Bin Ji
JPU: Bridging Jailbreak Defense and Unlearning via On-Policy Path Rectification
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Despite extensive safety alignment, Large Language Models (LLMs) often fail against jailbreak attacks. While machine unlearning has emerged as a promising defense by erasing specific harmful parameters, current methods remain vulnerable to diverse jailbreaks. We first conduct an empirical study and discover that this failure mechanism is caused by jailbreaks primarily activating non-erased parameters in the intermediate layers. Further, by probing the underlying mechanism through which these circumvented parameters reassemble into the prohibited output, we verify the persistent existence of dynamic $\textbf{jailbreak paths}$ and show that the inability to rectify them constitutes the fundamental gap in existing unlearning defenses. To bridge this gap, we propose $\textbf{J}$ailbreak $\textbf{P}$ath $\textbf{U}$nlearning (JPU), which is the first to rectify dynamic jailbreak paths towards safety anchors by dynamically mining on-policy adversarial samples to expose vulnerabilities and identify jailbreak paths. Extensive experiments demonstrate that JPU significantly enhances jailbreak resistance against dynamic attacks while preserving the model's utility.
Step More: Going Beyond Single Backpropagation in Meta Learning Based Model Editing
Aug 06, 2025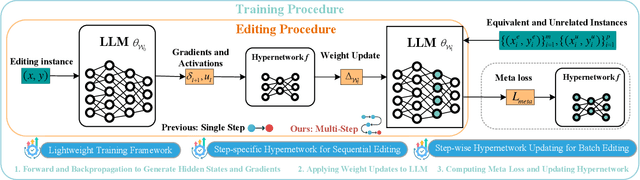

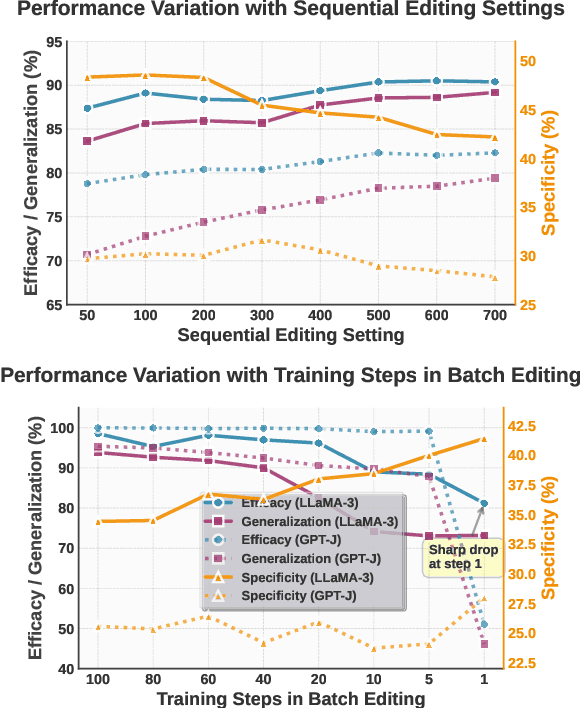

Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) underpin many AI applications, but their static nature makes updating knowledge costly. Model editing offers an efficient alternative by injecting new information through targeted parameter modifications. In particular, meta-learning-based model editing (MLBME) methods have demonstrated notable advantages in both editing effectiveness and efficiency. Despite this, we find that MLBME exhibits suboptimal performance in low-data scenarios, and its training efficiency is bottlenecked by the computation of KL divergence. To address these, we propose $\textbf{S}$tep $\textbf{M}$ore $\textbf{Edit}$ ($\textbf{SMEdit}$), a novel MLBME method that adopts $\textbf{M}$ultiple $\textbf{B}$ackpro$\textbf{P}$agation $\textbf{S}$teps ($\textbf{MBPS}$) to improve editing performance under limited supervision and a norm regularization on weight updates to improve training efficiency. Experimental results on two datasets and two LLMs demonstrate that SMEdit outperforms prior MLBME baselines and the MBPS strategy can be seamlessly integrated into existing methods to further boost their performance. Our code will be released soon.
FixTalk: Taming Identity Leakage for High-Quality Talking Head Generation in Extreme Cases
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:Talking head generation is gaining significant importance across various domains, with a growing demand for high-quality rendering. However, existing methods often suffer from identity leakage (IL) and rendering artifacts (RA), particularly in extreme cases. Through an in-depth analysis of previous approaches, we identify two key insights: (1) IL arises from identity information embedded within motion features, and (2) this identity information can be leveraged to address RA. Building on these findings, this paper introduces FixTalk, a novel framework designed to simultaneously resolve both issues for high-quality talking head generation. Firstly, we propose an Enhanced Motion Indicator (EMI) to effectively decouple identity information from motion features, mitigating the impact of IL on generated talking heads. To address RA, we introduce an Enhanced Detail Indicator (EDI), which utilizes the leaked identity information to supplement missing details, thus fixing the artifacts. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FixTalk effectively mitigates IL and RA, achieving superior performance compared to state-of-the-art methods.
Towards Synthesized and Editable Motion In-Betweening Through Part-Wise Phase Representation
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Styled motion in-betweening is crucial for computer animation and gaming. However, existing methods typically encode motion styles by modeling whole-body motions, often overlooking the representation of individual body parts. This limitation reduces the flexibility of infilled motion, particularly in adjusting the motion styles of specific limbs independently. To overcome this challenge, we propose a novel framework that models motion styles at the body-part level, enhancing both the diversity and controllability of infilled motions. Our approach enables more nuanced and expressive animations by allowing precise modifications to individual limb motions while maintaining overall motion coherence. Leveraging phase-related insights, our framework employs periodic autoencoders to automatically extract the phase of each body part, capturing distinctive local style features. Additionally, we effectively decouple the motion source from synthesis control by integrating motion manifold learning and conditional generation techniques from both image and motion domains. This allows the motion source to generate high-quality motions across various styles, with extracted motion and style features readily available for controlled synthesis in subsequent tasks. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate that our method achieves superior speed, robust generalization, and effective generation of extended motion sequences.
Rethinking the Residual Distribution of Locate-then-Editing Methods in Model Editing
Feb 06, 2025Abstract:Model editing is a powerful technique for updating the knowledge of Large Language Models (LLMs). Locate-then-edit methods are a popular class of approaches that first identify the critical layers storing knowledge, then compute the residual of the last critical layer based on the edited knowledge, and finally perform multi-layer updates using a least-squares solution by evenly distributing the residual from the first critical layer to the last. Although these methods achieve promising results, they have been shown to degrade the original knowledge of LLMs. We argue that residual distribution leads to this issue. To explore this, we conduct a comprehensive analysis of residual distribution in locate-then-edit methods from both empirical and theoretical perspectives, revealing that residual distribution introduces editing errors, leading to inaccurate edits. To address this issue, we propose the Boundary Layer UpdatE (BLUE) strategy to enhance locate-then-edit methods. Sequential batch editing experiments on three LLMs and two datasets demonstrate that BLUE not only delivers an average performance improvement of 35.59\%, significantly advancing the state of the art in model editing, but also enhances the preservation of LLMs' general capabilities. Our code is available at https://github.com/xpq-tech/BLUE.
LSAQ: Layer-Specific Adaptive Quantization for Large Language Model Deployment
Dec 24, 2024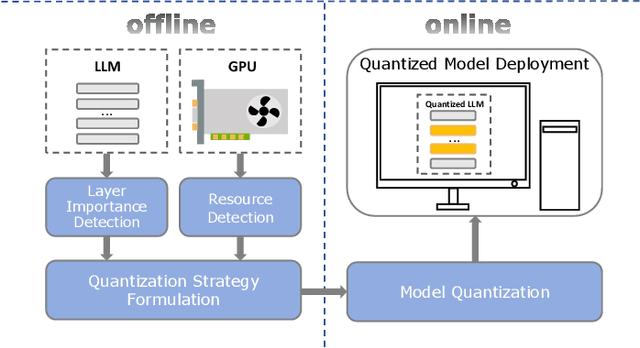
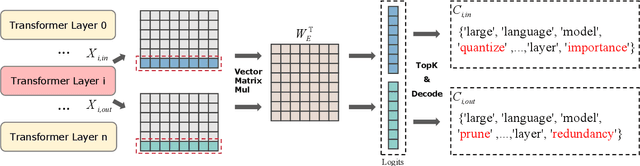
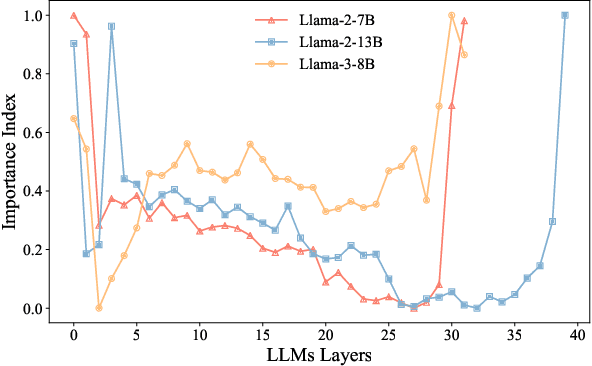
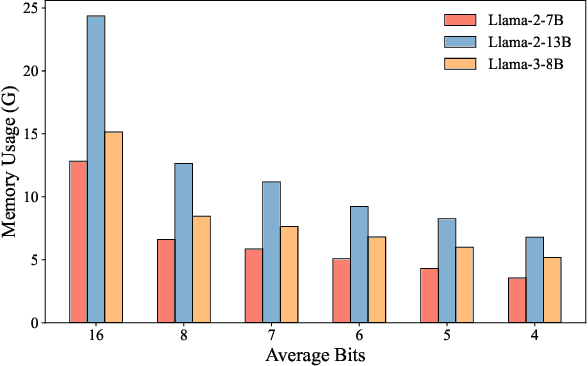
Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) demonstrate exceptional performance across various domains, the deployment of these models on edge devices has emerged as a new trend. Quantization techniques, which reduce the size and memory footprint of LLMs, are effective for enabling deployment on resource-constrained edge devices. However, existing one-size-fits-all quantization methods often fail to dynamically adjust the memory consumption of LLMs based on specific hardware characteristics and usage scenarios. To address this limitation, we propose LSAQ (Layer-Specific Adaptive Quantization), a system for adaptive quantization and dynamic deployment of LLMs based on layer importance. LSAQ evaluates layer importance by constructing top-k token sets from the inputs and outputs of each layer and calculating their Jaccard coefficient. Using this evaluation, the system adaptively adjusts quantization strategies in real time according to the resource availability of edge devices, assigning different precision levels to layers of varying importance. This approach significantly reduces the storage requirements of LLMs while maintaining model performance, enabling efficient deployment across diverse hardware platforms and usage scenarios.
Model Editing for LLMs4Code: How Far are We?
Nov 11, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models for Code (LLMs4Code) have been found to exhibit outstanding performance in the software engineering domain, especially the remarkable performance in coding tasks. However, even the most advanced LLMs4Code can inevitably contain incorrect or outdated code knowledge. Due to the high cost of training LLMs4Code, it is impractical to re-train the models for fixing these problematic code knowledge. Model editing is a new technical field for effectively and efficiently correcting erroneous knowledge in LLMs, where various model editing techniques and benchmarks have been proposed recently. Despite that, a comprehensive study that thoroughly compares and analyzes the performance of the state-of-the-art model editing techniques for adapting the knowledge within LLMs4Code across various code-related tasks is notably absent. To bridge this gap, we perform the first systematic study on applying state-of-the-art model editing approaches to repair the inaccuracy of LLMs4Code. To that end, we introduce a benchmark named CLMEEval, which consists of two datasets, i.e., CoNaLa-Edit (CNLE) with 21K+ code generation samples and CodeSearchNet-Edit (CSNE) with 16K+ code summarization samples. With the help of CLMEEval, we evaluate six advanced model editing techniques on three LLMs4Code: CodeLlama (7B), CodeQwen1.5 (7B), and Stable-Code (3B). Our findings include that the external memorization-based GRACE approach achieves the best knowledge editing effectiveness and specificity (the editing does not influence untargeted knowledge), while generalization (whether the editing can generalize to other semantically-identical inputs) is a universal challenge for existing techniques. Furthermore, building on in-depth case analysis, we introduce an enhanced version of GRACE called A-GRACE, which incorporates contrastive learning to better capture the semantics of the inputs.
Identifying Knowledge Editing Types in Large Language Models
Sep 29, 2024Abstract:Knowledge editing has emerged as an efficient approach for updating the knowledge of large language models (LLMs), attracting increasing attention in recent research. However, there is a notable lack of effective measures to prevent the malicious misuse of this technology, which could lead to harmful edits in LLMs. These malicious modifications have the potential to cause LLMs to generate toxic content, misleading users into inappropriate actions. To address this issue, we introduce a novel task, \textbf{K}nowledge \textbf{E}diting \textbf{T}ype \textbf{I}dentification (KETI), aimed at identifying malicious edits in LLMs. As part of this task, we present KETIBench, a benchmark that includes five types of malicious updates and one type of benign update. Furthermore, we develop four classical classification models and three BERT-based models as baseline identifiers for both open-source and closed-source LLMs. Our experimental results, spanning 42 trials involving two models and three knowledge editing methods, demonstrate that all seven baseline identifiers achieve decent identification performance, highlighting the feasibility of identifying malicious edits in LLMs. Additional analyses reveal that the performance of the identifiers is independent of the efficacy of the knowledge editing methods and exhibits cross-domain generalization, enabling the identification of edits from unknown sources. All data and code are available in https://github.com/xpq-tech/KETI. Warning: This paper contains examples of toxic text.
Generalization-Enhanced Code Vulnerability Detection via Multi-Task Instruction Fine-Tuning
Jun 06, 2024



Abstract:Code Pre-trained Models (CodePTMs) based vulnerability detection have achieved promising results over recent years. However, these models struggle to generalize as they typically learn superficial mapping from source code to labels instead of understanding the root causes of code vulnerabilities, resulting in poor performance in real-world scenarios beyond the training instances. To tackle this challenge, we introduce VulLLM, a novel framework that integrates multi-task learning with Large Language Models (LLMs) to effectively mine deep-seated vulnerability features. Specifically, we construct two auxiliary tasks beyond the vulnerability detection task. First, we utilize the vulnerability patches to construct a vulnerability localization task. Second, based on the vulnerability features extracted from patches, we leverage GPT-4 to construct a vulnerability interpretation task. VulLLM innovatively augments vulnerability classification by leveraging generative LLMs to understand complex vulnerability patterns, thus compelling the model to capture the root causes of vulnerabilities rather than overfitting to spurious features of a single task. The experiments conducted on six large datasets demonstrate that VulLLM surpasses seven state-of-the-art models in terms of effectiveness, generalization, and robustness.
DWE+: Dual-Way Matching Enhanced Framework for Multimodal Entity Linking
Apr 07, 2024Abstract:Multimodal entity linking (MEL) aims to utilize multimodal information (usually textual and visual information) to link ambiguous mentions to unambiguous entities in knowledge base. Current methods facing main issues: (1)treating the entire image as input may contain redundant information. (2)the insufficient utilization of entity-related information, such as attributes in images. (3)semantic inconsistency between the entity in knowledge base and its representation. To this end, we propose DWE+ for multimodal entity linking. DWE+ could capture finer semantics and dynamically maintain semantic consistency with entities. This is achieved by three aspects: (a)we introduce a method for extracting fine-grained image features by partitioning the image into multiple local objects. Then, hierarchical contrastive learning is used to further align semantics between coarse-grained information(text and image) and fine-grained (mention and visual objects). (b)we explore ways to extract visual attributes from images to enhance fusion feature such as facial features and identity. (c)we leverage Wikipedia and ChatGPT to capture the entity representation, achieving semantic enrichment from both static and dynamic perspectives, which better reflects the real-world entity semantics. Experiments on Wikimel, Richpedia, and Wikidiverse datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of DWE+ in improving MEL performance. Specifically, we optimize these datasets and achieve state-of-the-art performance on the enhanced datasets. The code and enhanced datasets are released on https://github.com/season1blue/DWET
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge