorly to real surgical scenarios. Although a few works have explored single-image real-world desmoking in unpaired learning manners, they still encounter challenges in handling dense smoke. In this work, we address these issues together by introducing the self-supervised surgery video desmoking (SelfSVD). On the one hand, we observe that the frame captured before the activation of high-energy devices is generally clear (named pre-smoke frame, PS frame), thus it can serve as supervision for other smoky frames, making real-world self-supervised video desmoking practically feasible. On the other hand, in order to enhance the desmoking performance, we further feed the valuable information from PS frame into models, where a masking strategy and a regularization term are presented to avoid trivial solutions. In addition, we construct a real surgery video dataset for desmoking, which covers a variety of smoky scenes. Extensive experiments on the dataset show that our SelfSVD can remove smoke more effectively and efficiently while recovering more photo-realistic details than the state-of-the-art methods. The dataset, codes, and pre-trained models are available at \url{https://github.com/ZcsrenlongZ/SelfSVD}.
Multiple Domain Experts Collaborative Learning: Multi-Source Domain Generalization For Person Re-Identification
May 26, 2021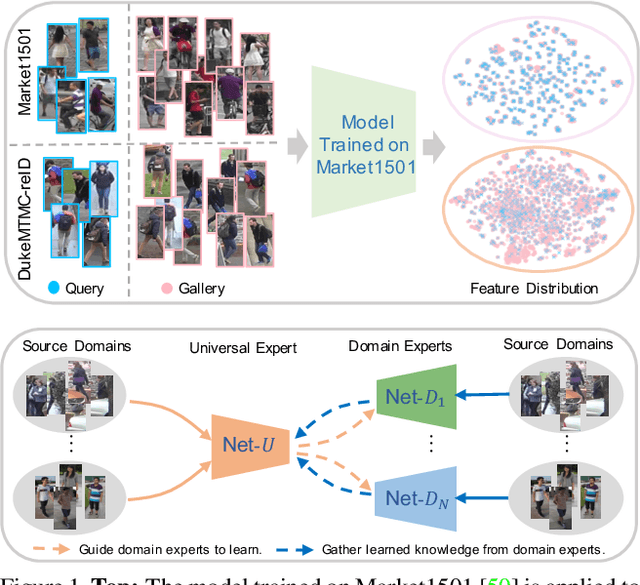
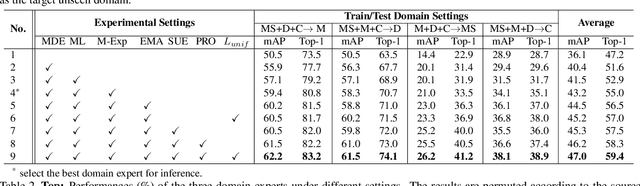
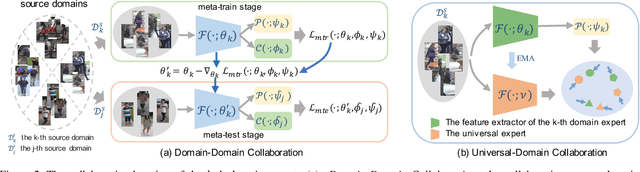
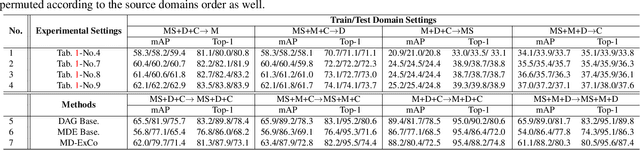
Abstract:Recent years have witnessed significant progress in person re-identification (ReID). However, current ReID approaches suffer from considerable performance degradation when the test target domains exhibit different characteristics from the training ones, known as the domain shift problem. To make ReID more practical and generalizable, we formulate person re-identification as a Domain Generalization (DG) problem and propose a novel training framework, named Multiple Domain Experts Collaborative Learning (MD-ExCo). Specifically, the MD-ExCo consists of a universal expert and several domain experts. Each domain expert focuses on learning from a specific domain, and periodically communicates with other domain experts to regulate its learning strategy in the meta-learning manner to avoid overfitting. Besides, the universal expert gathers knowledge from the domain experts, and also provides supervision to them as feedback. Extensive experiments on DG-ReID benchmarks show that our MD-ExCo outperforms the state-of-the-art methods by a large margin, showing its ability to improve the generalization capability of the ReID models.
Neighbourhood-guided Feature Reconstruction for Occluded Person Re-Identification
May 16, 2021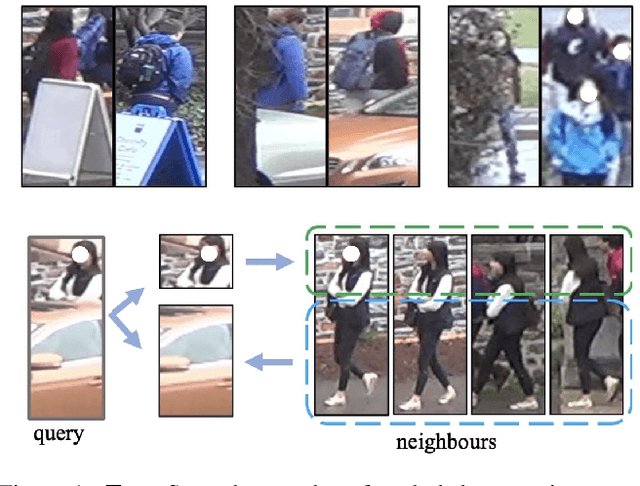
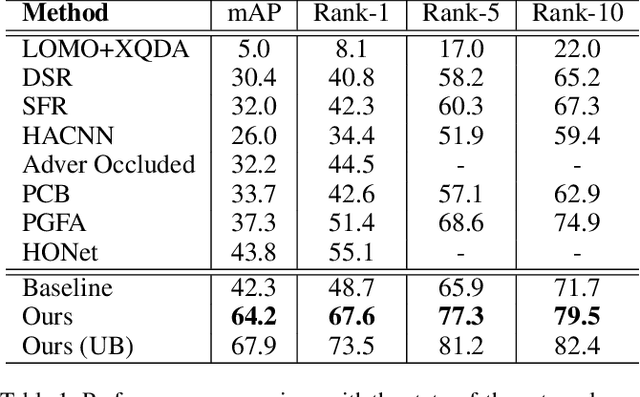
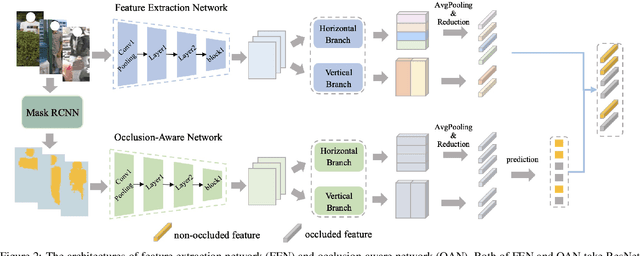
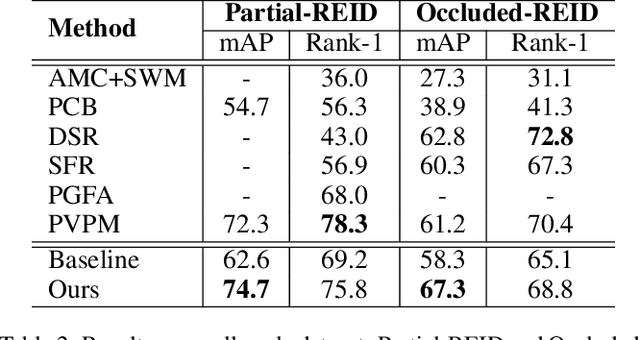
Abstract:Person images captured by surveillance cameras are often occluded by various obstacles, which lead to defective feature representation and harm person re-identification (Re-ID) performance. To tackle this challenge, we propose to reconstruct the feature representation of occluded parts by fully exploiting the information of its neighborhood in a gallery image set. Specifically, we first introduce a visible part-based feature by body mask for each person image. Then we identify its neighboring samples using the visible features and reconstruct the representation of the full body by an outlier-removable graph neural network with all the neighboring samples as input. Extensive experiments show that the proposed approach obtains significant improvements. In the large-scale Occluded-DukeMTMC benchmark, our approach achieves 64.2% mAP and 67.6% rank-1 accuracy which outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches by large margins, i.e.,20.4% and 12.5%, respectively, indicating the effectiveness of our method on occluded Re-ID problem.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge