Xiaoguang Mao
MOSABench: Multi-Object Sentiment Analysis Benchmark for Evaluating Multimodal Large Language Models Understanding of Complex Image
Nov 25, 2024



Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have shown remarkable progress in high-level semantic tasks such as visual question answering, image captioning, and emotion recognition. However, despite advancements, there remains a lack of standardized benchmarks for evaluating MLLMs performance in multi-object sentiment analysis, a key task in semantic understanding. To address this gap, we introduce MOSABench, a novel evaluation dataset designed specifically for multi-object sentiment analysis. MOSABench includes approximately 1,000 images with multiple objects, requiring MLLMs to independently assess the sentiment of each object, thereby reflecting real-world complexities. Key innovations in MOSABench include distance-based target annotation, post-processing for evaluation to standardize outputs, and an improved scoring mechanism. Our experiments reveal notable limitations in current MLLMs: while some models, like mPLUG-owl and Qwen-VL2, demonstrate effective attention to sentiment-relevant features, others exhibit scattered focus and performance declines, especially as the spatial distance between objects increases. This research underscores the need for MLLMs to enhance accuracy in complex, multi-object sentiment analysis tasks and establishes MOSABench as a foundational tool for advancing sentiment analysis capabilities in MLLMs.
PTA: Enhancing Multimodal Sentiment Analysis through Pipelined Prediction and Translation-based Alignment
May 23, 2024
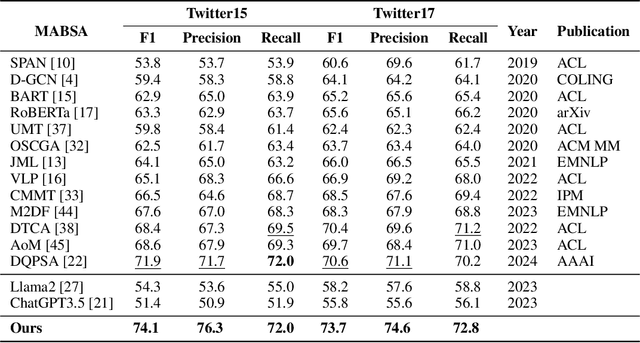


Abstract:Multimodal aspect-based sentiment analysis (MABSA) aims to understand opinions in a granular manner, advancing human-computer interaction and other fields. Traditionally, MABSA methods use a joint prediction approach to identify aspects and sentiments simultaneously. However, we argue that joint models are not always superior. Our analysis shows that joint models struggle to align relevant text tokens with image patches, leading to misalignment and ineffective image utilization. In contrast, a pipeline framework first identifies aspects through MATE (Multimodal Aspect Term Extraction) and then aligns these aspects with image patches for sentiment classification (MASC: Multimodal Aspect-Oriented Sentiment Classification). This method is better suited for multimodal scenarios where effective image use is crucial. We present three key observations: (a) MATE and MASC have different feature requirements, with MATE focusing on token-level features and MASC on sequence-level features; (b) the aspect identified by MATE is crucial for effective image utilization; and (c) images play a trivial role in previous MABSA methods due to high noise. Based on these observations, we propose a pipeline framework that first predicts the aspect and then uses translation-based alignment (TBA) to enhance multimodal semantic consistency for better image utilization. Our method achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on widely used MABSA datasets Twitter-15 and Twitter-17. This demonstrates the effectiveness of the pipeline approach and its potential to provide valuable insights for future MABSA research. For reproducibility, the code and checkpoint will be released.
DWE+: Dual-Way Matching Enhanced Framework for Multimodal Entity Linking
Apr 07, 2024Abstract:Multimodal entity linking (MEL) aims to utilize multimodal information (usually textual and visual information) to link ambiguous mentions to unambiguous entities in knowledge base. Current methods facing main issues: (1)treating the entire image as input may contain redundant information. (2)the insufficient utilization of entity-related information, such as attributes in images. (3)semantic inconsistency between the entity in knowledge base and its representation. To this end, we propose DWE+ for multimodal entity linking. DWE+ could capture finer semantics and dynamically maintain semantic consistency with entities. This is achieved by three aspects: (a)we introduce a method for extracting fine-grained image features by partitioning the image into multiple local objects. Then, hierarchical contrastive learning is used to further align semantics between coarse-grained information(text and image) and fine-grained (mention and visual objects). (b)we explore ways to extract visual attributes from images to enhance fusion feature such as facial features and identity. (c)we leverage Wikipedia and ChatGPT to capture the entity representation, achieving semantic enrichment from both static and dynamic perspectives, which better reflects the real-world entity semantics. Experiments on Wikimel, Richpedia, and Wikidiverse datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of DWE+ in improving MEL performance. Specifically, we optimize these datasets and achieve state-of-the-art performance on the enhanced datasets. The code and enhanced datasets are released on https://github.com/season1blue/DWET
A Dual-way Enhanced Framework from Text Matching Point of View for Multimodal Entity Linking
Dec 19, 2023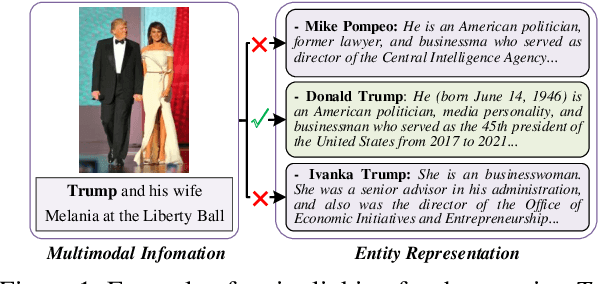



Abstract:Multimodal Entity Linking (MEL) aims at linking ambiguous mentions with multimodal information to entity in Knowledge Graph (KG) such as Wikipedia, which plays a key role in many applications. However, existing methods suffer from shortcomings, including modality impurity such as noise in raw image and ambiguous textual entity representation, which puts obstacles to MEL. We formulate multimodal entity linking as a neural text matching problem where each multimodal information (text and image) is treated as a query, and the model learns the mapping from each query to the relevant entity from candidate entities. This paper introduces a dual-way enhanced (DWE) framework for MEL: (1) our model refines queries with multimodal data and addresses semantic gaps using cross-modal enhancers between text and image information. Besides, DWE innovatively leverages fine-grained image attributes, including facial characteristic and scene feature, to enhance and refine visual features. (2)By using Wikipedia descriptions, DWE enriches entity semantics and obtains more comprehensive textual representation, which reduces between textual representation and the entities in KG. Extensive experiments on three public benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance, indicating the superiority of our model. The code is released on https://github.com/season1blue/DWE
StyleFlow: Disentangle Latent Representations via Normalizing Flow for Unsupervised Text Style Transfer
Dec 19, 2022



Abstract:Text style transfer aims to alter the style of a sentence while preserving its content. Due to the lack of parallel corpora, most recent work focuses on unsupervised methods and often uses cycle construction to train models. Since cycle construction helps to improve the style transfer ability of the model by rebuilding transferred sentences back to original-style sentences, it brings about a content loss in unsupervised text style transfer tasks. In this paper, we propose a novel disentanglement-based style transfer model StyleFlow to enhance content preservation. Instead of the typical encoder-decoder scheme, StyleFlow can not only conduct the forward process to obtain the output, but also infer to the input through the output. We design an attention-aware coupling layers to disentangle the content representations and the style representations of a sentence. Besides, we propose a data augmentation method based on Normalizing Flow to improve the robustness of the model. Experiment results demonstrate that our model preserves content effectively and achieves the state-of-the-art performance on the most metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge