Zhuohang Jiang
QA-Dragon: Query-Aware Dynamic RAG System for Knowledge-Intensive Visual Question Answering
Aug 07, 2025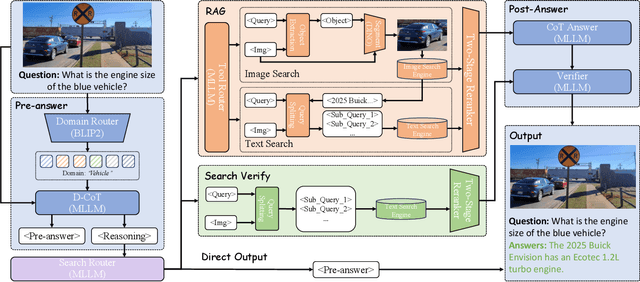
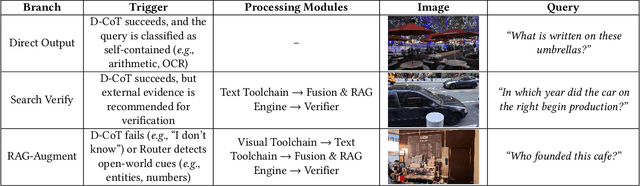
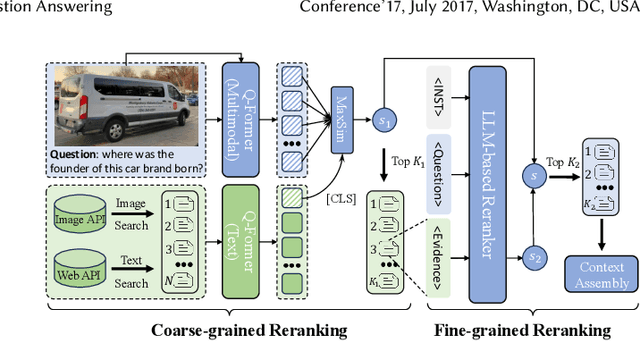
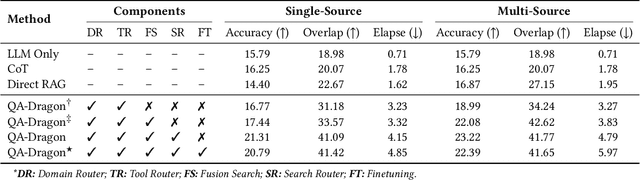
Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has been introduced to mitigate hallucinations in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) by incorporating external knowledge into the generation process, and it has become a widely adopted approach for knowledge-intensive Visual Question Answering (VQA). However, existing RAG methods typically retrieve from either text or images in isolation, limiting their ability to address complex queries that require multi-hop reasoning or up-to-date factual knowledge. To address this limitation, we propose QA-Dragon, a Query-Aware Dynamic RAG System for Knowledge-Intensive VQA. Specifically, QA-Dragon introduces a domain router to identify the query's subject domain for domain-specific reasoning, along with a search router that dynamically selects optimal retrieval strategies. By orchestrating both text and image search agents in a hybrid setup, our system supports multimodal, multi-turn, and multi-hop reasoning, enabling it to tackle complex VQA tasks effectively. We evaluate our QA-Dragon on the Meta CRAG-MM Challenge at KDD Cup 2025, where it significantly enhances the reasoning performance of base models under challenging scenarios. Our framework achieves substantial improvements in both answer accuracy and knowledge overlap scores, outperforming baselines by 5.06% on the single-source task, 6.35% on the multi-source task, and 5.03% on the multi-turn task.
A Survey of WebAgents: Towards Next-Generation AI Agents for Web Automation with Large Foundation Models
Mar 30, 2025Abstract:With the advancement of web techniques, they have significantly revolutionized various aspects of people's lives. Despite the importance of the web, many tasks performed on it are repetitive and time-consuming, negatively impacting overall quality of life. To efficiently handle these tedious daily tasks, one of the most promising approaches is to advance autonomous agents based on Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques, referred to as AI Agents, as they can operate continuously without fatigue or performance degradation. In the context of the web, leveraging AI Agents -- termed WebAgents -- to automatically assist people in handling tedious daily tasks can dramatically enhance productivity and efficiency. Recently, Large Foundation Models (LFMs) containing billions of parameters have exhibited human-like language understanding and reasoning capabilities, showing proficiency in performing various complex tasks. This naturally raises the question: `Can LFMs be utilized to develop powerful AI Agents that automatically handle web tasks, providing significant convenience to users?' To fully explore the potential of LFMs, extensive research has emerged on WebAgents designed to complete daily web tasks according to user instructions, significantly enhancing the convenience of daily human life. In this survey, we comprehensively review existing research studies on WebAgents across three key aspects: architectures, training, and trustworthiness. Additionally, several promising directions for future research are explored to provide deeper insights.
HiBench: Benchmarking LLMs Capability on Hierarchical Structure Reasoning
Mar 02, 2025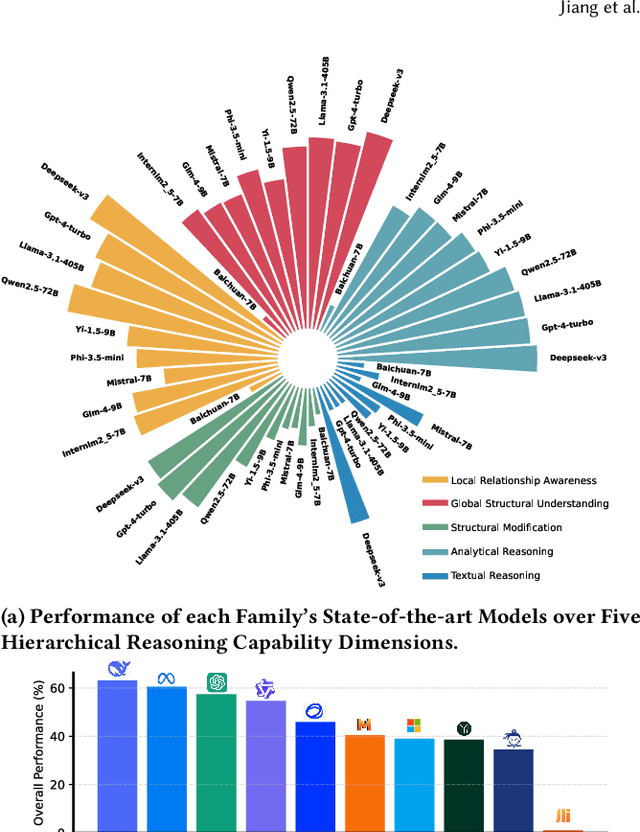
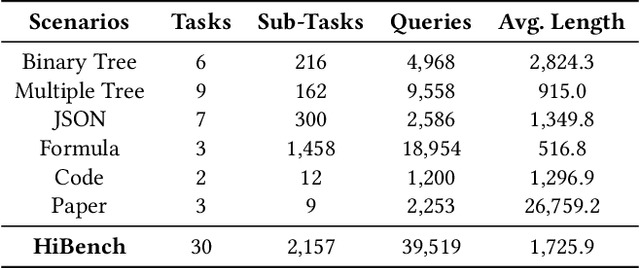
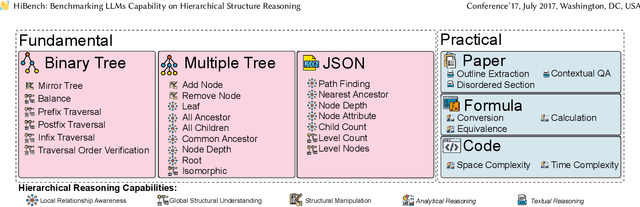
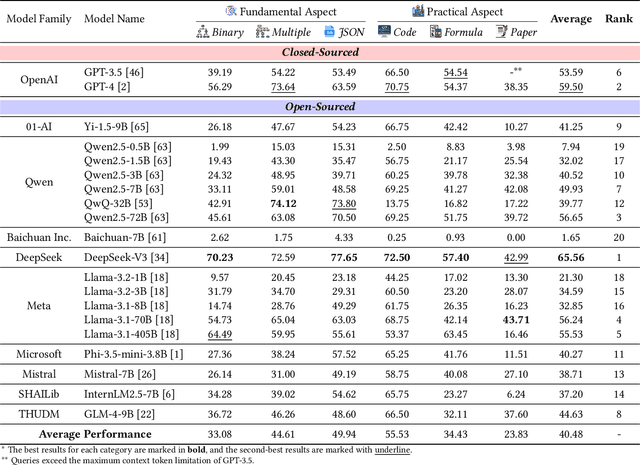
Abstract:Structure reasoning is a fundamental capability of large language models (LLMs), enabling them to reason about structured commonsense and answer multi-hop questions. However, existing benchmarks for structure reasoning mainly focus on horizontal and coordinate structures (\emph{e.g.} graphs), overlooking the hierarchical relationships within them. Hierarchical structure reasoning is crucial for human cognition, particularly in memory organization and problem-solving. It also plays a key role in various real-world tasks, such as information extraction and decision-making. To address this gap, we propose HiBench, the first framework spanning from initial structure generation to final proficiency assessment, designed to benchmark the hierarchical reasoning capabilities of LLMs systematically. HiBench encompasses six representative scenarios, covering both fundamental and practical aspects, and consists of 30 tasks with varying hierarchical complexity, totaling 39,519 queries. To evaluate LLMs comprehensively, we develop five capability dimensions that depict different facets of hierarchical structure understanding. Through extensive evaluation of 20 LLMs from 10 model families, we reveal key insights into their capabilities and limitations: 1) existing LLMs show proficiency in basic hierarchical reasoning tasks; 2) they still struggle with more complex structures and implicit hierarchical representations, especially in structural modification and textual reasoning. Based on these findings, we create a small yet well-designed instruction dataset, which enhances LLMs' performance on HiBench by an average of 88.84\% (Llama-3.1-8B) and 31.38\% (Qwen2.5-7B) across all tasks. The HiBench dataset and toolkit are available here, https://github.com/jzzzzh/HiBench, to encourage evaluation.
Mesoscopic Insights: Orchestrating Multi-scale & Hybrid Architecture for Image Manipulation Localization
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:The mesoscopic level serves as a bridge between the macroscopic and microscopic worlds, addressing gaps overlooked by both. Image manipulation localization (IML), a crucial technique to pursue truth from fake images, has long relied on low-level (microscopic-level) traces. However, in practice, most tampering aims to deceive the audience by altering image semantics. As a result, manipulation commonly occurs at the object level (macroscopic level), which is equally important as microscopic traces. Therefore, integrating these two levels into the mesoscopic level presents a new perspective for IML research. Inspired by this, our paper explores how to simultaneously construct mesoscopic representations of micro and macro information for IML and introduces the Mesorch architecture to orchestrate both. Specifically, this architecture i) combines Transformers and CNNs in parallel, with Transformers extracting macro information and CNNs capturing micro details, and ii) explores across different scales, assessing micro and macro information seamlessly. Additionally, based on the Mesorch architecture, the paper introduces two baseline models aimed at solving IML tasks through mesoscopic representation. Extensive experiments across four datasets have demonstrated that our models surpass the current state-of-the-art in terms of performance, computational complexity, and robustness.
Beyond Visual Appearances: Privacy-sensitive Objects Identification via Hybrid Graph Reasoning
Jun 18, 2024Abstract:The Privacy-sensitive Object Identification (POI) task allocates bounding boxes for privacy-sensitive objects in a scene. The key to POI is settling an object's privacy class (privacy-sensitive or non-privacy-sensitive). In contrast to conventional object classes which are determined by the visual appearance of an object, one object's privacy class is derived from the scene contexts and is subject to various implicit factors beyond its visual appearance. That is, visually similar objects may be totally opposite in their privacy classes. To explicitly derive the objects' privacy class from the scene contexts, in this paper, we interpret the POI task as a visual reasoning task aimed at the privacy of each object in the scene. Following this interpretation, we propose the PrivacyGuard framework for POI. PrivacyGuard contains three stages. i) Structuring: an unstructured image is first converted into a structured, heterogeneous scene graph that embeds rich scene contexts. ii) Data Augmentation: a contextual perturbation oversampling strategy is proposed to create slightly perturbed privacy-sensitive objects in a scene graph, thereby balancing the skewed distribution of privacy classes. iii) Hybrid Graph Generation & Reasoning: the balanced, heterogeneous scene graph is then transformed into a hybrid graph by endowing it with extra "node-node" and "edge-edge" homogeneous paths. These homogeneous paths allow direct message passing between nodes or edges, thereby accelerating reasoning and facilitating the capturing of subtle context changes. Based on this hybrid graph... **For the full abstract, see the original paper.**
IMDL-BenCo: A Comprehensive Benchmark and Codebase for Image Manipulation Detection & Localization
Jun 15, 2024
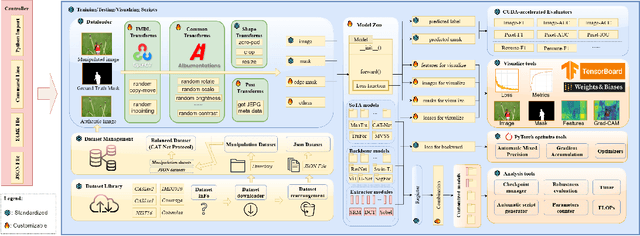
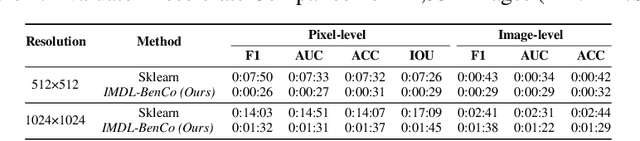
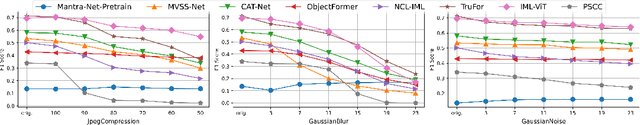
Abstract:A comprehensive benchmark is yet to be established in the Image Manipulation Detection \& Localization (IMDL) field. The absence of such a benchmark leads to insufficient and misleading model evaluations, severely undermining the development of this field. However, the scarcity of open-sourced baseline models and inconsistent training and evaluation protocols make conducting rigorous experiments and faithful comparisons among IMDL models challenging. To address these challenges, we introduce IMDL-BenCo, the first comprehensive IMDL benchmark and modular codebase. IMDL-BenCo:~\textbf{i)} decomposes the IMDL framework into standardized, reusable components and revises the model construction pipeline, improving coding efficiency and customization flexibility;~\textbf{ii)} fully implements or incorporates training code for state-of-the-art models to establish a comprehensive IMDL benchmark; and~\textbf{iii)} conducts deep analysis based on the established benchmark and codebase, offering new insights into IMDL model architecture, dataset characteristics, and evaluation standards. Specifically, IMDL-BenCo includes common processing algorithms, 8 state-of-the-art IMDL models (1 of which are reproduced from scratch), 2 sets of standard training and evaluation protocols, 15 GPU-accelerated evaluation metrics, and 3 kinds of robustness evaluation. This benchmark and codebase represent a significant leap forward in calibrating the current progress in the IMDL field and inspiring future breakthroughs. Code is available at: https://github.com/scu-zjz/IMDLBenCo
SHAN: Object-Level Privacy Detection via Inference on Scene Heterogeneous Graph
Mar 14, 2024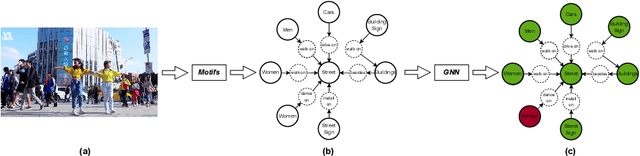
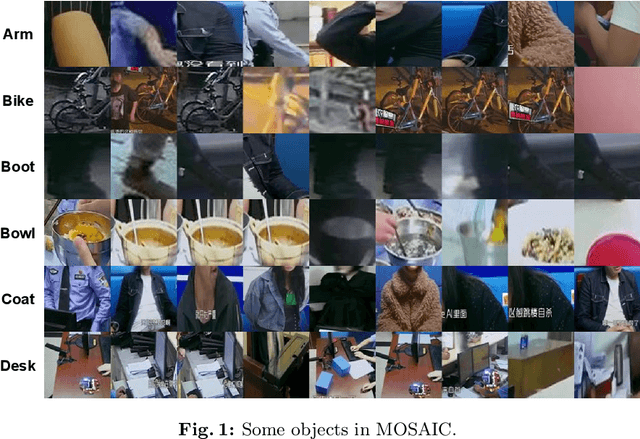
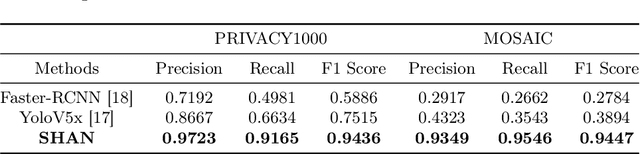

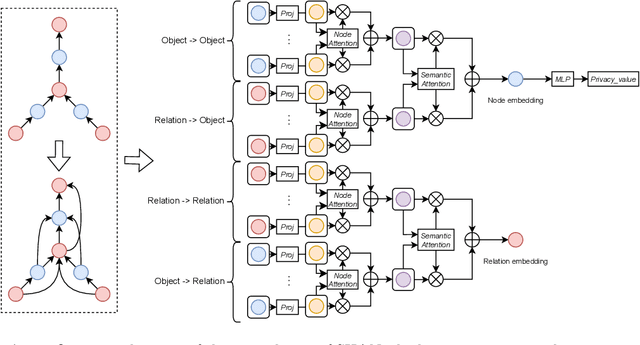
Abstract:With the rise of social platforms, protecting privacy has become an important issue. Privacy object detection aims to accurately locate private objects in images. It is the foundation of safeguarding individuals' privacy rights and ensuring responsible data handling practices in the digital age. Since privacy of object is not shift-invariant, the essence of the privacy object detection task is inferring object privacy based on scene information. However, privacy object detection has long been studied as a subproblem of common object detection tasks. Therefore, existing methods suffer from serious deficiencies in accuracy, generalization, and interpretability. Moreover, creating large-scale privacy datasets is difficult due to legal constraints and existing privacy datasets lack label granularity. The granularity of existing privacy detection methods remains limited to the image level. To address the above two issues, we introduce two benchmark datasets for object-level privacy detection and propose SHAN, Scene Heterogeneous graph Attention Network, a model constructs a scene heterogeneous graph from an image and utilizes self-attention mechanisms for scene inference to obtain object privacy. Through experiments, we demonstrated that SHAN performs excellently in privacy object detection tasks, with all metrics surpassing those of the baseline model.
Perceptual MAE for Image Manipulation Localization: A High-level Vision Learner Focusing on Low-level Features
Oct 10, 2023



Abstract:Nowadays, multimedia forensics faces unprecedented challenges due to the rapid advancement of multimedia generation technology thereby making Image Manipulation Localization (IML) crucial in the pursuit of truth. The key to IML lies in revealing the artifacts or inconsistencies between the tampered and authentic areas, which are evident under pixel-level features. Consequently, existing studies treat IML as a low-level vision task, focusing on allocating tampered masks by crafting pixel-level features such as image RGB noises, edge signals, or high-frequency features. However, in practice, tampering commonly occurs at the object level, and different classes of objects have varying likelihoods of becoming targets of tampering. Therefore, object semantics are also vital in identifying the tampered areas in addition to pixel-level features. This necessitates IML models to carry out a semantic understanding of the entire image. In this paper, we reformulate the IML task as a high-level vision task that greatly benefits from low-level features. Based on such an interpretation, we propose a method to enhance the Masked Autoencoder (MAE) by incorporating high-resolution inputs and a perceptual loss supervision module, which is termed Perceptual MAE (PMAE). While MAE has demonstrated an impressive understanding of object semantics, PMAE can also compensate for low-level semantics with our proposed enhancements. Evidenced by extensive experiments, this paradigm effectively unites the low-level and high-level features of the IML task and outperforms state-of-the-art tampering localization methods on all five publicly available datasets.
IML-ViT: Benchmarking Image Manipulation Localization by Vision Transformer
Aug 07, 2023



Abstract:Advanced image tampering techniques are increasingly challenging the trustworthiness of multimedia, leading to the development of Image Manipulation Localization (IML). But what makes a good IML model? The answer lies in the way to capture artifacts. Exploiting artifacts requires the model to extract non-semantic discrepancies between manipulated and authentic regions, necessitating explicit comparisons between the two areas. With the self-attention mechanism, naturally, the Transformer should be a better candidate to capture artifacts. However, due to limited datasets, there is currently no pure ViT-based approach for IML to serve as a benchmark, and CNNs dominate the entire task. Nevertheless, CNNs suffer from weak long-range and non-semantic modeling. To bridge this gap, based on the fact that artifacts are sensitive to image resolution, amplified under multi-scale features, and massive at the manipulation border, we formulate the answer to the former question as building a ViT with high-resolution capacity, multi-scale feature extraction capability, and manipulation edge supervision that could converge with a small amount of data. We term this simple but effective ViT paradigm IML-ViT, which has significant potential to become a new benchmark for IML. Extensive experiments on five benchmark datasets verified our model outperforms the state-of-the-art manipulation localization methods.Code and models are available at \url{https://github.com/SunnyHaze/IML-ViT}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge