Shanru Lin
HD-Prot: A Protein Language Model for Joint Sequence-Structure Modeling with Continuous Structure Tokens
Dec 17, 2025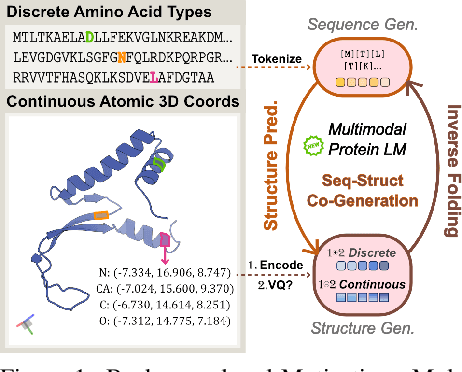
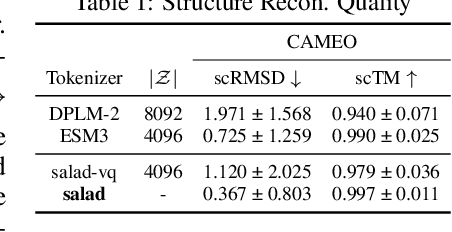
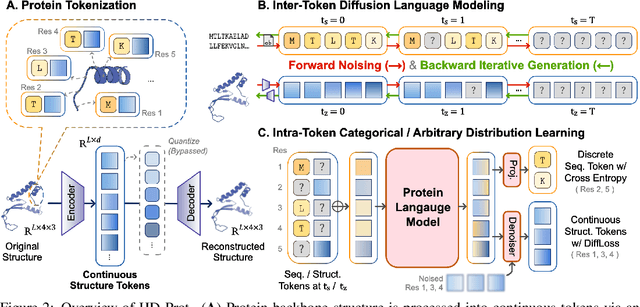
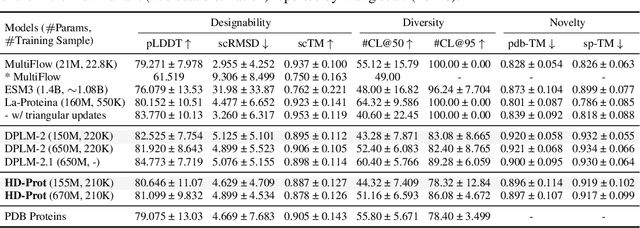
Abstract:Proteins inherently possess a consistent sequence-structure duality. The abundance of protein sequence data, which can be readily represented as discrete tokens, has driven fruitful developments in protein language models (pLMs). A key remaining challenge, however, is how to effectively integrate continuous structural knowledge into pLMs. Current methods often discretize protein structures to accommodate the language modeling framework, which inevitably results in the loss of fine-grained information and limits the performance potential of multimodal pLMs. In this paper, we argue that such concerns can be circumvented: a sequence-based pLM can be extended to incorporate the structure modality through continuous tokens, i.e., high-fidelity protein structure latents that avoid vector quantization. Specifically, we propose a hybrid diffusion protein language model, HD-Prot, which embeds a continuous-valued diffusion head atop a discrete pLM, enabling seamless operation with both discrete and continuous tokens for joint sequence-structure modeling. It captures inter-token dependencies across modalities through a unified absorbing diffusion process, and estimates per-token distributions via categorical prediction for sequences and continuous diffusion for structures. Extensive empirical results show that HD-Prot achieves competitive performance in unconditional sequence-structure co-generation, motif-scaffolding, protein structure prediction, and inverse folding tasks, performing on par with state-of-the-art multimodal pLMs despite being developed under limited computational resources. It highlights the viability of simultaneously estimating categorical and continuous distributions within a unified language model architecture, offering a promising alternative direction for multimodal pLMs.
Generative Recommendation with Continuous-Token Diffusion
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:In recent years, there has been a significant trend toward using large language model (LLM)-based recommender systems (RecSys). Current research primarily focuses on representing complex user-item interactions within a discrete space to align with the inherent discrete nature of language models. However, this approach faces limitations due to its discrete nature: (i) information is often compressed during discretization; (ii) the tokenization and generation for the vast number of users and items in real-world scenarios are constrained by a limited vocabulary. Embracing continuous data presents a promising alternative to enhance expressive capabilities, though this approach is still in its early stages. To address this gap, we propose a novel framework, DeftRec, which incorporates \textbf{de}noising di\textbf{f}fusion models to enable LLM-based RecSys to seamlessly support continuous \textbf{t}oken as input and target. First, we introduce a robust tokenizer with a masking operation and an additive K-way architecture to index users and items, capturing their complex collaborative relationships into continuous tokens. Crucially, we develop a denoising diffusion model to process user preferences within continuous domains by conditioning on reasoning content from pre-trained large language model. During the denoising process, we reformulate the objective to include negative interactions, building a comprehensive understanding of user preferences for effective and accurate recommendation generation. Finally, given a continuous token as output, recommendations can be easily generated through score-based retrieval. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed methods, showing that DeftRec surpasses competitive benchmarks, including both traditional and emerging LLM-based RecSys.
A Survey of WebAgents: Towards Next-Generation AI Agents for Web Automation with Large Foundation Models
Mar 30, 2025Abstract:With the advancement of web techniques, they have significantly revolutionized various aspects of people's lives. Despite the importance of the web, many tasks performed on it are repetitive and time-consuming, negatively impacting overall quality of life. To efficiently handle these tedious daily tasks, one of the most promising approaches is to advance autonomous agents based on Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques, referred to as AI Agents, as they can operate continuously without fatigue or performance degradation. In the context of the web, leveraging AI Agents -- termed WebAgents -- to automatically assist people in handling tedious daily tasks can dramatically enhance productivity and efficiency. Recently, Large Foundation Models (LFMs) containing billions of parameters have exhibited human-like language understanding and reasoning capabilities, showing proficiency in performing various complex tasks. This naturally raises the question: `Can LFMs be utilized to develop powerful AI Agents that automatically handle web tasks, providing significant convenience to users?' To fully explore the potential of LFMs, extensive research has emerged on WebAgents designed to complete daily web tasks according to user instructions, significantly enhancing the convenience of daily human life. In this survey, we comprehensively review existing research studies on WebAgents across three key aspects: architectures, training, and trustworthiness. Additionally, several promising directions for future research are explored to provide deeper insights.
Adaptive Self-supervised Learning for Social Recommendations
Dec 25, 2024Abstract:In recent years, researchers have attempted to exploit social relations to improve the performance in recommendation systems. Generally, most existing social recommendation methods heavily depends on substantial domain knowledge and expertise in primary recommendation tasks for designing useful auxiliary tasks. Meanwhile, Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) recently has received considerable attention in the field of recommendation, since it can provide self-supervision signals in assisting the improvement of target recommendation systems by constructing self-supervised auxiliary tasks from raw data without human-annotated labels. Despite the great success, these SSL-based social recommendations are insufficient to adaptively balance various self-supervised auxiliary tasks, since assigning equal weights on various auxiliary tasks can result in sub-optimal recommendation performance, where different self-supervised auxiliary tasks may contribute differently to improving the primary social recommendation across different datasets. To address this issue, in this work, we propose Adaptive Self-supervised Learning for Social Recommendations (AdasRec) by taking advantage of various self-supervised auxiliary tasks. More specifically, an adaptive weighting mechanism is proposed to learn adaptive weights for various self-supervised auxiliary tasks, so as to balance the contribution of such self-supervised auxiliary tasks for enhancing representation learning in social recommendations. The adaptive weighting mechanism is used to assign different weights on auxiliary tasks to achieve an overall weighting of the entire auxiliary tasks and ultimately assist the primary recommendation task, achieved by a meta learning optimization problem with an adaptive weighting network. Comprehensive experiments on various real-world datasets are constructed to verify the effectiveness of our proposed method.
Efficient and Robust Regularized Federated Recommendation
Nov 03, 2024



Abstract:Recommender systems play a pivotal role across practical scenarios, showcasing remarkable capabilities in user preference modeling. However, the centralized learning paradigm predominantly used raises serious privacy concerns. The federated recommender system (FedRS) addresses this by updating models on clients, while a central server orchestrates training without accessing private data. Existing FedRS approaches, however, face unresolved challenges, including non-convex optimization, vulnerability, potential privacy leakage risk, and communication inefficiency. This paper addresses these challenges by reformulating the federated recommendation problem as a convex optimization issue, ensuring convergence to the global optimum. Based on this, we devise a novel method, RFRec, to tackle this optimization problem efficiently. In addition, we propose RFRecF, a highly efficient version that incorporates non-uniform stochastic gradient descent to improve communication efficiency. In user preference modeling, both methods learn local and global models, collaboratively learning users' common and personalized interests under the federated learning setting. Moreover, both methods significantly enhance communication efficiency, robustness, and privacy protection, with theoretical support. Comprehensive evaluations on four benchmark datasets demonstrate RFRec and RFRecF's superior performance compared to diverse baselines.
LLM-enhanced Reranking in Recommender Systems
Jun 18, 2024Abstract:Reranking is a critical component in recommender systems, playing an essential role in refining the output of recommendation algorithms. Traditional reranking models have focused predominantly on accuracy, but modern applications demand consideration of additional criteria such as diversity and fairness. Existing reranking approaches often fail to harmonize these diverse criteria effectively at the model level. Moreover, these models frequently encounter challenges with scalability and personalization due to their complexity and the varying significance of different reranking criteria in diverse scenarios. In response, we introduce a comprehensive reranking framework enhanced by LLM, designed to seamlessly integrate various reranking criteria while maintaining scalability and facilitating personalized recommendations. This framework employs a fully connected graph structure, allowing the LLM to simultaneously consider multiple aspects such as accuracy, diversity, and fairness through a coherent Chain-of-Thought (CoT) process. A customizable input mechanism is also integrated, enabling the tuning of the language model's focus to meet specific reranking needs. We validate our approach using three popular public datasets, where our framework demonstrates superior performance over existing state-of-the-art reranking models in balancing multiple criteria. The code for this implementation is publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge