Ling Yan
SocioVerse: A World Model for Social Simulation Powered by LLM Agents and A Pool of 10 Million Real-World Users
Apr 14, 2025


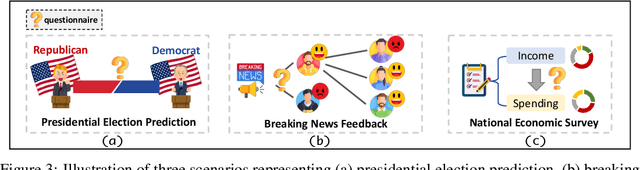
Abstract:Social simulation is transforming traditional social science research by modeling human behavior through interactions between virtual individuals and their environments. With recent advances in large language models (LLMs), this approach has shown growing potential in capturing individual differences and predicting group behaviors. However, existing methods face alignment challenges related to the environment, target users, interaction mechanisms, and behavioral patterns. To this end, we introduce SocioVerse, an LLM-agent-driven world model for social simulation. Our framework features four powerful alignment components and a user pool of 10 million real individuals. To validate its effectiveness, we conducted large-scale simulation experiments across three distinct domains: politics, news, and economics. Results demonstrate that SocioVerse can reflect large-scale population dynamics while ensuring diversity, credibility, and representativeness through standardized procedures and minimal manual adjustments.
GPRec: Bi-level User Modeling for Deep Recommenders
Oct 28, 2024



Abstract:GPRec explicitly categorizes users into groups in a learnable manner and aligns them with corresponding group embeddings. We design the dual group embedding space to offer a diverse perspective on group preferences by contrasting positive and negative patterns. On the individual level, GPRec identifies personal preferences from ID-like features and refines the obtained individual representations to be independent of group ones, thereby providing a robust complement to the group-level modeling. We also present various strategies for the flexible integration of GPRec into various DRS models. Rigorous testing of GPRec on three public datasets has demonstrated significant improvements in recommendation quality.
Boosting Box-supervised Instance Segmentation with Pseudo Depth
Mar 02, 2024Abstract:The realm of Weakly Supervised Instance Segmentation (WSIS) under box supervision has garnered substantial attention, showcasing remarkable advancements in recent years. However, the limitations of box supervision become apparent in its inability to furnish effective information for distinguishing foreground from background within the specified target box. This research addresses this challenge by introducing pseudo-depth maps into the training process of the instance segmentation network, thereby boosting its performance by capturing depth differences between instances. These pseudo-depth maps are generated using a readily available depth predictor and are not necessary during the inference stage. To enable the network to discern depth features when predicting masks, we integrate a depth prediction layer into the mask prediction head. This innovative approach empowers the network to simultaneously predict masks and depth, enhancing its ability to capture nuanced depth-related information during the instance segmentation process. We further utilize the mask generated in the training process as supervision to distinguish the foreground from the background. When selecting the best mask for each box through the Hungarian algorithm, we use depth consistency as one calculation cost item. The proposed method achieves significant improvements on Cityscapes and COCO dataset.
Conditional Generative Data-Free Knowledge Distillation based on Attention Transfer
Dec 31, 2021



Abstract:Knowledge distillation has made remarkable achievements in model compression. However, most existing methods demand original training data, while real data in practice are often unavailable due to privacy, security and transmission limitation. To address this problem, we propose a conditional generative data-free knowledge distillation (CGDD) framework to train efficient portable network without any real data. In this framework, except using the knowledge extracted from teacher model, we introduce preset labels as additional auxiliary information to train the generator. Then, the trained generator can produce meaningful training samples of specified category as required. In order to promote distillation process, except using conventional distillation loss, we treat preset label as ground truth label so that student network is directly supervised by the category of synthetic training sample. Moreover, we force student network to mimic the attention maps of teacher model and further improve its performance. To verify the superiority of our method, we design a new evaluation metric is called as relative accuracy to directly compare the effectiveness of different distillation methods. Trained portable network learned with proposed data-free distillation method obtains 99.63%, 99.07% and 99.84% relative accuracy on CIFAR10, CIFAR100 and Caltech101, respectively. The experimental results demonstrate the superiority of proposed method.
Markdowns in E-Commerce Fresh Retail: A Counterfactual Prediction and Multi-Period Optimization Approach
May 19, 2021



Abstract:In this paper, by leveraging abundant observational transaction data, we propose a novel data-driven and interpretable pricing approach for markdowns, consisting of counterfactual prediction and multi-period price optimization. Firstly, we build a semi-parametric structural model to learn individual price elasticity and predict counterfactual demand. This semi-parametric model takes advantage of both the predictability of nonparametric machine learning model and the interpretability of economic model. Secondly, we propose a multi-period dynamic pricing algorithm to maximize the overall profit of a perishable product over its finite selling horizon. Different with the traditional approaches that use the deterministic demand, we model the uncertainty of counterfactual demand since it inevitably has randomness in the prediction process. Based on the stochastic model, we derive a sequential pricing strategy by Markov decision process, and design a two-stage algorithm to solve it. The proposed algorithm is very efficient. It reduces the time complexity from exponential to polynomial. Experimental results show the advantages of our pricing algorithm, and the proposed framework has been successfully deployed to the well-known e-commerce fresh retail scenario - Freshippo.
A Unified Framework for Marketing Budget Allocation
Feb 04, 2019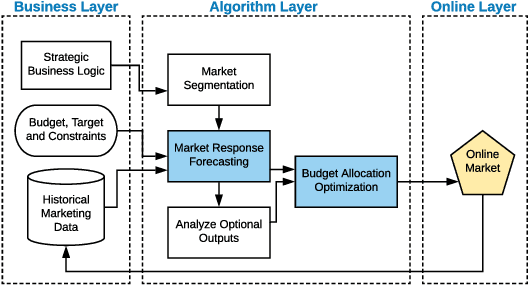
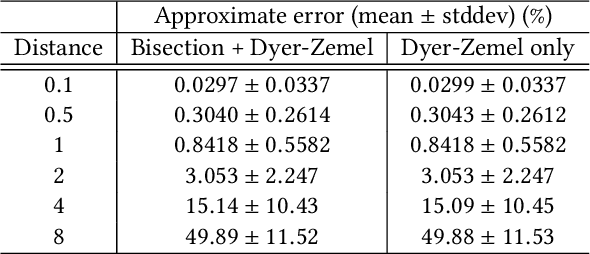
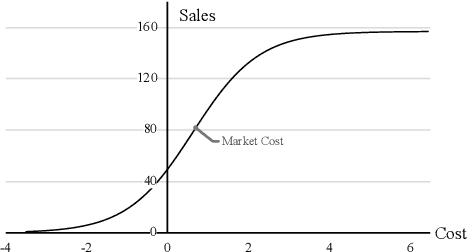
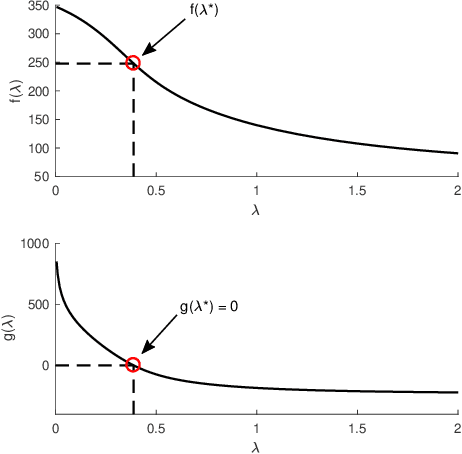
Abstract:While marketing budget allocation has been studied for decades in traditional business, nowadays online business brings much more challenges due to the dynamic environment and complex decision-making process. In this paper, we present a novel unified framework for marketing budget allocation. By leveraging abundant data, the proposed data-driven approach can help us to overcome the challenges and make more informed decisions. In our approach, a semi-black-box model is built to forecast the dynamic market response and an efficient optimization method is proposed to solve the complex allocation task. First, the response in each market-segment is forecasted by exploring historical data through a semi-black-box model, where the capability of logit demand curve is enhanced by neural networks. The response model reveals relationship between sales and marketing cost. Based on the learned model, budget allocation is then formulated as an optimization problem, and we design efficient algorithms to solve it in both continuous and discrete settings. Several kinds of business constraints are supported in one unified optimization paradigm, including cost upper bound, profit lower bound, or ROI lower bound. The proposed framework is easy to implement and readily to handle large-scale problems. It has been successfully applied to many scenarios in Alibaba Group. The results of both offline experiments and online A/B testing demonstrate its effectiveness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge