Xuetao Wei
ARGOS: Automated Functional Safety Requirement Synthesis for Embodied AI via Attribute-Guided Combinatorial Reasoning
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Ensuring functional safety is essential for the deployment of Embodied AI in complex open-world environments. However, traditional Hazard Analysis and Risk Assessment (HARA) methods struggle to scale in this domain. While HARA relies on enumerating risks for finite and pre-defined function lists, Embodied AI operates on open-ended natural language instructions, creating a challenge of combinatorial interaction risks. Whereas Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged as a promising solution to this scalability challenge, they often lack physical grounding, yielding semantically superficial and incoherent hazard descriptions. To overcome these limitations, we propose a new framework ARGOS (AttRibute-Guided cOmbinatorial reaSoning), which bridges the gap between open-ended user instructions and concrete physical attributes. By dynamically decomposing entities from instructions into these fine-grained properties, ARGOS grounds LLM reasoning in causal risk factors to generate physically plausible hazard scenarios. It then instantiates abstract safety standards, such as ISO 13482, into context-specific Functional Safety Requirements (FSRs) by integrating these scenarios with robot capabilities. Extensive experiments validate that ARGOS produces high-quality FSRs and outperforms baselines in identifying long-tail risks. Overall, this work paves the way for systematic and grounded functional safety requirement generation, a critical step toward the safe industrial deployment of Embodied AI.
Renormalization Group Guided Tensor Network Structure Search
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Tensor network structure search (TN-SS) aims to automatically discover optimal network topologies and rank configurations for efficient tensor decomposition in high-dimensional data representation. Despite recent advances, existing TN-SS methods face significant limitations in computational tractability, structure adaptivity, and optimization robustness across diverse tensor characteristics. They struggle with three key challenges: single-scale optimization missing multi-scale structures, discrete search spaces hindering smooth structure evolution, and separated structure-parameter optimization causing computational inefficiency. We propose RGTN (Renormalization Group guided Tensor Network search), a physics-inspired framework transforming TN-SS via multi-scale renormalization group flows. Unlike fixed-scale discrete search methods, RGTN uses dynamic scale-transformation for continuous structure evolution across resolutions. Its core innovation includes learnable edge gates for optimization-stage topology modification and intelligent proposals based on physical quantities like node tension measuring local stress and edge information flow quantifying connectivity importance. Starting from low-complexity coarse scales and refining to finer ones, RGTN finds compact structures while escaping local minima via scale-induced perturbations. Extensive experiments on light field data, high-order synthetic tensors, and video completion tasks show RGTN achieves state-of-the-art compression ratios and runs 4-600$\times$ faster than existing methods, validating the effectiveness of our physics-inspired approach.
Boosting Fine-Grained Urban Flow Inference via Lightweight Architecture and Focalized Optimization
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Fine-grained urban flow inference is crucial for urban planning and intelligent transportation systems, enabling precise traffic management and resource allocation. However, the practical deployment of existing methods is hindered by two key challenges: the prohibitive computational cost of over-parameterized models and the suboptimal performance of conventional loss functions on the highly skewed distribution of urban flows. To address these challenges, we propose a unified solution that synergizes architectural efficiency with adaptive optimization. Specifically, we first introduce PLGF, a lightweight yet powerful architecture that employs a Progressive Local-Global Fusion strategy to effectively capture both fine-grained details and global contextual dependencies. Second, we propose DualFocal Loss, a novel function that integrates dual-space supervision with a difficulty-aware focusing mechanism, enabling the model to adaptively concentrate on hard-to-predict regions. Extensive experiments on 4 real-world scenarios validate the effectiveness and scalability of our method. Notably, while achieving state-of-the-art performance, PLGF reduces the model size by up to 97% compared to current high-performing methods. Furthermore, under comparable parameter budgets, our model yields an accuracy improvement of over 10% against strong baselines. The implementation is included in the https://github.com/Yasoz/PLGF.
ChineseEEG-2: An EEG Dataset for Multimodal Semantic Alignment and Neural Decoding during Reading and Listening
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:EEG-based neural decoding requires large-scale benchmark datasets. Paired brain-language data across speaking, listening, and reading modalities are essential for aligning neural activity with the semantic representation of large language models (LLMs). However, such datasets are rare, especially for non-English languages. Here, we present ChineseEEG-2, a high-density EEG dataset designed for benchmarking neural decoding models under real-world language tasks. Building on our previous ChineseEEG dataset, which focused on silent reading, ChineseEEG-2 adds two active modalities: Reading Aloud (RA) and Passive Listening (PL), using the same Chinese corpus. EEG and audio were simultaneously recorded from four participants during ~10.7 hours of reading aloud. These recordings were then played to eight other participants, collecting ~21.6 hours of EEG during listening. This setup enables speech temporal and semantic alignment across the RA and PL modalities. ChineseEEG-2 includes EEG signals, precise audio, aligned semantic embeddings from pre-trained language models, and task labels. Together with ChineseEEG, this dataset supports joint semantic alignment learning across speaking, listening, and reading. It enables benchmarking of neural decoding algorithms and promotes brain-LLM alignment under multimodal language tasks, especially in Chinese. ChineseEEG-2 provides a benchmark dataset for next-generation neural semantic decoding.
Automatic Robustness Stress Testing of LLMs as Mathematical Problem Solvers
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have achieved distinguished performance on various reasoning-intensive tasks. However, LLMs might still face the challenges of robustness issues and fail unexpectedly in some simple reasoning tasks. Previous works evaluate the LLM robustness with hand-crafted templates or a limited set of perturbation rules, indicating potential data contamination in pre-training or fine-tuning datasets. In this work, inspired by stress testing in software engineering, we propose a novel framework, Automatic Robustness Checker (AR-Checker), to generate mathematical problem variants that maintain the semantic meanings of the original one but might fail the LLMs. The AR-Checker framework generates mathematical problem variants through multi-round parallel streams of LLM-based rewriting and verification. Our framework can generate benchmark variants dynamically for each LLM, thus minimizing the risk of data contamination. Experiments on GSM8K and MATH-500 demonstrate the strong performance of AR-Checker on mathematical tasks. We also evaluate AR-Checker on benchmarks beyond mathematics, including MMLU, MMLU-Pro, and CommonsenseQA, where it also achieves strong performance, further proving the effectiveness of AR-Checker.
Learning Generalized and Flexible Trajectory Models from Omni-Semantic Supervision
May 23, 2025Abstract:The widespread adoption of mobile devices and data collection technologies has led to an exponential increase in trajectory data, presenting significant challenges in spatio-temporal data mining, particularly for efficient and accurate trajectory retrieval. However, existing methods for trajectory retrieval face notable limitations, including inefficiencies in large-scale data, lack of support for condition-based queries, and reliance on trajectory similarity measures. To address the above challenges, we propose OmniTraj, a generalized and flexible omni-semantic trajectory retrieval framework that integrates four complementary modalities or semantics -- raw trajectories, topology, road segments, and regions -- into a unified system. Unlike traditional approaches that are limited to computing and processing trajectories as a single modality, OmniTraj designs dedicated encoders for each modality, which are embedded and fused into a shared representation space. This design enables OmniTraj to support accurate and flexible queries based on any individual modality or combination thereof, overcoming the rigidity of traditional similarity-based methods. Extensive experiments on two real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of OmniTraj in handling large-scale data, providing flexible, multi-modality queries, and supporting downstream tasks and applications.
STAR-Rec: Making Peace with Length Variance and Pattern Diversity in Sequential Recommendation
May 06, 2025Abstract:Recent deep sequential recommendation models often struggle to effectively model key characteristics of user behaviors, particularly in handling sequence length variations and capturing diverse interaction patterns. We propose STAR-Rec, a novel architecture that synergistically combines preference-aware attention and state-space modeling through a sequence-level mixture-of-experts framework. STAR-Rec addresses these challenges by: (1) employing preference-aware attention to capture both inherently similar item relationships and diverse preferences, (2) utilizing state-space modeling to efficiently process variable-length sequences with linear complexity, and (3) incorporating a mixture-of-experts component that adaptively routes different behavioral patterns to specialized experts, handling both focused category-specific browsing and diverse category exploration patterns. We theoretically demonstrate how the state space model and attention mechanisms can be naturally unified in recommendation scenarios, where SSM captures temporal dynamics through state compression while attention models both similar and diverse item relationships. Extensive experiments on four real-world datasets demonstrate that STAR-Rec consistently outperforms state-of-the-art sequential recommendation methods, particularly in scenarios involving diverse user behaviors and varying sequence lengths.
ImPart: Importance-Aware Delta-Sparsification for Improved Model Compression and Merging in LLMs
Apr 17, 2025Abstract:With the proliferation of task-specific large language models, delta compression has emerged as a method to mitigate the resource challenges of deploying numerous such models by effectively compressing the delta model parameters. Previous delta-sparsification methods either remove parameters randomly or truncate singular vectors directly after singular value decomposition (SVD). However, these methods either disregard parameter importance entirely or evaluate it with too coarse a granularity. In this work, we introduce ImPart, a novel importance-aware delta sparsification approach. Leveraging SVD, it dynamically adjusts sparsity ratios of different singular vectors based on their importance, effectively retaining crucial task-specific knowledge even at high sparsity ratios. Experiments show that ImPart achieves state-of-the-art delta sparsification performance, demonstrating $2\times$ higher compression ratio than baselines at the same performance level. When integrated with existing methods, ImPart sets a new state-of-the-art on delta quantization and model merging.
Sliding Window Attention Training for Efficient Large Language Models
Feb 26, 2025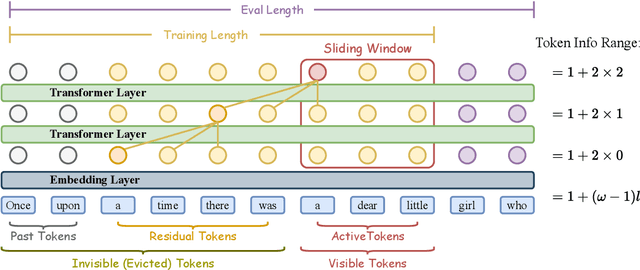
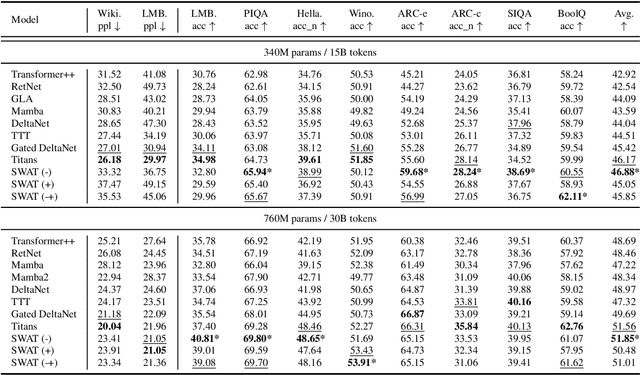
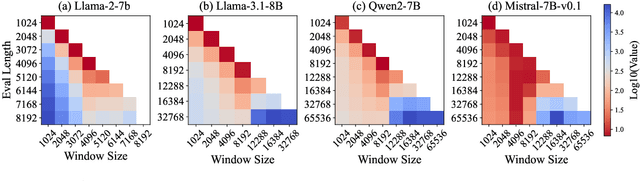
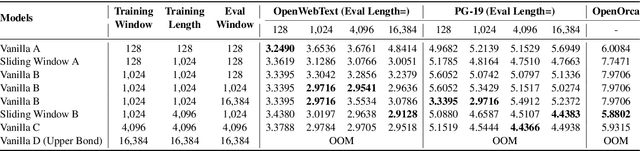
Abstract:Recent advances in transformer-based Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across various tasks. However, their quadratic computational complexity concerning sequence length remains a significant bottleneck for processing long documents. As a result, many efforts like sparse attention and state space models have been proposed to improve the efficiency of LLMs over long sequences. Though effective, these approaches compromise the performance or introduce structural complexity. This calls for a simple yet efficient model that preserves the fundamental Transformer architecture. To this end, we introduce SWAT, which enables efficient long-context handling via Sliding Window Attention Training. This paper first attributes the inefficiency of Transformers to the attention sink phenomenon resulting from the high variance of softmax operation. Then, we replace softmax with the sigmoid function and utilize a balanced ALiBi and Rotary Position Embedding for efficient information compression and retention. Experiments demonstrate that SWAT achieves SOTA performance compared with state-of-the-art linear recurrent architectures on eight benchmarks. Code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/SWAT-attention.
DreaMark: Rooting Watermark in Score Distillation Sampling Generated Neural Radiance Fields
Dec 18, 2024Abstract:Recent advancements in text-to-3D generation can generate neural radiance fields (NeRFs) with score distillation sampling, enabling 3D asset creation without real-world data capture. With the rapid advancement in NeRF generation quality, protecting the copyright of the generated NeRF has become increasingly important. While prior works can watermark NeRFs in a post-generation way, they suffer from two vulnerabilities. First, a delay lies between NeRF generation and watermarking because the secret message is embedded into the NeRF model post-generation through fine-tuning. Second, generating a non-watermarked NeRF as an intermediate creates a potential vulnerability for theft. To address both issues, we propose Dreamark to embed a secret message by backdooring the NeRF during NeRF generation. In detail, we first pre-train a watermark decoder. Then, the Dreamark generates backdoored NeRFs in a way that the target secret message can be verified by the pre-trained watermark decoder on an arbitrary trigger viewport. We evaluate the generation quality and watermark robustness against image- and model-level attacks. Extensive experiments show that the watermarking process will not degrade the generation quality, and the watermark achieves 90+% accuracy among both image-level attacks (e.g., Gaussian noise) and model-level attacks (e.g., pruning attack).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge