Hao Liang
BrowseComp-$V^3$: A Visual, Vertical, and Verifiable Benchmark for Multimodal Browsing Agents
Feb 13, 2026Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs), equipped with increasingly advanced planning and tool-use capabilities, are evolving into autonomous agents capable of performing multimodal web browsing and deep search in open-world environments. However, existing benchmarks for multimodal browsing remain limited in task complexity, evidence accessibility, and evaluation granularity, hindering comprehensive and reproducible assessments of deep search capabilities. To address these limitations, we introduce BrowseComp-$V^3$, a novel benchmark consisting of 300 carefully curated and challenging questions spanning diverse domains. The benchmark emphasizes deep, multi-level, and cross-modal multi-hop reasoning, where critical evidence is interleaved across textual and visual modalities within and across web pages. All supporting evidence is strictly required to be publicly searchable, ensuring fairness and reproducibility. Beyond final-answer accuracy, we incorporate an expert-validated, subgoal-driven process evaluation mechanism that enables fine-grained analysis of intermediate reasoning behaviors and systematic characterization of capability boundaries. In addition, we propose OmniSeeker, a unified multimodal browsing agent framework integrating diverse web search and visual perception tools. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that even state-of-the-art models achieve only 36% accuracy on our benchmark, revealing critical bottlenecks in multimodal information integration and fine-grained perception. Our results highlight a fundamental gap between current model capabilities and robust multimodal deep search in real-world settings.
Canvas-of-Thought: Grounding Reasoning via Mutable Structured States
Feb 11, 2026Abstract:While Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting has significantly advanced the reasoning capabilities of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), relying solely on linear text sequences remains a bottleneck for complex tasks. We observe that even when auxiliary visual elements are interleaved, they are often treated as static snapshots within a one-dimensional, unstructured reasoning chain. We argue that such approaches treat reasoning history as an immutable stream: correcting a local error necessitates either generating verbose downstream corrections or regenerating the entire context. This forces the model to implicitly maintain and track state updates, significantly increasing token consumption and cognitive load. This limitation is particularly acute in high-dimensional domains, such as geometry and SVG design, where the textual expression of CoT lacks explicit visual guidance, further constraining the model's reasoning precision. To bridge this gap, we introduce \textbf{Canvas-of-Thought (Canvas-CoT)}. By leveraging a HTML Canvas as an external reasoning substrate, Canvas-CoT empowers the model to perform atomic, DOM-based CRUD operations. This architecture enables in-place state revisions without disrupting the surrounding context, allowing the model to explicitly maintain the "ground truth". Furthermore, we integrate a rendering-based critique loop that serves as a hard constraint validator, providing explicit visual feedback to resolve complex tasks that are difficult to articulate through text alone. Extensive experiments on VCode, RBench-V, and MathVista demonstrate that Canvas-CoT significantly outperforms existing baselines, establishing a new paradigm for context-efficient multimodal reasoning.
M2A: Multimodal Memory Agent with Dual-Layer Hybrid Memory for Long-Term Personalized Interactions
Feb 07, 2026Abstract:This work addresses the challenge of personalized question answering in long-term human-machine interactions: when conversational history spans weeks or months and exceeds the context window, existing personalization mechanisms struggle to continuously absorb and leverage users' incremental concepts, aliases, and preferences. Current personalized multimodal models are predominantly static-concepts are fixed at initialization and cannot evolve during interactions. We propose M2A, an agentic dual-layer hybrid memory system that maintains personalized multimodal information through online updates. The system employs two collaborative agents: ChatAgent manages user interactions and autonomously decides when to query or update memory, while MemoryManager breaks down memory requests from ChatAgent into detailed operations on the dual-layer memory bank, which couples a RawMessageStore (immutable conversation log) with a SemanticMemoryStore (high-level observations), providing memories at different granularities. In addition, we develop a reusable data synthesis pipeline that injects concept-grounded sessions from Yo'LLaVA and MC-LLaVA into LoCoMo long conversations while preserving temporal coherence. Experiments show that M2A significantly outperforms baselines, demonstrating that transforming personalization from one-shot configuration to a co-evolving memory mechanism provides a viable path for high-quality individualized responses in long-term multimodal interactions. The code is available at https://github.com/Little-Fridge/M2A.
How Does the Lagrangian Guide Safe Reinforcement Learning through Diffusion Models?
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Diffusion policy sampling enables reinforcement learning (RL) to represent multimodal action distributions beyond suboptimal unimodal Gaussian policies. However, existing diffusion-based RL methods primarily focus on offline settings for reward maximization, with limited consideration of safety in online settings. To address this gap, we propose Augmented Lagrangian-Guided Diffusion (ALGD), a novel algorithm for off-policy safe RL. By revisiting optimization theory and energy-based model, we show that the instability of primal-dual methods arises from the non-convex Lagrangian landscape. In diffusion-based safe RL, the Lagrangian can be interpreted as an energy function guiding the denoising dynamics. Counterintuitively, direct usage destabilizes both policy generation and training. ALGD resolves this issue by introducing an augmented Lagrangian that locally convexifies the energy landscape, yielding a stabilized policy generation and training process without altering the distribution of the optimal policy. Theoretical analysis and extensive experiments demonstrate that ALGD is both theoretically grounded and empirically effective, achieving strong and stable performance across diverse environments.
Research on World Models Is Not Merely Injecting World Knowledge into Specific Tasks
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:World models have emerged as a critical frontier in AI research, aiming to enhance large models by infusing them with physical dynamics and world knowledge. The core objective is to enable agents to understand, predict, and interact with complex environments. However, current research landscape remains fragmented, with approaches predominantly focused on injecting world knowledge into isolated tasks, such as visual prediction, 3D estimation, or symbol grounding, rather than establishing a unified definition or framework. While these task-specific integrations yield performance gains, they often lack the systematic coherence required for holistic world understanding. In this paper, we analyze the limitations of such fragmented approaches and propose a unified design specification for world models. We suggest that a robust world model should not be a loose collection of capabilities but a normative framework that integrally incorporates interaction, perception, symbolic reasoning, and spatial representation. This work aims to provide a structured perspective to guide future research toward more general, robust, and principled models of the world.
Why GRPO Needs Normalization: A Local-Curvature Perspective on Adaptive Gradients
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has become a key driver of language model reasoning. Among RL algorithms, Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) is the de facto standard, avoiding the need for a critic by using per-prompt baselines and variance normalization. Yet why and when this normalization helps remains unclear. In this work, we provide an explanation through the lens of local curvature of the sequence-level policy gradient: standard deviation normalization implements an adaptive gradient. Theoretically, under mild conditions, GRPO enjoys a strictly improved convergence rate over unnormalized REINFORCE, with gains characterized by the average within-prompt reward standard deviation across prompts and iterations. Empirically, our analysis on GSM8K and MATH benchmarks reveals three distinct training phases governed by the interplay between feature orthogonality and reward variance: (I) an early acceleration phase where high variance and orthogonality favor adaptive scaling; (II) a relatively stable transition phase; and (III) a late-stage regime where the loss of orthogonality limits further gains. Together, these results provide a principled account of when std normalization helps in GRPO, and offer broader insights into the design of critic-free RL algorithms.
Is Pure Exploitation Sufficient in Exogenous MDPs with Linear Function Approximation?
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Exogenous MDPs (Exo-MDPs) capture sequential decision-making where uncertainty comes solely from exogenous inputs that evolve independently of the learner's actions. This structure is especially common in operations research applications such as inventory control, energy storage, and resource allocation, where exogenous randomness (e.g., demand, arrivals, or prices) drives system behavior. Despite decades of empirical evidence that greedy, exploitation-only methods work remarkably well in these settings, theory has lagged behind: all existing regret guarantees for Exo-MDPs rely on explicit exploration or tabular assumptions. We show that exploration is unnecessary. We propose Pure Exploitation Learning (PEL) and prove the first general finite-sample regret bounds for exploitation-only algorithms in Exo-MDPs. In the tabular case, PEL achieves $\widetilde{O}(H^2|Ξ|\sqrt{K})$. For large, continuous endogenous state spaces, we introduce LSVI-PE, a simple linear-approximation method whose regret is polynomial in the feature dimension, exogenous state space, and horizon, independent of the endogenous state and action spaces. Our analysis introduces two new tools: counterfactual trajectories and Bellman-closed feature transport, which together allow greedy policies to have accurate value estimates without optimism. Experiments on synthetic and resource-management tasks show that PEL consistently outperforming baselines. Overall, our results overturn the conventional wisdom that exploration is required, demonstrating that in Exo-MDPs, pure exploitation is enough.
MathMixup: Boosting LLM Mathematical Reasoning with Difficulty-Controllable Data Synthesis and Curriculum Learning
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:In mathematical reasoning tasks, the advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs) relies heavily on high-quality training data with clearly defined and well-graded difficulty levels. However, existing data synthesis methods often suffer from limited diversity and lack precise control over problem difficulty, making them insufficient for supporting efficient training paradigms such as curriculum learning. To address these challenges, we propose MathMixup, a novel data synthesis paradigm that systematically generates high-quality, difficulty-controllable mathematical reasoning problems through hybrid and decomposed strategies. Automated self-checking and manual screening are incorporated to ensure semantic clarity and a well-structured difficulty gradient in the synthesized data. Building on this, we construct the MathMixupQA dataset and design a curriculum learning strategy that leverages these graded problems, supporting flexible integration with other datasets. Experimental results show that MathMixup and its curriculum learning strategy significantly enhance the mathematical reasoning performance of LLMs. Fine-tuned Qwen2.5-7B achieves an average score of 52.6\% across seven mathematical benchmarks, surpassing previous state-of-the-art methods. These results fully validate the effectiveness and broad applicability of MathMixup in improving the mathematical reasoning abilities of LLMs and advancing data-centric curriculum learning.
DataFlow: An LLM-Driven Framework for Unified Data Preparation and Workflow Automation in the Era of Data-Centric AI
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:The rapidly growing demand for high-quality data in Large Language Models (LLMs) has intensified the need for scalable, reliable, and semantically rich data preparation pipelines. However, current practices remain dominated by ad-hoc scripts and loosely specified workflows, which lack principled abstractions, hinder reproducibility, and offer limited support for model-in-the-loop data generation. To address these challenges, we present DataFlow, a unified and extensible LLM-driven data preparation framework. DataFlow is designed with system-level abstractions that enable modular, reusable, and composable data transformations, and provides a PyTorch-style pipeline construction API for building debuggable and optimizable dataflows. The framework consists of nearly 200 reusable operators and six domain-general pipelines spanning text, mathematical reasoning, code, Text-to-SQL, agentic RAG, and large-scale knowledge extraction. To further improve usability, we introduce DataFlow-Agent, which automatically translates natural-language specifications into executable pipelines via operator synthesis, pipeline planning, and iterative verification. Across six representative use cases, DataFlow consistently improves downstream LLM performance. Our math, code, and text pipelines outperform curated human datasets and specialized synthetic baselines, achieving up to +3\% execution accuracy in Text-to-SQL over SynSQL, +7\% average improvements on code benchmarks, and 1--3 point gains on MATH, GSM8K, and AIME. Moreover, a unified 10K-sample dataset produced by DataFlow enables base models to surpass counterparts trained on 1M Infinity-Instruct data. These results demonstrate that DataFlow provides a practical and high-performance substrate for reliable, reproducible, and scalable LLM data preparation, and establishes a system-level foundation for future data-centric AI development.
Scone: Bridging Composition and Distinction in Subject-Driven Image Generation via Unified Understanding-Generation Modeling
Dec 14, 2025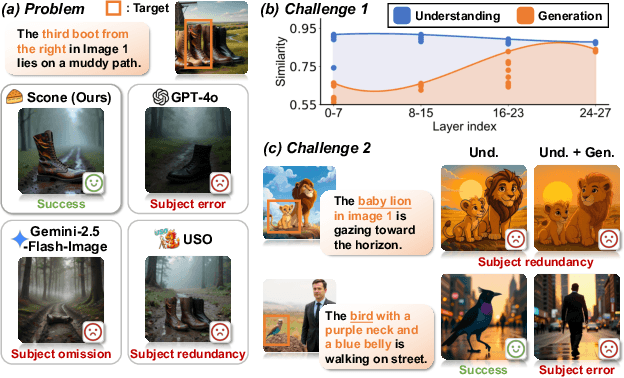
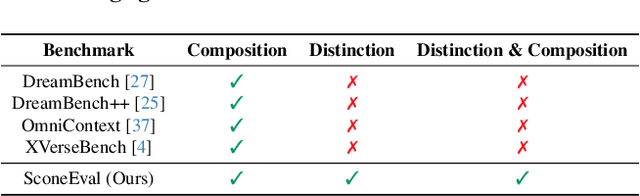
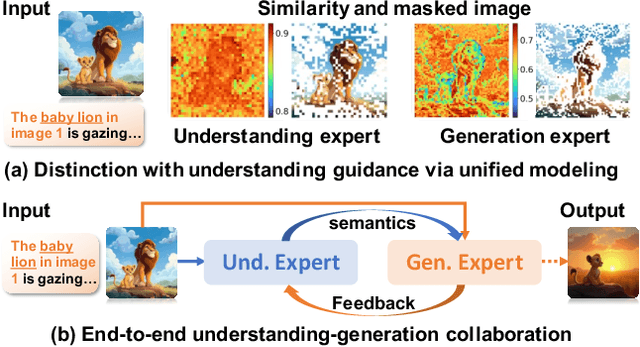
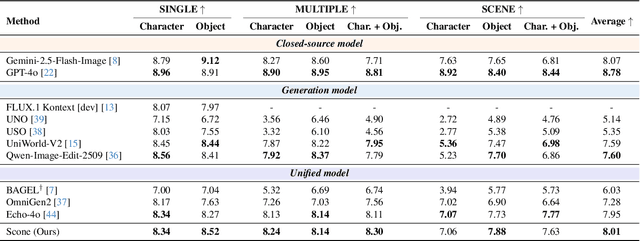
Abstract:Subject-driven image generation has advanced from single- to multi-subject composition, while neglecting distinction, the ability to identify and generate the correct subject when inputs contain multiple candidates. This limitation restricts effectiveness in complex, realistic visual settings. We propose Scone, a unified understanding-generation method that integrates composition and distinction. Scone enables the understanding expert to act as a semantic bridge, conveying semantic information and guiding the generation expert to preserve subject identity while minimizing interference. A two-stage training scheme first learns composition, then enhances distinction through semantic alignment and attention-based masking. We also introduce SconeEval, a benchmark for evaluating both composition and distinction across diverse scenarios. Experiments demonstrate that Scone outperforms existing open-source models in composition and distinction tasks on two benchmarks. Our model, benchmark, and training data are available at: https://github.com/Ryann-Ran/Scone.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge