Xiaowei Gao
Adaptive Classifier-Free Guidance via Dynamic Low-Confidence Masking
May 26, 2025Abstract:Classifier-Free Guidance (CFG) significantly enhances controllability in generative models by interpolating conditional and unconditional predictions. However, standard CFG often employs a static unconditional input, which can be suboptimal for iterative generation processes where model uncertainty varies dynamically. We introduce Adaptive Classifier-Free Guidance (A-CFG), a novel method that tailors the unconditional input by leveraging the model's instantaneous predictive confidence. At each step of an iterative (masked) diffusion language model, A-CFG identifies tokens in the currently generated sequence for which the model exhibits low confidence. These tokens are temporarily re-masked to create a dynamic, localized unconditional input. This focuses CFG's corrective influence precisely on areas of ambiguity, leading to more effective guidance. We integrate A-CFG into a state-of-the-art masked diffusion language model and demonstrate its efficacy. Experiments on diverse language generation benchmarks show that A-CFG yields substantial improvements over standard CFG, achieving, for instance, a 3.9 point gain on GPQA. Our work highlights the benefit of dynamically adapting guidance mechanisms to model uncertainty in iterative generation.
MSD-LLM: Predicting Ship Detention in Port State Control Inspections with Large Language Model
May 26, 2025Abstract:Maritime transportation is the backbone of global trade, making ship inspection essential for ensuring maritime safety and environmental protection. Port State Control (PSC), conducted by national ports, enforces compliance with safety regulations, with ship detention being the most severe consequence, impacting both ship schedules and company reputations. Traditional machine learning methods for ship detention prediction are limited by the capacity of representation learning and thus suffer from low accuracy. Meanwhile, autoencoder-based deep learning approaches face challenges due to the severe data imbalance in learning historical PSC detention records. To address these limitations, we propose Maritime Ship Detention with Large Language Models (MSD-LLM), integrating a dual robust subspace recovery (DSR) layer-based autoencoder with a progressive learning pipeline to handle imbalanced data and extract meaningful PSC representations. Then, a large language model groups and ranks features to identify likely detention cases, enabling dynamic thresholding for flexible detention predictions. Extensive evaluations on 31,707 PSC inspection records from the Asia-Pacific region show that MSD-LLM outperforms state-of-the-art methods more than 12\% on Area Under the Curve (AUC) for Singapore ports. Additionally, it demonstrates robustness to real-world challenges, making it adaptable to diverse maritime risk assessment scenarios.
SMA-Hyper: Spatiotemporal Multi-View Fusion Hypergraph Learning for Traffic Accident Prediction
Jul 24, 2024
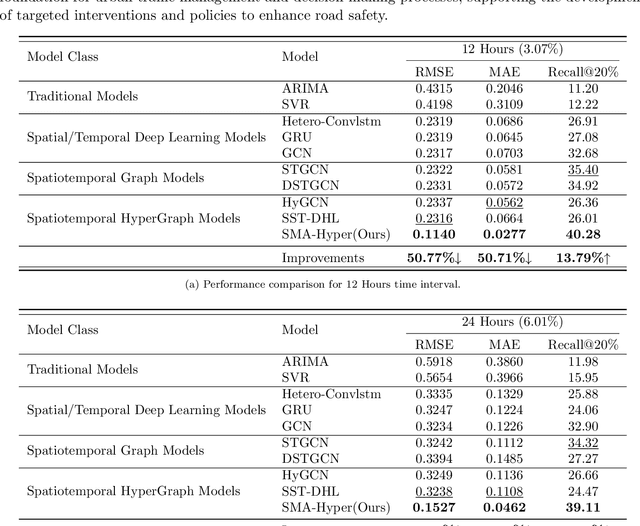

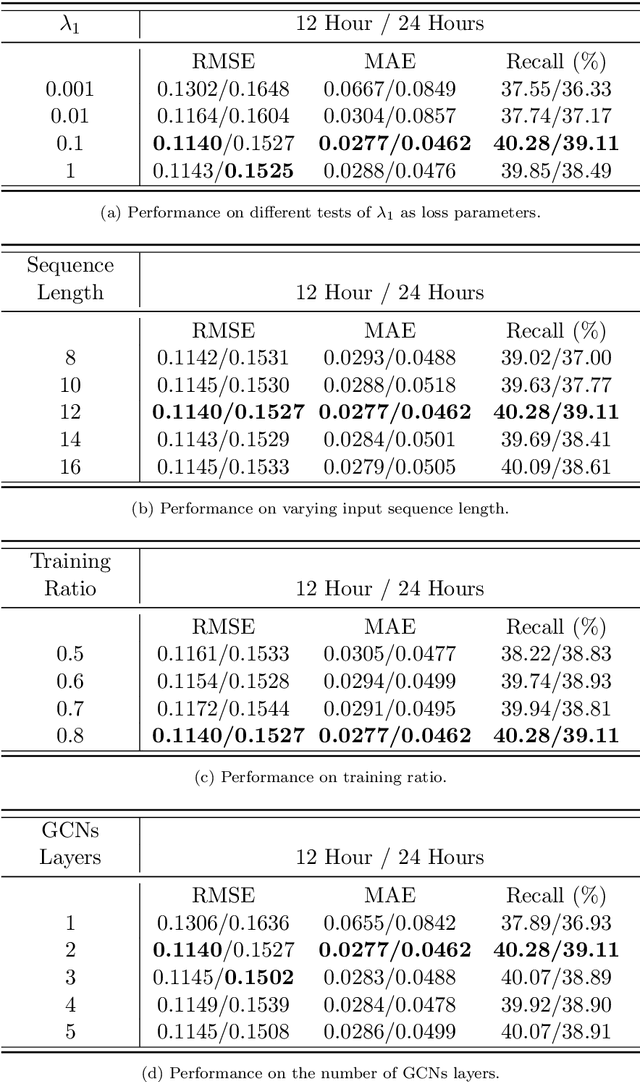
Abstract:Predicting traffic accidents is the key to sustainable city management, which requires effective address of the dynamic and complex spatiotemporal characteristics of cities. Current data-driven models often struggle with data sparsity and typically overlook the integration of diverse urban data sources and the high-order dependencies within them. Additionally, they frequently rely on predefined topologies or weights, limiting their adaptability in spatiotemporal predictions. To address these issues, we introduce the Spatiotemporal Multiview Adaptive HyperGraph Learning (SMA-Hyper) model, a dynamic deep learning framework designed for traffic accident prediction. Building on previous research, this innovative model incorporates dual adaptive spatiotemporal graph learning mechanisms that enable high-order cross-regional learning through hypergraphs and dynamic adaptation to evolving urban data. It also utilises contrastive learning to enhance global and local data representations in sparse datasets and employs an advance attention mechanism to fuse multiple views of accident data and urban functional features, thereby enriching the contextual understanding of risk factors. Extensive testing on the London traffic accident dataset demonstrates that the SMA-Hyper model significantly outperforms baseline models across various temporal horizons and multistep outputs, affirming the effectiveness of its multiview fusion and adaptive learning strategies. The interpretability of the results further underscores its potential to improve urban traffic management and safety by leveraging complex spatiotemporal urban data, offering a scalable framework adaptable to diverse urban environments.
Multiple Object Detection and Tracking in Panoramic Videos for Cycling Safety Analysis
Jul 21, 2024Abstract:Panoramic cycling videos can record 360{\deg} views around the cyclists. Thus, it is essential to conduct automatic road user analysis on them using computer vision models to provide data for studies on cycling safety. However, the features of panoramic data such as severe distortions, large number of small objects and boundary continuity have brought great challenges to the existing CV models, including poor performance and evaluation methods that are no longer applicable. In addition, due to the lack of data with annotations, it is not easy to re-train the models. In response to these problems, the project proposed and implemented a three-step methodology: (1) improve the prediction performance of the pre-trained object detection models on panoramic data by projecting the original image into 4 perspective sub-images; (2) introduce supports for boundary continuity and category information into DeepSORT, a commonly used multiple object tracking model, and set an improved detection model as its detector; (3) using the tracking results, develop an application for detecting the overtaking behaviour of the surrounding vehicles. Evaluated on the panoramic cycling dataset built by the project, the proposed methodology improves the average precision of YOLO v5m6 and Faster RCNN-FPN under any input resolution setting. In addition, it raises MOTA and IDF1 of DeepSORT by 7.6\% and 9.7\% respectively. When detecting the overtakes in the test videos, it achieves the F-score of 0.88. The code is available on GitHub at github.com/cuppp1998/360_object_tracking to ensure the reproducibility and further improvements of results.
OwLore: Outlier-weighed Layerwise Sampled Low-Rank Projection for Memory-Efficient LLM Fine-tuning
May 28, 2024



Abstract:The rapid advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized various natural language processing tasks. However, the substantial size of LLMs presents significant challenges in training or fine-tuning. While parameter-efficient approaches such as low-rank adaptation (LoRA) have gained popularity, they often compromise performance compared to full-rank fine-tuning. In this paper, we propose Outlier-weighed Layerwise Sampled Low-Rank Projection (OwLore), a new memory-efficient fine-tuning approach, inspired by the layerwise outlier distribution of LLMs, which dynamically samples pre-trained layers to fine-tune instead of adding additional adaptors. We first interpret the outlier phenomenon through the lens of Heavy-Tailed Self-Regularization theory (HT-SR), discovering that layers with more outliers tend to be more heavy-tailed and consequently better trained. Inspired by this finding, OwLore strategically assigns higher sampling probabilities to layers with more outliers to better leverage the knowledge stored in pre-trained LLMs. To further mitigate the memory demands of fine-tuning, we integrate gradient low-rank projection into our approach, which facilitates each layer to be efficiently trained in a low-rank manner. By incorporating the efficient characteristics of low-rank and optimal layerwise sampling, OwLore significantly improves the memory-performance trade-off in LLM pruning. Our extensive experiments across various architectures, including LLaMa2, LLaMa3, and Mistral, demonstrate that OwLore consistently outperforms baseline approaches, including full fine-tuning. Specifically, it achieves up to a 1.1% average accuracy gain on the Commonsense Reasoning benchmark, a 3.0% improvement on MMLU, and a notable 10% boost on MT-Bench, while being more memory efficient. OwLore allows us to fine-tune LLaMa2-7B with only 21GB of memory.
Do Sentence Transformers Learn Quasi-Geospatial Concepts from General Text?
Apr 05, 2024



Abstract:Sentence transformers are language models designed to perform semantic search. This study investigates the capacity of sentence transformers, fine-tuned on general question-answering datasets for asymmetric semantic search, to associate descriptions of human-generated routes across Great Britain with queries often used to describe hiking experiences. We find that sentence transformers have some zero-shot capabilities to understand quasi-geospatial concepts, such as route types and difficulty, suggesting their potential utility for routing recommendation systems.
Timeseries Suppliers Allocation Risk Optimization via Deep Black Litterman Model
Jan 30, 2024



Abstract:We introduce the BL model and the Perspective Matrix to optimize supplier selection and order allocation, focusing on both temporal and spatial dynamics. Our development of a Supplier Relationship Network, using a Spatio-Temporal Graph Neural Network, enhances the understanding of complex supplier interdependencies. Additionally, we address credibility issues in zero-order scenarios with a Masked Ranking Mechanism, improving supplier ranking efficiency. Our model demonstrates superior results on two datasets compared to the traditional models. Our evaluations using real-world datasets highlight DBLM's superiority in providing accurate predictions and precise confidence intervals, particularly in high-resolution scenarios.
Spatiotemporal Graph Neural Networks with Uncertainty Quantification for Traffic Incident Risk Prediction
Sep 10, 2023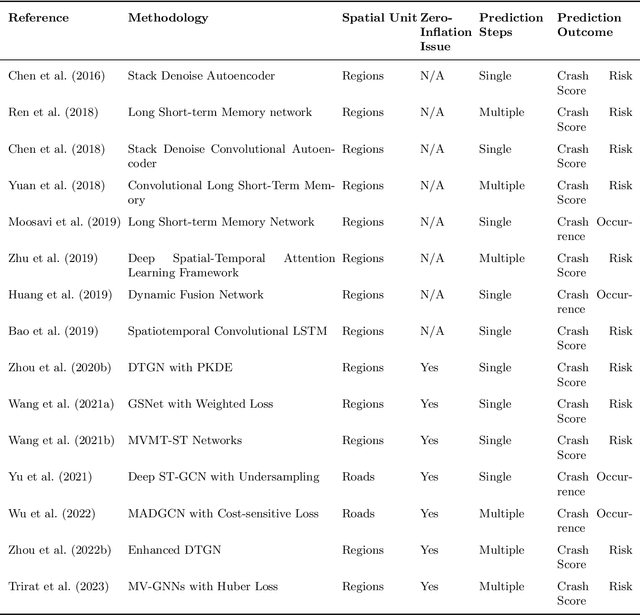
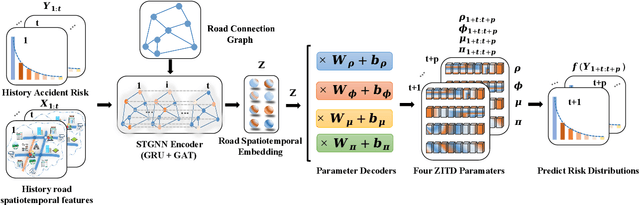

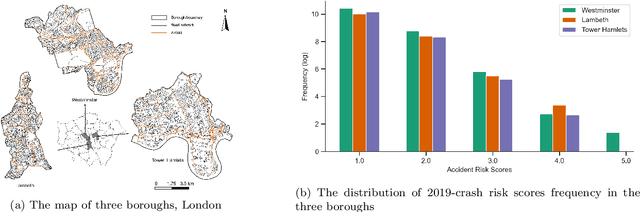
Abstract:Predicting traffic incident risks at granular spatiotemporal levels is challenging. The datasets predominantly feature zero values, indicating no incidents, with sporadic high-risk values for severe incidents. Notably, a majority of current models, especially deep learning methods, focus solely on estimating risk values, overlooking the uncertainties arising from the inherently unpredictable nature of incidents. To tackle this challenge, we introduce the Spatiotemporal Zero-Inflated Tweedie Graph Neural Networks (STZITD-GNNs). Our model merges the reliability of traditional statistical models with the flexibility of graph neural networks, aiming to precisely quantify uncertainties associated with road-level traffic incident risks. This model strategically employs a compound model from the Tweedie family, as a Poisson distribution to model risk frequency and a Gamma distribution to account for incident severity. Furthermore, a zero-inflated component helps to identify the non-incident risk scenarios. As a result, the STZITD-GNNs effectively capture the dataset's skewed distribution, placing emphasis on infrequent but impactful severe incidents. Empirical tests using real-world traffic data from London, UK, demonstrate that our model excels beyond current benchmarks. The forte of STZITD-GNN resides not only in its accuracy but also in its adeptness at curtailing uncertainties, delivering robust predictions over short (7 days) and extended (14 days) timeframes.
Uncertainty Quantification via Spatial-Temporal Tweedie Model for Zero-inflated and Long-tail Travel Demand Prediction
Jun 16, 2023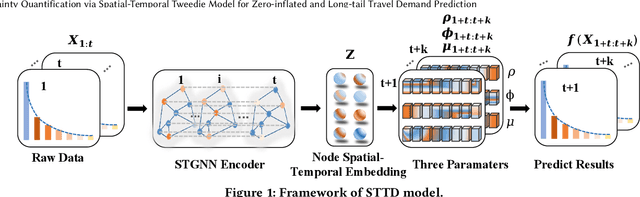
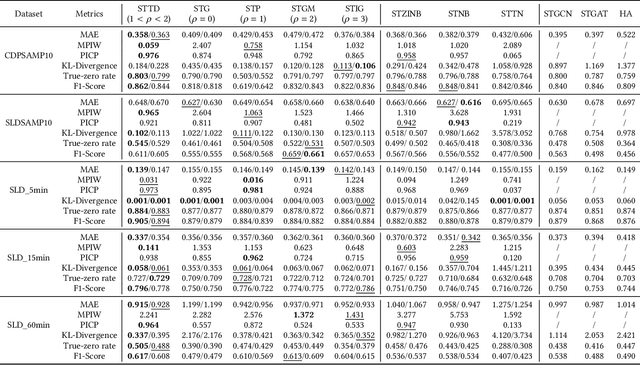
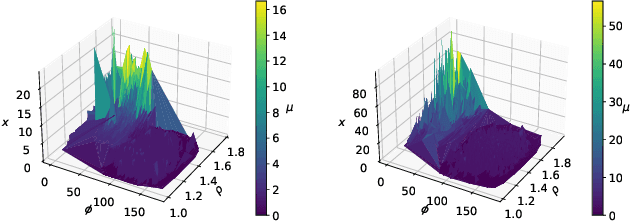
Abstract:crucial for transportation management. However, traditional spatial-temporal deep learning models grapple with addressing the sparse and long-tail characteristics in high-resolution O-D matrices and quantifying prediction uncertainty. This dilemma arises from the numerous zeros and over-dispersed demand patterns within these matrices, which challenge the Gaussian assumption inherent to deterministic deep learning models. To address these challenges, we propose a novel approach: the Spatial-Temporal Tweedie Graph Neural Network (STTD). The STTD introduces the Tweedie distribution as a compelling alternative to the traditional 'zero-inflated' model and leverages spatial and temporal embeddings to parameterize travel demand distributions. Our evaluations using real-world datasets highlight STTD's superiority in providing accurate predictions and precise confidence intervals, particularly in high-resolution scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge