Ran He
Learning Fair Domain Adaptation with Virtual Label Distribution
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) aims to mitigate performance degradation when training and testing data are sampled from different distributions. While significant progress has been made in enhancing overall accuracy, most existing methods overlook performance disparities across categories-an issue we refer to as category fairness. Our empirical analysis reveals that UDA classifiers tend to favor certain easy categories while neglecting difficult ones. To address this, we propose Virtual Label-distribution-aware Learning (VILL), a simple yet effective framework designed to improve worst-case performance while preserving high overall accuracy. The core of VILL is an adaptive re-weighting strategy that amplifies the influence of hard-to-classify categories. Furthermore, we introduce a KL-divergence-based re-balancing strategy, which explicitly adjusts decision boundaries to enhance category fairness. Experiments on commonly used datasets demonstrate that VILL can be seamlessly integrated as a plug-and-play module into existing UDA methods, significantly improving category fairness.
AgentHallu: Benchmarking Automated Hallucination Attribution of LLM-based Agents
Jan 11, 2026Abstract:As LLM-based agents operate over sequential multi-step reasoning, hallucinations arising at intermediate steps risk propagating along the trajectory, thus degrading overall reliability. Unlike hallucination detection in single-turn responses, diagnosing hallucinations in multi-step workflows requires identifying which step causes the initial divergence. To fill this gap, we propose a new research task, automated hallucination attribution of LLM-based agents, aiming to identify the step responsible for the hallucination and explain why. To support this task, we introduce AgentHallu, a comprehensive benchmark with: (1) 693 high-quality trajectories spanning 7 agent frameworks and 5 domains, (2) a hallucination taxonomy organized into 5 categories (Planning, Retrieval, Reasoning, Human-Interaction, and Tool-Use) and 14 sub-categories, and (3) multi-level annotations curated by humans, covering binary labels, hallucination-responsible steps, and causal explanations. We evaluate 13 leading models, and results show the task is challenging even for top-tier models (like GPT-5, Gemini-2.5-Pro). The best-performing model achieves only 41.1\% step localization accuracy, where tool-use hallucinations are the most challenging at just 11.6\%. We believe AgentHallu will catalyze future research into developing robust, transparent, and reliable agentic systems.
AWPO: Enhancing Tool-Use of Large Language Models through Explicit Integration of Reasoning Rewards
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:While reinforcement learning (RL) shows promise in training tool-use large language models (LLMs) using verifiable outcome rewards, existing methods largely overlook the potential of explicit reasoning rewards to bolster reasoning and tool utilization. Furthermore, natively combining reasoning and outcome rewards may yield suboptimal performance or conflict with the primary optimization objective. To address this, we propose advantage-weighted policy optimization (AWPO) -- a principled RL framework that effectively integrates explicit reasoning rewards to enhance tool-use capability. AWPO incorporates variance-aware gating and difficulty-aware weighting to adaptively modulate advantages from reasoning signals based on group-relative statistics, alongside a tailored clipping mechanism for stable optimization. Extensive experiments demonstrate that AWPO achieves state-of-the-art performance across standard tool-use benchmarks, significantly outperforming strong baselines and leading closed-source models in challenging multi-turn scenarios. Notably, with exceptional parameter efficiency, our 4B model surpasses Grok-4 by 16.0 percent in multi-turn accuracy while preserving generalization capability on the out-of-distribution MMLU-Pro benchmark.
Expand and Prune: Maximizing Trajectory Diversity for Effective GRPO in Generative Models
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) is a powerful technique for aligning generative models, but its effectiveness is bottlenecked by the conflict between large group sizes and prohibitive computational costs. In this work, we investigate the trade-off through empirical studies, yielding two key observations. First, we discover the reward clustering phenomenon in which many trajectories collapse toward the group-mean reward, offering limited optimization value. Second, we design a heuristic strategy named Optimal Variance Filtering (OVF), and verify that a high-variance subset of trajectories, selected by OVF can outperform the larger, unfiltered group. However, this static, post-sampling OVF approach still necessitates critical computational overhead, as it performs unnecessary sampling for trajectories that are ultimately discarded. To resolve this, we propose Pro-GRPO (Proactive GRPO), a novel dynamic framework that integrates latent feature-based trajectory pruning into the sampling process. Through the early termination of reward-clustered trajectories, Pro-GRPO reduces computational overhead. Leveraging its efficiency, Pro-GRPO employs an "Expand-and-Prune" strategy. This strategy first expands the size of initial sampling group to maximize trajectory diversity, then it applies multi-step OVF to the latents, avoiding prohibitive computational costs. Extensive experiments on both diffusion-based and flow-based models demonstrate the generality and effectiveness of our Pro-GRPO framework.
VITA-VLA: Efficiently Teaching Vision-Language Models to Act via Action Expert Distillation
Oct 10, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language Action (VLA) models significantly advance robotic manipulation by leveraging the strong perception capabilities of pretrained vision-language models (VLMs). By integrating action modules into these pretrained models, VLA methods exhibit improved generalization. However, training them from scratch is costly. In this work, we propose a simple yet effective distillation-based framework that equips VLMs with action-execution capability by transferring knowledge from pretrained small action models. Our architecture retains the original VLM structure, adding only an action token and a state encoder to incorporate physical inputs. To distill action knowledge, we adopt a two-stage training strategy. First, we perform lightweight alignment by mapping VLM hidden states into the action space of the small action model, enabling effective reuse of its pretrained action decoder and avoiding expensive pretraining. Second, we selectively fine-tune the language model, state encoder, and action modules, enabling the system to integrate multimodal inputs with precise action generation. Specifically, the action token provides the VLM with a direct handle for predicting future actions, while the state encoder allows the model to incorporate robot dynamics not captured by vision alone. This design yields substantial efficiency gains over training large VLA models from scratch. Compared with previous state-of-the-art methods, our method achieves 97.3% average success rate on LIBERO (11.8% improvement) and 93.5% on LIBERO-LONG (24.5% improvement). In real-world experiments across five manipulation tasks, our method consistently outperforms the teacher model, achieving 82.0% success rate (17% improvement), which demonstrate that action distillation effectively enables VLMs to generate precise actions while substantially reducing training costs.
Towards Robust Defense against Customization via Protective Perturbation Resistant to Diffusion-based Purification
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models like Stable Diffusion have become prominent in visual synthesis tasks due to their powerful customization capabilities, which also introduce significant security risks, including deepfakes and copyright infringement. In response, a class of methods known as protective perturbation emerged, which mitigates image misuse by injecting imperceptible adversarial noise. However, purification can remove protective perturbations, thereby exposing images again to the risk of malicious forgery. In this work, we formalize the anti-purification task, highlighting challenges that hinder existing approaches, and propose a simple diagnostic protective perturbation named AntiPure. AntiPure exposes vulnerabilities of purification within the "purification-customization" workflow, owing to two guidance mechanisms: 1) Patch-wise Frequency Guidance, which reduces the model's influence over high-frequency components in the purified image, and 2) Erroneous Timestep Guidance, which disrupts the model's denoising strategy across different timesteps. With additional guidance, AntiPure embeds imperceptible perturbations that persist under representative purification settings, achieving effective post-customization distortion. Experiments show that, as a stress test for purification, AntiPure achieves minimal perceptual discrepancy and maximal distortion, outperforming other protective perturbation methods within the purification-customization workflow.
A Comprehensive Survey on Trustworthiness in Reasoning with Large Language Models
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:The development of Long-CoT reasoning has advanced LLM performance across various tasks, including language understanding, complex problem solving, and code generation. This paradigm enables models to generate intermediate reasoning steps, thereby improving both accuracy and interpretability. However, despite these advancements, a comprehensive understanding of how CoT-based reasoning affects the trustworthiness of language models remains underdeveloped. In this paper, we survey recent work on reasoning models and CoT techniques, focusing on five core dimensions of trustworthy reasoning: truthfulness, safety, robustness, fairness, and privacy. For each aspect, we provide a clear and structured overview of recent studies in chronological order, along with detailed analyses of their methodologies, findings, and limitations. Future research directions are also appended at the end for reference and discussion. Overall, while reasoning techniques hold promise for enhancing model trustworthiness through hallucination mitigation, harmful content detection, and robustness improvement, cutting-edge reasoning models themselves often suffer from comparable or even greater vulnerabilities in safety, robustness, and privacy. By synthesizing these insights, we hope this work serves as a valuable and timely resource for the AI safety community to stay informed on the latest progress in reasoning trustworthiness. A full list of related papers can be found at \href{https://github.com/ybwang119/Awesome-reasoning-safety}{https://github.com/ybwang119/Awesome-reasoning-safety}.
InfiniteTalk: Audio-driven Video Generation for Sparse-Frame Video Dubbing
Aug 19, 2025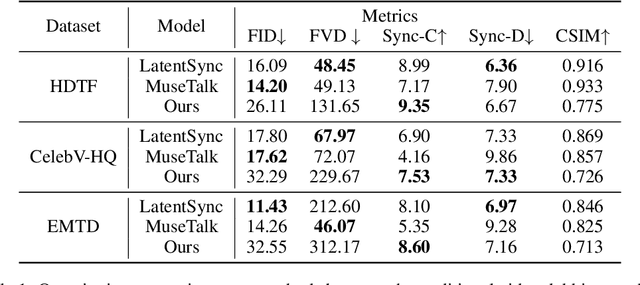
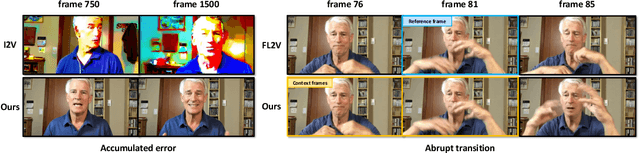
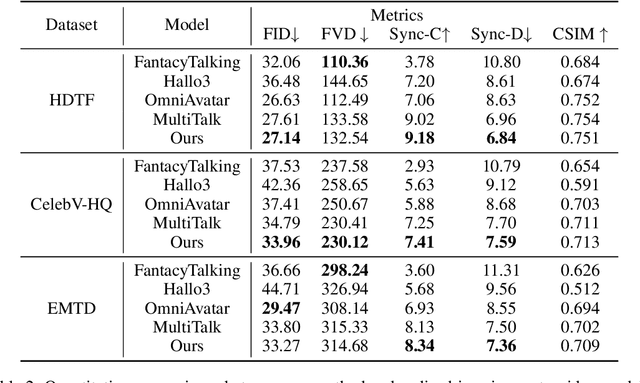
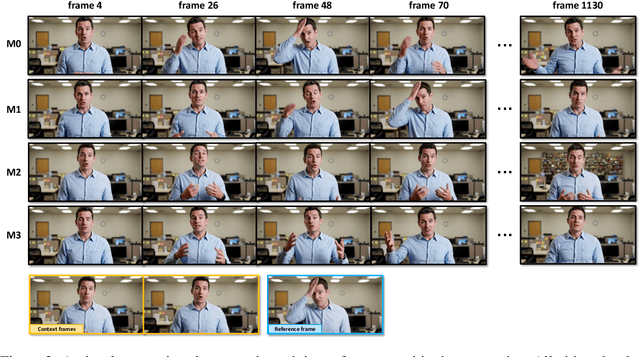
Abstract:Recent breakthroughs in video AIGC have ushered in a transformative era for audio-driven human animation. However, conventional video dubbing techniques remain constrained to mouth region editing, resulting in discordant facial expressions and body gestures that compromise viewer immersion. To overcome this limitation, we introduce sparse-frame video dubbing, a novel paradigm that strategically preserves reference keyframes to maintain identity, iconic gestures, and camera trajectories while enabling holistic, audio-synchronized full-body motion editing. Through critical analysis, we identify why naive image-to-video models fail in this task, particularly their inability to achieve adaptive conditioning. Addressing this, we propose InfiniteTalk, a streaming audio-driven generator designed for infinite-length long sequence dubbing. This architecture leverages temporal context frames for seamless inter-chunk transitions and incorporates a simple yet effective sampling strategy that optimizes control strength via fine-grained reference frame positioning. Comprehensive evaluations on HDTF, CelebV-HQ, and EMTD datasets demonstrate state-of-the-art performance. Quantitative metrics confirm superior visual realism, emotional coherence, and full-body motion synchronization.
Adapting Vision-Language Models Without Labels: A Comprehensive Survey
Aug 07, 2025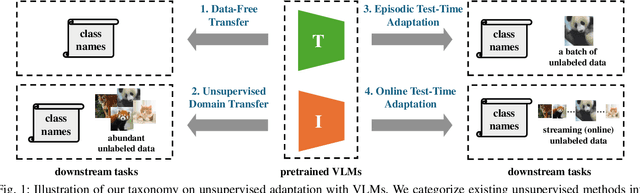
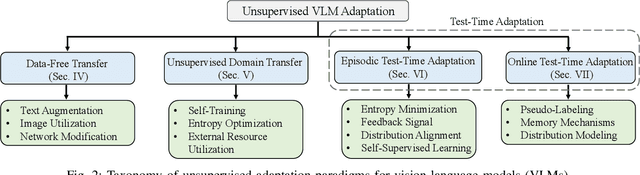
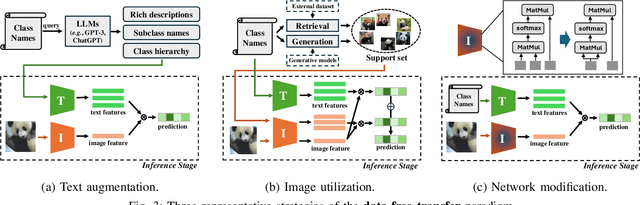
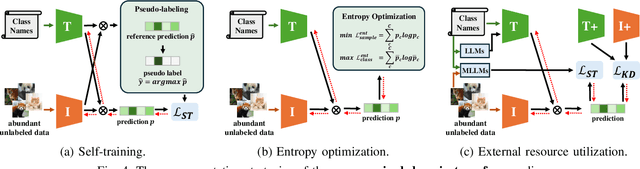
Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have demonstrated remarkable generalization capabilities across a wide range of tasks. However, their performance often remains suboptimal when directly applied to specific downstream scenarios without task-specific adaptation. To enhance their utility while preserving data efficiency, recent research has increasingly focused on unsupervised adaptation methods that do not rely on labeled data. Despite the growing interest in this area, there remains a lack of a unified, task-oriented survey dedicated to unsupervised VLM adaptation. To bridge this gap, we present a comprehensive and structured overview of the field. We propose a taxonomy based on the availability and nature of unlabeled visual data, categorizing existing approaches into four key paradigms: Data-Free Transfer (no data), Unsupervised Domain Transfer (abundant data), Episodic Test-Time Adaptation (batch data), and Online Test-Time Adaptation (streaming data). Within this framework, we analyze core methodologies and adaptation strategies associated with each paradigm, aiming to establish a systematic understanding of the field. Additionally, we review representative benchmarks across diverse applications and highlight open challenges and promising directions for future research. An actively maintained repository of relevant literature is available at https://github.com/tim-learn/Awesome-LabelFree-VLMs.
Test-Time Immunization: A Universal Defense Framework Against Jailbreaks for (Multimodal) Large Language Models
May 28, 2025Abstract:While (multimodal) large language models (LLMs) have attracted widespread attention due to their exceptional capabilities, they remain vulnerable to jailbreak attacks. Various defense methods are proposed to defend against jailbreak attacks, however, they are often tailored to specific types of jailbreak attacks, limiting their effectiveness against diverse adversarial strategies. For instance, rephrasing-based defenses are effective against text adversarial jailbreaks but fail to counteract image-based attacks. To overcome these limitations, we propose a universal defense framework, termed Test-time IMmunization (TIM), which can adaptively defend against various jailbreak attacks in a self-evolving way. Specifically, TIM initially trains a gist token for efficient detection, which it subsequently applies to detect jailbreak activities during inference. When jailbreak attempts are identified, TIM implements safety fine-tuning using the detected jailbreak instructions paired with refusal answers. Furthermore, to mitigate potential performance degradation in the detector caused by parameter updates during safety fine-tuning, we decouple the fine-tuning process from the detection module. Extensive experiments on both LLMs and multimodal LLMs demonstrate the efficacy of TIM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge