Xiaochen Ma
Research on World Models Is Not Merely Injecting World Knowledge into Specific Tasks
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:World models have emerged as a critical frontier in AI research, aiming to enhance large models by infusing them with physical dynamics and world knowledge. The core objective is to enable agents to understand, predict, and interact with complex environments. However, current research landscape remains fragmented, with approaches predominantly focused on injecting world knowledge into isolated tasks, such as visual prediction, 3D estimation, or symbol grounding, rather than establishing a unified definition or framework. While these task-specific integrations yield performance gains, they often lack the systematic coherence required for holistic world understanding. In this paper, we analyze the limitations of such fragmented approaches and propose a unified design specification for world models. We suggest that a robust world model should not be a loose collection of capabilities but a normative framework that integrally incorporates interaction, perception, symbolic reasoning, and spatial representation. This work aims to provide a structured perspective to guide future research toward more general, robust, and principled models of the world.
GIFT: Unlocking Global Optimality in Post-Training via Finite-Temperature Gibbs Initialization
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:The prevailing post-training paradigm for Large Reasoning Models (LRMs)--Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) followed by Reinforcement Learning (RL)--suffers from an intrinsic optimization mismatch: the rigid supervision inherent in SFT induces distributional collapse, thereby exhausting the exploration space necessary for subsequent RL. In this paper, we reformulate SFT within a unified post-training framework and propose Gibbs Initialization with Finite Temperature (GIFT). We characterize standard SFT as a degenerate zero-temperature limit that suppresses base priors. Conversely, GIFT incorporates supervision as a finite-temperature energy potential, establishing a distributional bridge that ensures objective consistency throughout the post-training pipeline. Our experiments demonstrate that GIFT significantly outperforms standard SFT and other competitive baselines when utilized for RL initialization, providing a mathematically principled pathway toward achieving global optimality in post-training. Our code is available at https://github.com/zzy1127/GIFT.
DataFlow: An LLM-Driven Framework for Unified Data Preparation and Workflow Automation in the Era of Data-Centric AI
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:The rapidly growing demand for high-quality data in Large Language Models (LLMs) has intensified the need for scalable, reliable, and semantically rich data preparation pipelines. However, current practices remain dominated by ad-hoc scripts and loosely specified workflows, which lack principled abstractions, hinder reproducibility, and offer limited support for model-in-the-loop data generation. To address these challenges, we present DataFlow, a unified and extensible LLM-driven data preparation framework. DataFlow is designed with system-level abstractions that enable modular, reusable, and composable data transformations, and provides a PyTorch-style pipeline construction API for building debuggable and optimizable dataflows. The framework consists of nearly 200 reusable operators and six domain-general pipelines spanning text, mathematical reasoning, code, Text-to-SQL, agentic RAG, and large-scale knowledge extraction. To further improve usability, we introduce DataFlow-Agent, which automatically translates natural-language specifications into executable pipelines via operator synthesis, pipeline planning, and iterative verification. Across six representative use cases, DataFlow consistently improves downstream LLM performance. Our math, code, and text pipelines outperform curated human datasets and specialized synthetic baselines, achieving up to +3\% execution accuracy in Text-to-SQL over SynSQL, +7\% average improvements on code benchmarks, and 1--3 point gains on MATH, GSM8K, and AIME. Moreover, a unified 10K-sample dataset produced by DataFlow enables base models to surpass counterparts trained on 1M Infinity-Instruct data. These results demonstrate that DataFlow provides a practical and high-performance substrate for reliable, reproducible, and scalable LLM data preparation, and establishes a system-level foundation for future data-centric AI development.
Scone: Bridging Composition and Distinction in Subject-Driven Image Generation via Unified Understanding-Generation Modeling
Dec 14, 2025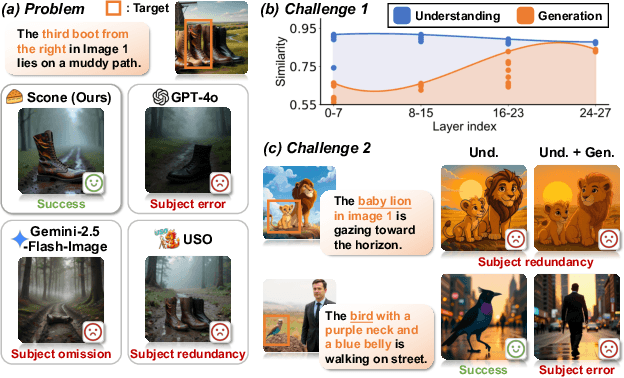
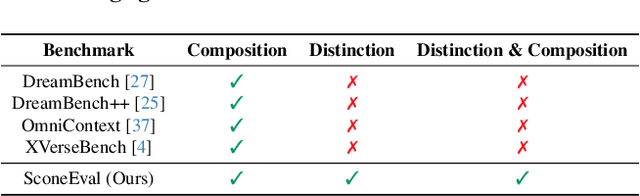
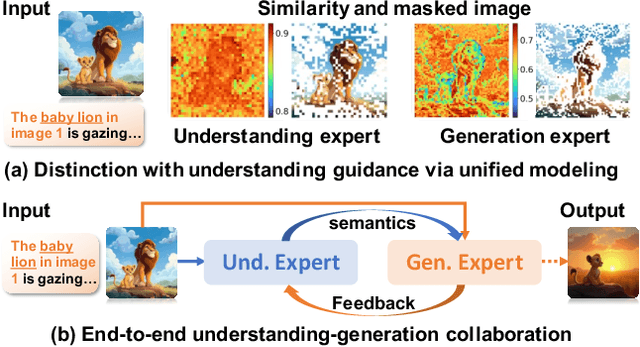
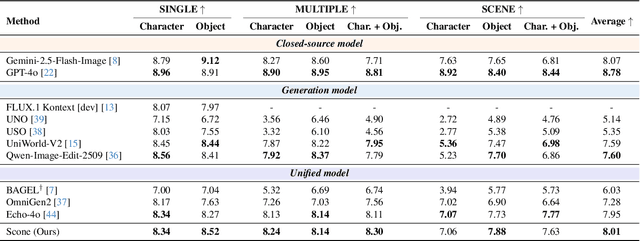
Abstract:Subject-driven image generation has advanced from single- to multi-subject composition, while neglecting distinction, the ability to identify and generate the correct subject when inputs contain multiple candidates. This limitation restricts effectiveness in complex, realistic visual settings. We propose Scone, a unified understanding-generation method that integrates composition and distinction. Scone enables the understanding expert to act as a semantic bridge, conveying semantic information and guiding the generation expert to preserve subject identity while minimizing interference. A two-stage training scheme first learns composition, then enhances distinction through semantic alignment and attention-based masking. We also introduce SconeEval, a benchmark for evaluating both composition and distinction across diverse scenarios. Experiments demonstrate that Scone outperforms existing open-source models in composition and distinction tasks on two benchmarks. Our model, benchmark, and training data are available at: https://github.com/Ryann-Ran/Scone.
Learning What Reinforcement Learning Can't: Interleaved Online Fine-Tuning for Hardest Questions
Jun 09, 2025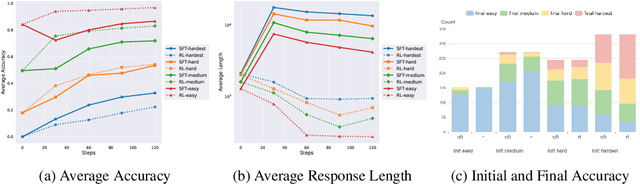
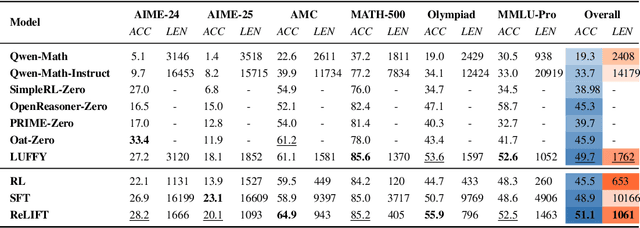
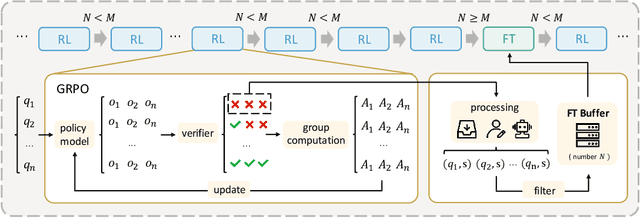
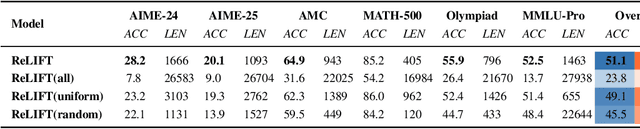
Abstract:Recent advances in large language model (LLM) reasoning have shown that sophisticated behaviors such as planning and self-reflection can emerge through reinforcement learning (RL). However, despite these successes, RL in its current form remains insufficient to induce capabilities that exceed the limitations of the base model, as it is primarily optimized based on existing knowledge of the model rather than facilitating the acquisition of new information. To address this limitation, we employ supervised fine-tuning (SFT) to learn what RL cannot, which enables the incorporation of new knowledge and reasoning patterns by leveraging high-quality demonstration data. We analyze the training dynamics of RL and SFT for LLM reasoning and find that RL excels at maintaining and improving performance on questions within the model's original capabilities, while SFT is more effective at enabling progress on questions beyond the current scope of the model. Motivated by the complementary strengths of RL and SFT, we introduce a novel training approach, \textbf{ReLIFT} (\textbf{Re}inforcement \textbf{L}earning \textbf{I}nterleaved with Online \textbf{F}ine-\textbf{T}uning). In ReLIFT, the model is primarily trained using RL, but when it encounters challenging questions, high-quality solutions are collected for fine-tuning, and the training process alternates between RL and fine-tuning to enhance the model's reasoning abilities. ReLIFT achieves an average improvement of over +5.2 points across five competition-level benchmarks and one out-of-distribution benchmark compared to other zero-RL models. Furthermore, we demonstrate that ReLIFT outperforms both RL and SFT while using only 13\% of the detailed demonstration data, highlighting its scalability. These results provide compelling evidence that ReLIFT overcomes the fundamental limitations of RL and underscores the significant potential.
ForensicHub: A Unified Benchmark & Codebase for All-Domain Fake Image Detection and Localization
May 16, 2025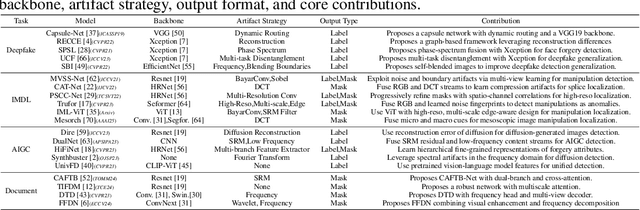
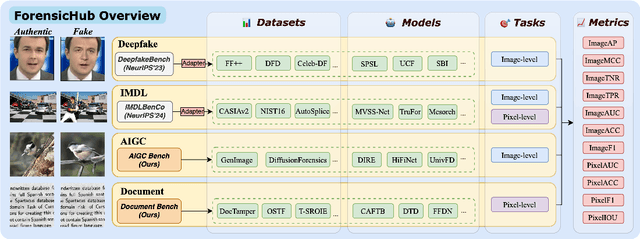
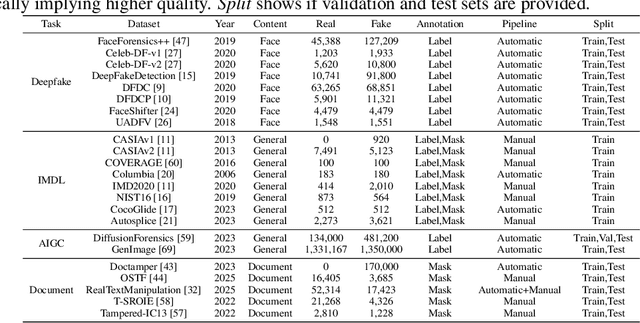
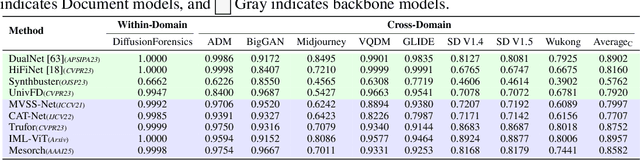
Abstract:The field of Fake Image Detection and Localization (FIDL) is highly fragmented, encompassing four domains: deepfake detection (Deepfake), image manipulation detection and localization (IMDL), artificial intelligence-generated image detection (AIGC), and document image manipulation localization (Doc). Although individual benchmarks exist in some domains, a unified benchmark for all domains in FIDL remains blank. The absence of a unified benchmark results in significant domain silos, where each domain independently constructs its datasets, models, and evaluation protocols without interoperability, preventing cross-domain comparisons and hindering the development of the entire FIDL field. To close the domain silo barrier, we propose ForensicHub, the first unified benchmark & codebase for all-domain fake image detection and localization. Considering drastic variations on dataset, model, and evaluation configurations across all domains, as well as the scarcity of open-sourced baseline models and the lack of individual benchmarks in some domains, ForensicHub: i) proposes a modular and configuration-driven architecture that decomposes forensic pipelines into interchangeable components across datasets, transforms, models, and evaluators, allowing flexible composition across all domains; ii) fully implements 10 baseline models, 6 backbones, 2 new benchmarks for AIGC and Doc, and integrates 2 existing benchmarks of DeepfakeBench and IMDLBenCo through an adapter-based design; iii) conducts indepth analysis based on the ForensicHub, offering 8 key actionable insights into FIDL model architecture, dataset characteristics, and evaluation standards. ForensicHub represents a significant leap forward in breaking the domain silos in the FIDL field and inspiring future breakthroughs.
Dataset Distillation via Committee Voting
Jan 13, 2025Abstract:Dataset distillation aims to synthesize a smaller, representative dataset that preserves the essential properties of the original data, enabling efficient model training with reduced computational resources. Prior work has primarily focused on improving the alignment or matching process between original and synthetic data, or on enhancing the efficiency of distilling large datasets. In this work, we introduce ${\bf C}$ommittee ${\bf V}$oting for ${\bf D}$ataset ${\bf D}$istillation (CV-DD), a novel and orthogonal approach that leverages the collective wisdom of multiple models or experts to create high-quality distilled datasets. We start by showing how to establish a strong baseline that already achieves state-of-the-art accuracy through leveraging recent advancements and thoughtful adjustments in model design and optimization processes. By integrating distributions and predictions from a committee of models while generating high-quality soft labels, our method captures a wider spectrum of data features, reduces model-specific biases and the adverse effects of distribution shifts, leading to significant improvements in generalization. This voting-based strategy not only promotes diversity and robustness within the distilled dataset but also significantly reduces overfitting, resulting in improved performance on post-eval tasks. Extensive experiments across various datasets and IPCs (images per class) demonstrate that Committee Voting leads to more reliable and adaptable distilled data compared to single/multi-model distillation methods, demonstrating its potential for efficient and accurate dataset distillation. Code is available at: https://github.com/Jiacheng8/CV-DD.
Can We Get Rid of Handcrafted Feature Extractors? SparseViT: Nonsemantics-Centered, Parameter-Efficient Image Manipulation Localization Through Spare-Coding Transformer
Dec 19, 2024
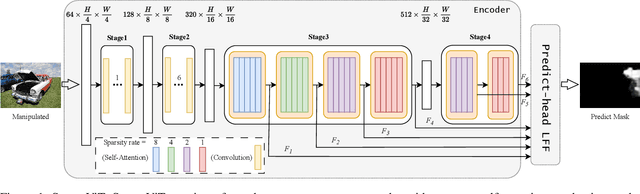
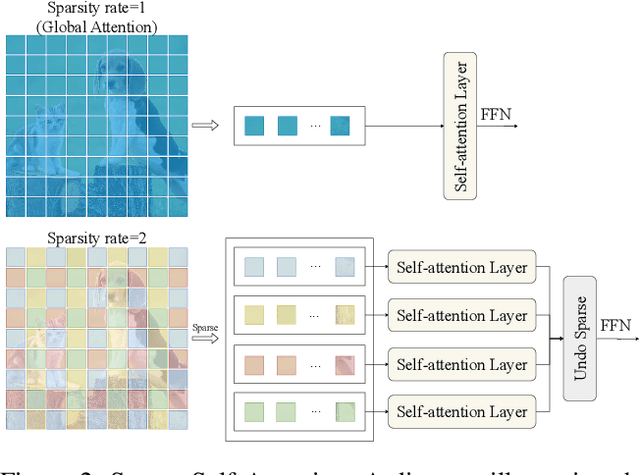
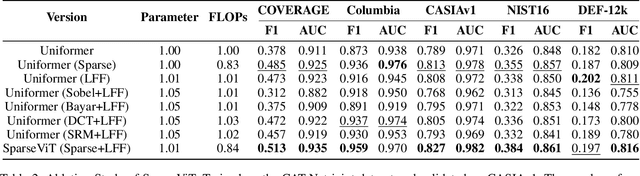
Abstract:Non-semantic features or semantic-agnostic features, which are irrelevant to image context but sensitive to image manipulations, are recognized as evidential to Image Manipulation Localization (IML). Since manual labels are impossible, existing works rely on handcrafted methods to extract non-semantic features. Handcrafted non-semantic features jeopardize IML model's generalization ability in unseen or complex scenarios. Therefore, for IML, the elephant in the room is: How to adaptively extract non-semantic features? Non-semantic features are context-irrelevant and manipulation-sensitive. That is, within an image, they are consistent across patches unless manipulation occurs. Then, spare and discrete interactions among image patches are sufficient for extracting non-semantic features. However, image semantics vary drastically on different patches, requiring dense and continuous interactions among image patches for learning semantic representations. Hence, in this paper, we propose a Sparse Vision Transformer (SparseViT), which reformulates the dense, global self-attention in ViT into a sparse, discrete manner. Such sparse self-attention breaks image semantics and forces SparseViT to adaptively extract non-semantic features for images. Besides, compared with existing IML models, the sparse self-attention mechanism largely reduced the model size (max 80% in FLOPs), achieving stunning parameter efficiency and computation reduction. Extensive experiments demonstrate that, without any handcrafted feature extractors, SparseViT is superior in both generalization and efficiency across benchmark datasets.
Mesoscopic Insights: Orchestrating Multi-scale & Hybrid Architecture for Image Manipulation Localization
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:The mesoscopic level serves as a bridge between the macroscopic and microscopic worlds, addressing gaps overlooked by both. Image manipulation localization (IML), a crucial technique to pursue truth from fake images, has long relied on low-level (microscopic-level) traces. However, in practice, most tampering aims to deceive the audience by altering image semantics. As a result, manipulation commonly occurs at the object level (macroscopic level), which is equally important as microscopic traces. Therefore, integrating these two levels into the mesoscopic level presents a new perspective for IML research. Inspired by this, our paper explores how to simultaneously construct mesoscopic representations of micro and macro information for IML and introduces the Mesorch architecture to orchestrate both. Specifically, this architecture i) combines Transformers and CNNs in parallel, with Transformers extracting macro information and CNNs capturing micro details, and ii) explores across different scales, assessing micro and macro information seamlessly. Additionally, based on the Mesorch architecture, the paper introduces two baseline models aimed at solving IML tasks through mesoscopic representation. Extensive experiments across four datasets have demonstrated that our models surpass the current state-of-the-art in terms of performance, computational complexity, and robustness.
M^3:Manipulation Mask Manufacturer for Arbitrary-Scale Super-Resolution Mask
Jul 04, 2024Abstract:In the field of image manipulation localization (IML), the small quantity and poor quality of existing datasets have always been major issues. A dataset containing various types of manipulations will greatly help improve the accuracy of IML models. Images on the internet (such as those on Baidu Tieba's PS Bar) are manipulated using various techniques, and creating a dataset from these images will significantly enrich the types of manipulations in our data. However, images on the internet suffer from resolution and clarity issues, and the masks obtained by simply subtracting the manipulated image from the original contain various noises. These noises are difficult to remove, rendering the masks unusable for IML models. Inspired by the field of change detection, we treat the original and manipulated images as changes over time for the same image and view the data generation task as a change detection task. However, due to clarity issues between images, conventional change detection models perform poorly. Therefore, we introduced a super-resolution module and proposed the Manipulation Mask Manufacturer (MMM) framework. It enhances the resolution of both the original and tampered images, thereby improving image details for better comparison. Simultaneously, the framework converts the original and tampered images into feature embeddings and concatenates them, effectively modeling the context. Additionally, we created the Manipulation Mask Manufacturer Dataset (MMMD), a dataset that covers a wide range of manipulation techniques. We aim to contribute to the fields of image forensics and manipulation detection by providing more realistic manipulation data through MMM and MMMD. Detailed information about MMMD and the download link can be found at: the code and datasets will be made available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge