Zeyu Lei
SurgVisAgent: Multimodal Agentic Model for Versatile Surgical Visual Enhancement
Jul 03, 2025



Abstract:Precise surgical interventions are vital to patient safety, and advanced enhancement algorithms have been developed to assist surgeons in decision-making. Despite significant progress, these algorithms are typically designed for single tasks in specific scenarios, limiting their effectiveness in complex real-world situations. To address this limitation, we propose SurgVisAgent, an end-to-end intelligent surgical vision agent built on multimodal large language models (MLLMs). SurgVisAgent dynamically identifies distortion categories and severity levels in endoscopic images, enabling it to perform a variety of enhancement tasks such as low-light enhancement, overexposure correction, motion blur elimination, and smoke removal. Specifically, to achieve superior surgical scenario understanding, we design a prior model that provides domain-specific knowledge. Additionally, through in-context few-shot learning and chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning, SurgVisAgent delivers customized image enhancements tailored to a wide range of distortion types and severity levels, thereby addressing the diverse requirements of surgeons. Furthermore, we construct a comprehensive benchmark simulating real-world surgical distortions, on which extensive experiments demonstrate that SurgVisAgent surpasses traditional single-task models, highlighting its potential as a unified solution for surgical assistance.
Can We Get Rid of Handcrafted Feature Extractors? SparseViT: Nonsemantics-Centered, Parameter-Efficient Image Manipulation Localization Through Spare-Coding Transformer
Dec 19, 2024
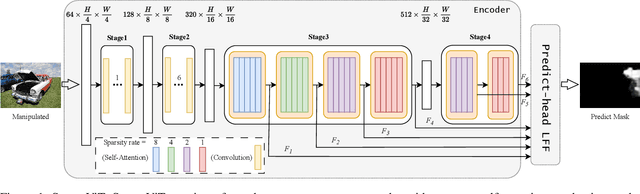
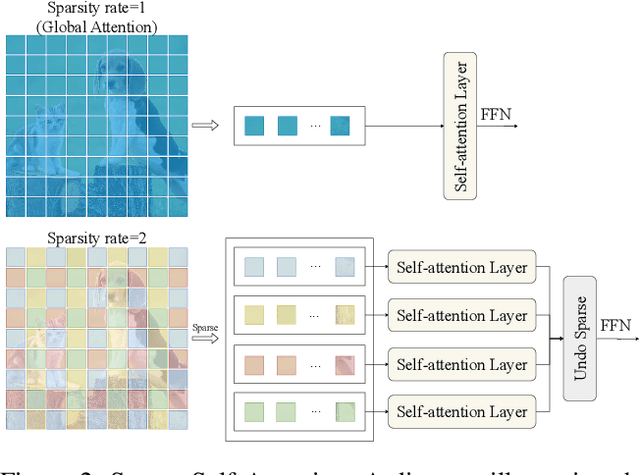
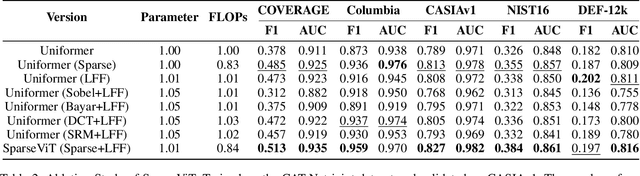
Abstract:Non-semantic features or semantic-agnostic features, which are irrelevant to image context but sensitive to image manipulations, are recognized as evidential to Image Manipulation Localization (IML). Since manual labels are impossible, existing works rely on handcrafted methods to extract non-semantic features. Handcrafted non-semantic features jeopardize IML model's generalization ability in unseen or complex scenarios. Therefore, for IML, the elephant in the room is: How to adaptively extract non-semantic features? Non-semantic features are context-irrelevant and manipulation-sensitive. That is, within an image, they are consistent across patches unless manipulation occurs. Then, spare and discrete interactions among image patches are sufficient for extracting non-semantic features. However, image semantics vary drastically on different patches, requiring dense and continuous interactions among image patches for learning semantic representations. Hence, in this paper, we propose a Sparse Vision Transformer (SparseViT), which reformulates the dense, global self-attention in ViT into a sparse, discrete manner. Such sparse self-attention breaks image semantics and forces SparseViT to adaptively extract non-semantic features for images. Besides, compared with existing IML models, the sparse self-attention mechanism largely reduced the model size (max 80% in FLOPs), achieving stunning parameter efficiency and computation reduction. Extensive experiments demonstrate that, without any handcrafted feature extractors, SparseViT is superior in both generalization and efficiency across benchmark datasets.
Mesoscopic Insights: Orchestrating Multi-scale & Hybrid Architecture for Image Manipulation Localization
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:The mesoscopic level serves as a bridge between the macroscopic and microscopic worlds, addressing gaps overlooked by both. Image manipulation localization (IML), a crucial technique to pursue truth from fake images, has long relied on low-level (microscopic-level) traces. However, in practice, most tampering aims to deceive the audience by altering image semantics. As a result, manipulation commonly occurs at the object level (macroscopic level), which is equally important as microscopic traces. Therefore, integrating these two levels into the mesoscopic level presents a new perspective for IML research. Inspired by this, our paper explores how to simultaneously construct mesoscopic representations of micro and macro information for IML and introduces the Mesorch architecture to orchestrate both. Specifically, this architecture i) combines Transformers and CNNs in parallel, with Transformers extracting macro information and CNNs capturing micro details, and ii) explores across different scales, assessing micro and macro information seamlessly. Additionally, based on the Mesorch architecture, the paper introduces two baseline models aimed at solving IML tasks through mesoscopic representation. Extensive experiments across four datasets have demonstrated that our models surpass the current state-of-the-art in terms of performance, computational complexity, and robustness.
M^3:Manipulation Mask Manufacturer for Arbitrary-Scale Super-Resolution Mask
Jul 04, 2024Abstract:In the field of image manipulation localization (IML), the small quantity and poor quality of existing datasets have always been major issues. A dataset containing various types of manipulations will greatly help improve the accuracy of IML models. Images on the internet (such as those on Baidu Tieba's PS Bar) are manipulated using various techniques, and creating a dataset from these images will significantly enrich the types of manipulations in our data. However, images on the internet suffer from resolution and clarity issues, and the masks obtained by simply subtracting the manipulated image from the original contain various noises. These noises are difficult to remove, rendering the masks unusable for IML models. Inspired by the field of change detection, we treat the original and manipulated images as changes over time for the same image and view the data generation task as a change detection task. However, due to clarity issues between images, conventional change detection models perform poorly. Therefore, we introduced a super-resolution module and proposed the Manipulation Mask Manufacturer (MMM) framework. It enhances the resolution of both the original and tampered images, thereby improving image details for better comparison. Simultaneously, the framework converts the original and tampered images into feature embeddings and concatenates them, effectively modeling the context. Additionally, we created the Manipulation Mask Manufacturer Dataset (MMMD), a dataset that covers a wide range of manipulation techniques. We aim to contribute to the fields of image forensics and manipulation detection by providing more realistic manipulation data through MMM and MMMD. Detailed information about MMMD and the download link can be found at: the code and datasets will be made available.
IMDL-BenCo: A Comprehensive Benchmark and Codebase for Image Manipulation Detection & Localization
Jun 15, 2024
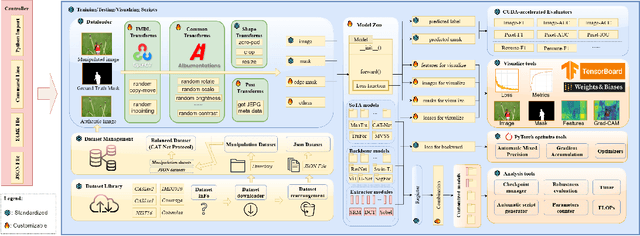
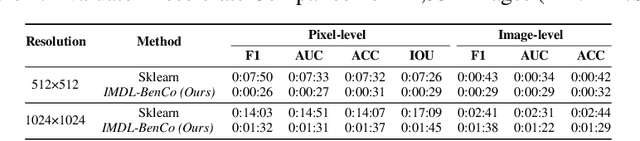
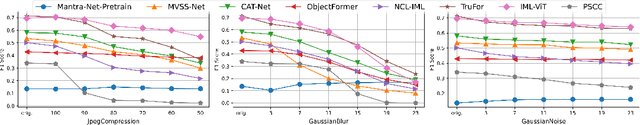
Abstract:A comprehensive benchmark is yet to be established in the Image Manipulation Detection \& Localization (IMDL) field. The absence of such a benchmark leads to insufficient and misleading model evaluations, severely undermining the development of this field. However, the scarcity of open-sourced baseline models and inconsistent training and evaluation protocols make conducting rigorous experiments and faithful comparisons among IMDL models challenging. To address these challenges, we introduce IMDL-BenCo, the first comprehensive IMDL benchmark and modular codebase. IMDL-BenCo:~\textbf{i)} decomposes the IMDL framework into standardized, reusable components and revises the model construction pipeline, improving coding efficiency and customization flexibility;~\textbf{ii)} fully implements or incorporates training code for state-of-the-art models to establish a comprehensive IMDL benchmark; and~\textbf{iii)} conducts deep analysis based on the established benchmark and codebase, offering new insights into IMDL model architecture, dataset characteristics, and evaluation standards. Specifically, IMDL-BenCo includes common processing algorithms, 8 state-of-the-art IMDL models (1 of which are reproduced from scratch), 2 sets of standard training and evaluation protocols, 15 GPU-accelerated evaluation metrics, and 3 kinds of robustness evaluation. This benchmark and codebase represent a significant leap forward in calibrating the current progress in the IMDL field and inspiring future breakthroughs. Code is available at: https://github.com/scu-zjz/IMDLBenCo
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge