Yujuan Ding
HV-Attack: Hierarchical Visual Attack for Multimodal Retrieval Augmented Generation
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Advanced multimodal Retrieval-Augmented Generation (MRAG) techniques have been widely applied to enhance the capabilities of Large Multimodal Models (LMMs), but they also bring along novel safety issues. Existing adversarial research has revealed the vulnerability of MRAG systems to knowledge poisoning attacks, which fool the retriever into recalling injected poisoned contents. However, our work considers a different setting: visual attack of MRAG by solely adding imperceptible perturbations at the image inputs of users, without manipulating any other components. This is challenging due to the robustness of fine-tuned retrievers and large-scale generators, and the effect of visual perturbation may be further weakened by propagation through the RAG chain. We propose a novel Hierarchical Visual Attack that misaligns and disrupts the two inputs (the multimodal query and the augmented knowledge) of MRAG's generator to confuse its generation. We further design a hierarchical two-stage strategy to obtain misaligned augmented knowledge. We disrupt the image input of the retriever to make it recall irrelevant knowledge from the original database, by optimizing the perturbation which first breaks the cross-modal alignment and then disrupts the multimodal semantic alignment. We conduct extensive experiments on two widely-used MRAG datasets: OK-VQA and InfoSeek. We use CLIP-based retrievers and two LMMs BLIP-2 and LLaVA as generators. Results demonstrate the effectiveness of our visual attack on MRAG through the significant decrease in both retrieval and generation performance.
WebRec: Enhancing LLM-based Recommendations with Attention-guided RAG from Web
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Recommender systems play a vital role in alleviating information overload and enriching users' online experience. In the era of large language models (LLMs), LLM-based recommender systems have emerged as a prevalent paradigm for advancing personalized recommendations. Recently, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has drawn growing interest to facilitate the recommendation capability of LLMs, incorporating useful information retrieved from external knowledge bases. However, as a rich source of up-to-date information, the web remains under-explored by existing RAG-based recommendations. In particular, unique challenges are posed from two perspectives: one is to generate effective queries for web retrieval, considering the inherent knowledge gap between web search and recommendations; another challenge lies in harnessing online websites that contain substantial noisy content. To tackle these limitations, we propose WebRec, a novel web-based RAG framework, which takes advantage of the reasoning capability of LLMs to interpret recommendation tasks into queries of user preferences that cater to web retrieval. Moreover, given noisy web-retrieved information, where relevant pieces of evidence are scattered far apart, an insightful MP-Head is designed to enhance LLM attentions between distant tokens of relevant information via message passing. Extensive experiments have been conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed web-based RAG methods in recommendation scenarios.
More Than One Teacher: Adaptive Multi-Guidance Policy Optimization for Diverse Exploration
Oct 02, 2025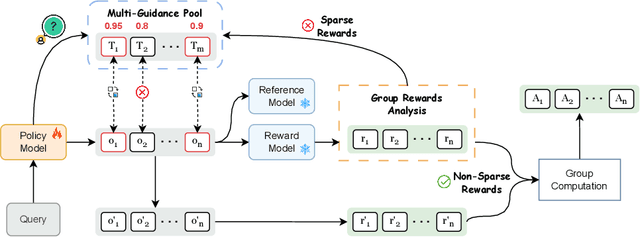
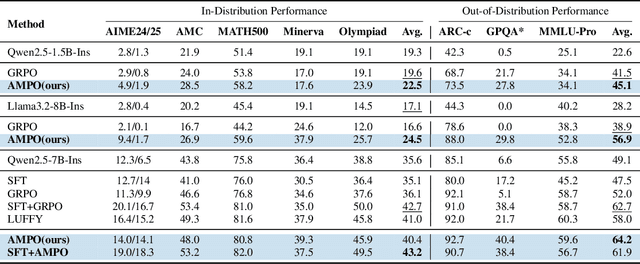

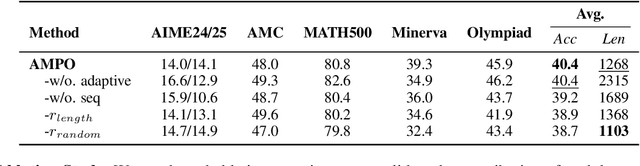
Abstract:Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) is a promising paradigm for enhancing the reasoning ability in Large Language Models (LLMs). However, prevailing methods primarily rely on self-exploration or a single off-policy teacher to elicit long chain-of-thought (LongCoT) reasoning, which may introduce intrinsic model biases and restrict exploration, ultimately limiting reasoning diversity and performance. Drawing inspiration from multi-teacher strategies in knowledge distillation, we introduce Adaptive Multi-Guidance Policy Optimization (AMPO), a novel framework that adaptively leverages guidance from multiple proficient teacher models, but only when the on-policy model fails to generate correct solutions. This "guidance-on-demand" approach expands exploration while preserving the value of self-discovery. Moreover, AMPO incorporates a comprehension-based selection mechanism, prompting the student to learn from the reasoning paths that it is most likely to comprehend, thus balancing broad exploration with effective exploitation. Extensive experiments show AMPO substantially outperforms a strong baseline (GRPO), with a 4.3% improvement on mathematical reasoning tasks and 12.2% on out-of-distribution tasks, while significantly boosting Pass@k performance and enabling more diverse exploration. Notably, using four peer-sized teachers, our method achieves comparable results to approaches that leverage a single, more powerful teacher (e.g., DeepSeek-R1) with more data. These results demonstrate a more efficient and scalable path to superior reasoning and generalizability. Our code is available at https://github.com/SII-Enigma/AMPO.
Explore Briefly, Then Decide: Mitigating LLM Overthinking via Cumulative Entropy Regulation
Oct 02, 2025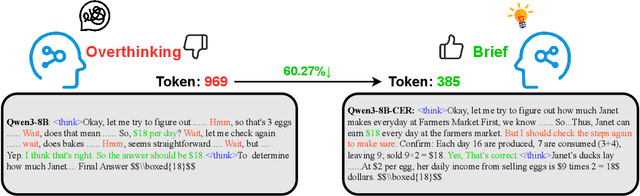
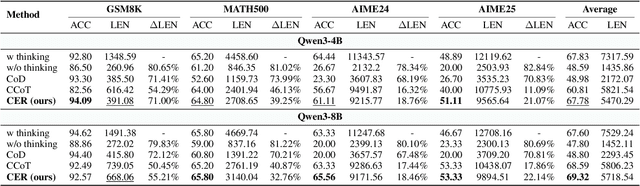
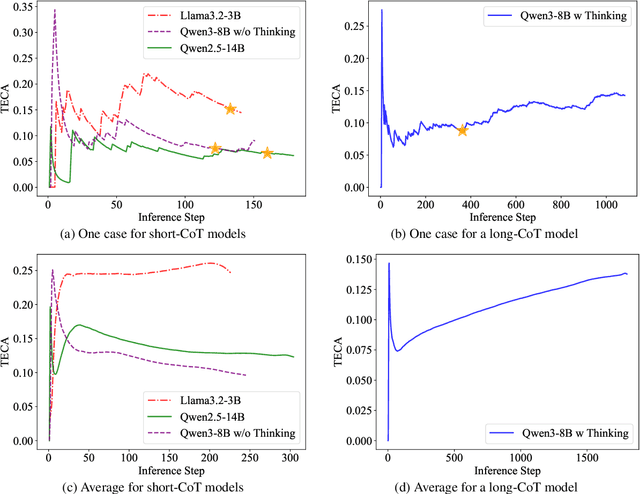
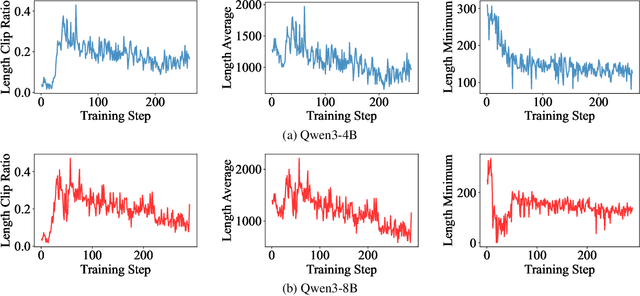
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable reasoning abilities on complex problems using long Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning. However, they often suffer from overthinking, meaning generating unnecessarily lengthy reasoning steps for simpler problems. This issue may degrade the efficiency of the models and make them difficult to adapt the reasoning depth to the complexity of problems. To address this, we introduce a novel metric Token Entropy Cumulative Average (TECA), which measures the extent of exploration throughout the reasoning process. We further propose a novel reasoning paradigm -- Explore Briefly, Then Decide -- with an associated Cumulative Entropy Regulation (CER) mechanism. This paradigm leverages TECA to help the model dynamically determine the optimal point to conclude its thought process and provide a final answer, thus achieving efficient reasoning. Experimental results across diverse mathematical benchmarks show that our approach substantially mitigates overthinking without sacrificing problem-solving ability. With our thinking paradigm, the average response length decreases by up to 71% on simpler datasets, demonstrating the effectiveness of our method in creating a more efficient and adaptive reasoning process.
A Survey of WebAgents: Towards Next-Generation AI Agents for Web Automation with Large Foundation Models
Mar 30, 2025Abstract:With the advancement of web techniques, they have significantly revolutionized various aspects of people's lives. Despite the importance of the web, many tasks performed on it are repetitive and time-consuming, negatively impacting overall quality of life. To efficiently handle these tedious daily tasks, one of the most promising approaches is to advance autonomous agents based on Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques, referred to as AI Agents, as they can operate continuously without fatigue or performance degradation. In the context of the web, leveraging AI Agents -- termed WebAgents -- to automatically assist people in handling tedious daily tasks can dramatically enhance productivity and efficiency. Recently, Large Foundation Models (LFMs) containing billions of parameters have exhibited human-like language understanding and reasoning capabilities, showing proficiency in performing various complex tasks. This naturally raises the question: `Can LFMs be utilized to develop powerful AI Agents that automatically handle web tasks, providing significant convenience to users?' To fully explore the potential of LFMs, extensive research has emerged on WebAgents designed to complete daily web tasks according to user instructions, significantly enhancing the convenience of daily human life. In this survey, we comprehensively review existing research studies on WebAgents across three key aspects: architectures, training, and trustworthiness. Additionally, several promising directions for future research are explored to provide deeper insights.
ChartAdapter: Large Vision-Language Model for Chart Summarization
Dec 30, 2024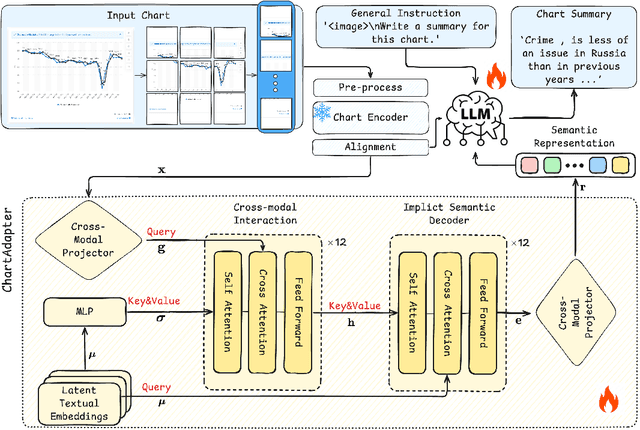
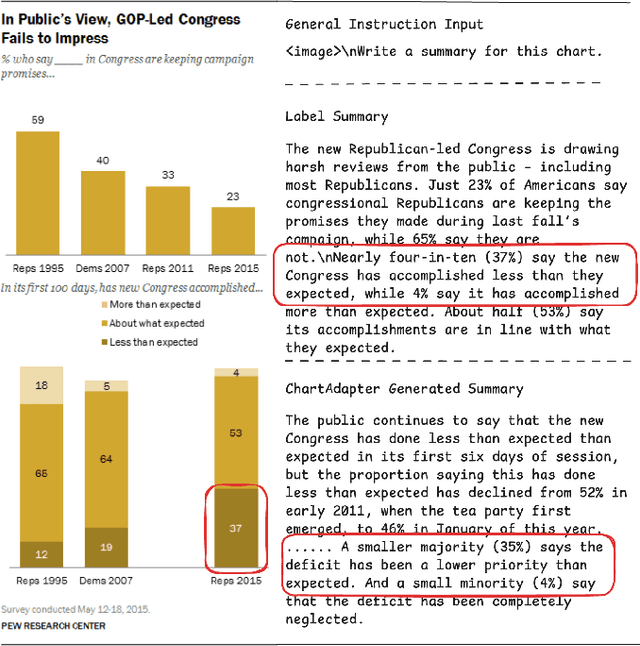
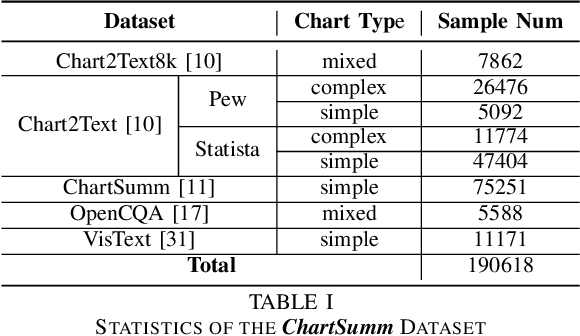
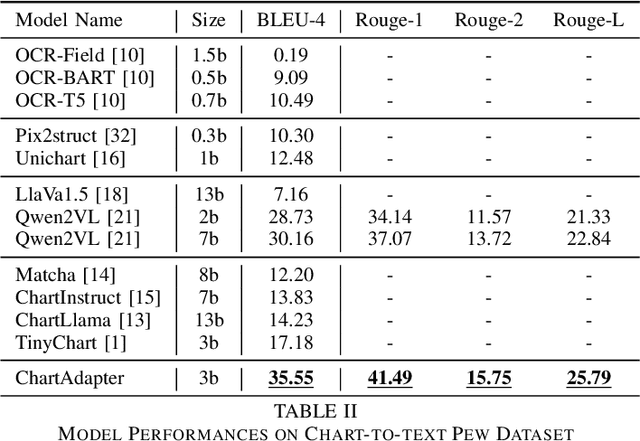
Abstract:Chart summarization, which focuses on extracting key information from charts and interpreting it in natural language, is crucial for generating and delivering insights through effective and accessible data analysis. Traditional methods for chart understanding and summarization often rely on multi-stage pipelines, which may produce suboptimal semantic alignment between visual and textual information. In comparison, recently developed LLM-based methods are more dependent on the capability of foundation images or languages, while ignoring the characteristics of chart data and its relevant challenges. To address these limitations, we propose ChartAdapter, a novel lightweight transformer module designed to bridge the gap between charts and textual summaries. ChartAdapter employs learnable query vectors to extract implicit semantics from chart data and incorporates a cross-modal alignment projector to enhance vision-to-language generative learning. By integrating ChartAdapter with an LLM, we enable end-to-end training and efficient chart summarization. To further enhance the training, we introduce a three-stage hierarchical training procedure and develop a large-scale dataset specifically curated for chart summarization, comprising 190,618 samples. Experimental results on the standard Chart-to-Text testing set demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms existing methods, including state-of-the-art models, in generating high-quality chart summaries. Ablation studies further validate the effectiveness of key components in ChartAdapter. This work highlights the potential of tailored LLM-based approaches to advance chart understanding and sets a strong foundation for future research in this area.
Leveraging Weak Cross-Modal Guidance for Coherence Modelling via Iterative Learning
Aug 01, 2024



Abstract:Cross-modal coherence modeling is essential for intelligent systems to help them organize and structure information, thereby understanding and creating content of the physical world coherently like human-beings. Previous work on cross-modal coherence modeling attempted to leverage the order information from another modality to assist the coherence recovering of the target modality. Despite of the effectiveness, labeled associated coherency information is not always available and might be costly to acquire, making the cross-modal guidance hard to leverage. To tackle this challenge, this paper explores a new way to take advantage of cross-modal guidance without gold labels on coherency, and proposes the Weak Cross-Modal Guided Ordering (WeGO) model. More specifically, it leverages high-confidence predicted pairwise order in one modality as reference information to guide the coherence modeling in another. An iterative learning paradigm is further designed to jointly optimize the coherence modeling in two modalities with selected guidance from each other. The iterative cross-modal boosting also functions in inference to further enhance coherence prediction in each modality. Experimental results on two public datasets have demonstrated that the proposed method outperforms existing methods for cross-modal coherence modeling tasks. Major technical modules have been evaluated effective through ablation studies. Codes are available at: \url{https://github.com/scvready123/IterWeGO}.
GalleryGPT: Analyzing Paintings with Large Multimodal Models
Aug 01, 2024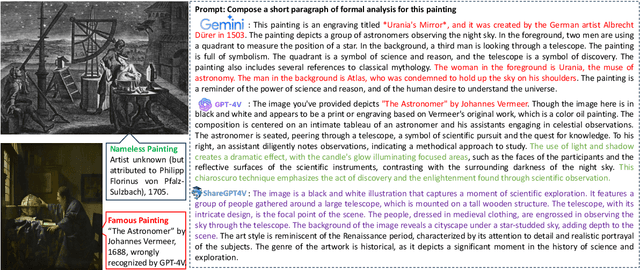
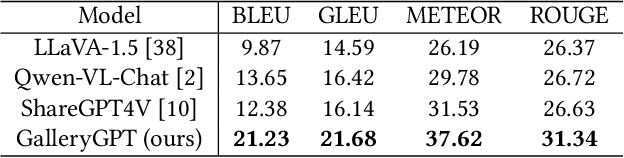
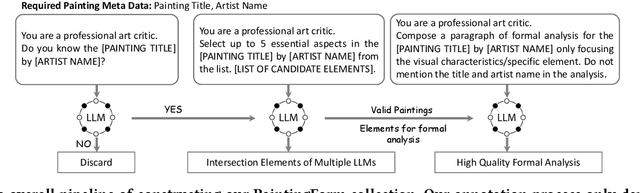
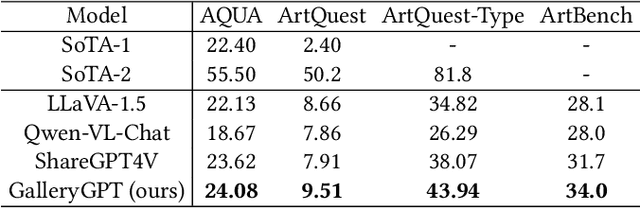
Abstract:Artwork analysis is important and fundamental skill for art appreciation, which could enrich personal aesthetic sensibility and facilitate the critical thinking ability. Understanding artworks is challenging due to its subjective nature, diverse interpretations, and complex visual elements, requiring expertise in art history, cultural background, and aesthetic theory. However, limited by the data collection and model ability, previous works for automatically analyzing artworks mainly focus on classification, retrieval, and other simple tasks, which is far from the goal of AI. To facilitate the research progress, in this paper, we step further to compose comprehensive analysis inspired by the remarkable perception and generation ability of large multimodal models. Specifically, we first propose a task of composing paragraph analysis for artworks, i.e., painting in this paper, only focusing on visual characteristics to formulate more comprehensive understanding of artworks. To support the research on formal analysis, we collect a large dataset PaintingForm, with about 19k painting images and 50k analysis paragraphs. We further introduce a superior large multimodal model for painting analysis composing, dubbed GalleryGPT, which is slightly modified and fine-tuned based on LLaVA architecture leveraging our collected data. We conduct formal analysis generation and zero-shot experiments across several datasets to assess the capacity of our model. The results show remarkable performance improvements comparing with powerful baseline LMMs, demonstrating its superb ability of art analysis and generalization. \textcolor{blue}{The codes and model are available at: https://github.com/steven640pixel/GalleryGPT.
A Survey on RAG Meets LLMs: Towards Retrieval-Augmented Large Language Models
May 10, 2024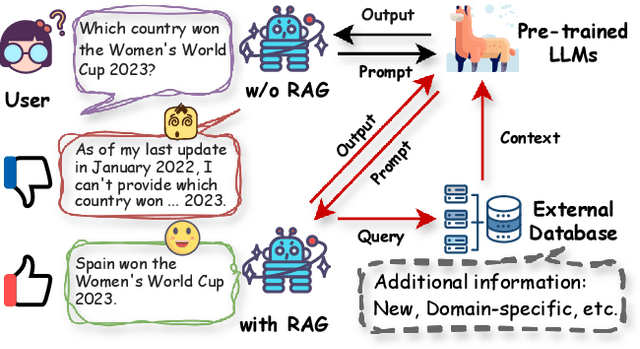
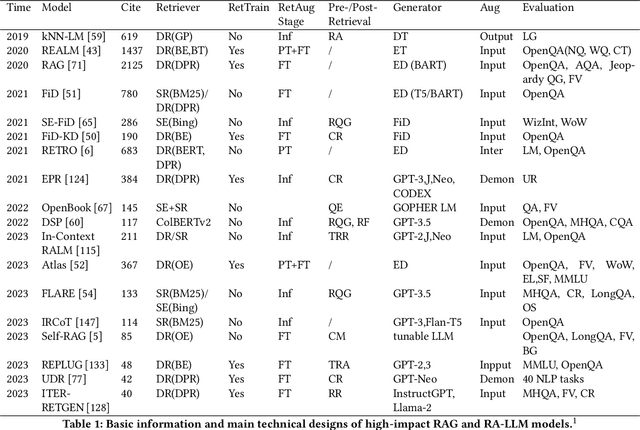
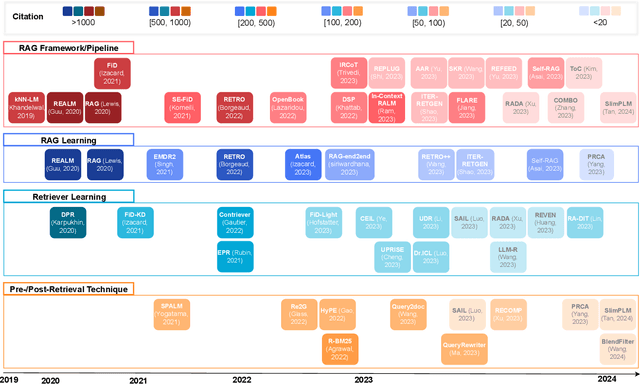
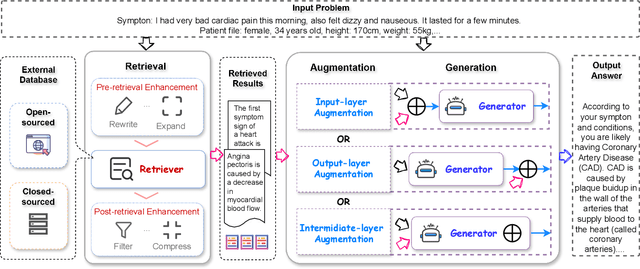
Abstract:As one of the most advanced techniques in AI, Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) techniques can offer reliable and up-to-date external knowledge, providing huge convenience for numerous tasks. Particularly in the era of AI-generated content (AIGC), the powerful capacity of retrieval in RAG in providing additional knowledge enables retrieval-augmented generation to assist existing generative AI in producing high-quality outputs. Recently, large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated revolutionary abilities in language understanding and generation, while still facing inherent limitations, such as hallucinations and out-of-date internal knowledge. Given the powerful abilities of RAG in providing the latest and helpful auxiliary information, retrieval-augmented large language models have emerged to harness external and authoritative knowledge bases, rather than solely relying on the model's internal knowledge, to augment the generation quality of LLMs. In this survey, we comprehensively review existing research studies in retrieval-augmented large language models (RA-LLMs), covering three primary technical perspectives: architectures, training strategies, and applications. As the preliminary knowledge, we briefly introduce the foundations and recent advances of LLMs. Then, to illustrate the practical significance of RAG for LLMs, we categorize mainstream relevant work by application areas, detailing specifically the challenges of each and the corresponding capabilities of RA-LLMs. Finally, to deliver deeper insights, we discuss current limitations and several promising directions for future research.
FashionReGen: LLM-Empowered Fashion Report Generation
Mar 11, 2024


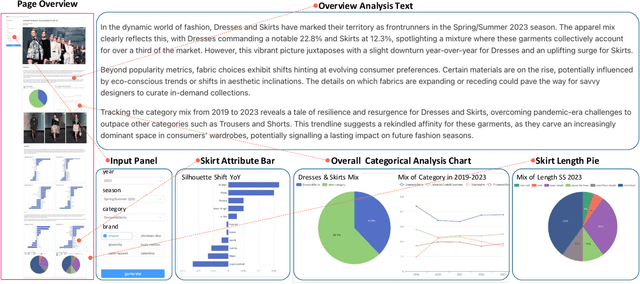
Abstract:Fashion analysis refers to the process of examining and evaluating trends, styles, and elements within the fashion industry to understand and interpret its current state, generating fashion reports. It is traditionally performed by fashion professionals based on their expertise and experience, which requires high labour cost and may also produce biased results for relying heavily on a small group of people. In this paper, to tackle the Fashion Report Generation (FashionReGen) task, we propose an intelligent Fashion Analyzing and Reporting system based the advanced Large Language Models (LLMs), debbed as GPT-FAR. Specifically, it tries to deliver FashionReGen based on effective catwalk analysis, which is equipped with several key procedures, namely, catwalk understanding, collective organization and analysis, and report generation. By posing and exploring such an open-ended, complex and domain-specific task of FashionReGen, it is able to test the general capability of LLMs in fashion domain. It also inspires the explorations of more high-level tasks with industrial significance in other domains. Video illustration and more materials of GPT-FAR can be found in https://github.com/CompFashion/FashionReGen.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge