Zheqi He
LaoBench: A Large-Scale Multidimensional Lao Benchmark for Large Language Models
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) has not been matched by their evaluation in low-resource languages, especially Southeast Asian languages like Lao. To fill this gap, we introduce LaoBench, the first large-scale, high-quality, and multidimensional benchmark dataset dedicated to assessing LLMs' comprehensive language understanding and reasoning abilities in Lao. LaoBench comprises over 17,000 carefully curated samples spanning three core dimensions: knowledge application, K12 foundational education, and bilingual translation among Lao, Chinese, and English. The dataset is divided into open-source and closed-source subsets, with the closed-source portion enabling black-box evaluation on an official platform to ensure fairness and data security. Our data construction pipeline integrates expert human curation with automated agent-assisted verification, ensuring linguistic accuracy, cultural relevance, and educational value. Benchmarking multiple state-of-the-art LLMs on LaoBench reveals that current models still face significant challenges in mastering Lao across diverse tasks. We hope LaoBench will catalyze further research and development of AI technologies for underrepresented Southeast Asian languages.
Do Vision-Language Models Measure Up? Benchmarking Visual Measurement Reading with MeasureBench
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:Reading measurement instruments is effortless for humans and requires relatively little domain expertise, yet it remains surprisingly challenging for current vision-language models (VLMs) as we find in preliminary evaluation. In this work, we introduce MeasureBench, a benchmark on visual measurement reading covering both real-world and synthesized images of various types of measurements, along with an extensible pipeline for data synthesis. Our pipeline procedurally generates a specified type of gauge with controllable visual appearance, enabling scalable variation in key details such as pointers, scales, fonts, lighting, and clutter. Evaluation on popular proprietary and open-weight VLMs shows that even the strongest frontier VLMs struggle measurement reading in general. A consistent failure mode is indicator localization: models can read digits or labels but misidentify the key positions of pointers or alignments, leading to big numeric errors despite plausible textual reasoning. We have also conducted preliminary experiments with reinforcement learning over synthetic data, and find encouraging results on in-domain synthetic subset but less promising for real-world images. Our analysis highlights a fundamental limitation of current VLMs in fine-grained spatial grounding. We hope this resource can help future advances on visually grounded numeracy and precise spatial perception of VLMs, bridging the gap between recognizing numbers and measuring the world.
RoboBrain 2.0 Technical Report
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:We introduce RoboBrain 2.0, our latest generation of embodied vision-language foundation models, designed to unify perception, reasoning, and planning for complex embodied tasks in physical environments. It comes in two variants: a lightweight 7B model and a full-scale 32B model, featuring a heterogeneous architecture with a vision encoder and a language model. Despite its compact size, RoboBrain 2.0 achieves strong performance across a wide spectrum of embodied reasoning tasks. On both spatial and temporal benchmarks, the 32B variant achieves leading results, surpassing prior open-source and proprietary models. In particular, it supports key real-world embodied AI capabilities, including spatial understanding (e.g., affordance prediction, spatial referring, trajectory forecasting) and temporal decision-making (e.g., closed-loop interaction, multi-agent long-horizon planning, and scene graph updating). This report details the model architecture, data construction, multi-stage training strategies, infrastructure and practical applications. We hope RoboBrain 2.0 advances embodied AI research and serves as a practical step toward building generalist embodied agents. The code, checkpoint and benchmark are available at https://superrobobrain.github.io.
FlagEvalMM: A Flexible Framework for Comprehensive Multimodal Model Evaluation
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:We present FlagEvalMM, an open-source evaluation framework designed to comprehensively assess multimodal models across a diverse range of vision-language understanding and generation tasks, such as visual question answering, text-to-image/video generation, and image-text retrieval. We decouple model inference from evaluation through an independent evaluation service, thus enabling flexible resource allocation and seamless integration of new tasks and models. Moreover, FlagEvalMM utilizes advanced inference acceleration tools (e.g., vLLM, SGLang) and asynchronous data loading to significantly enhance evaluation efficiency. Extensive experiments show that FlagEvalMM offers accurate and efficient insights into model strengths and limitations, making it a valuable tool for advancing multimodal research. The framework is publicly accessible athttps://github.com/flageval-baai/FlagEvalMM.
Video-SafetyBench: A Benchmark for Safety Evaluation of Video LVLMs
May 17, 2025Abstract:The increasing deployment of Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) raises safety concerns under potential malicious inputs. However, existing multimodal safety evaluations primarily focus on model vulnerabilities exposed by static image inputs, ignoring the temporal dynamics of video that may induce distinct safety risks. To bridge this gap, we introduce Video-SafetyBench, the first comprehensive benchmark designed to evaluate the safety of LVLMs under video-text attacks. It comprises 2,264 video-text pairs spanning 48 fine-grained unsafe categories, each pairing a synthesized video with either a harmful query, which contains explicit malice, or a benign query, which appears harmless but triggers harmful behavior when interpreted alongside the video. To generate semantically accurate videos for safety evaluation, we design a controllable pipeline that decomposes video semantics into subject images (what is shown) and motion text (how it moves), which jointly guide the synthesis of query-relevant videos. To effectively evaluate uncertain or borderline harmful outputs, we propose RJScore, a novel LLM-based metric that incorporates the confidence of judge models and human-aligned decision threshold calibration. Extensive experiments show that benign-query video composition achieves average attack success rates of 67.2%, revealing consistent vulnerabilities to video-induced attacks. We believe Video-SafetyBench will catalyze future research into video-based safety evaluation and defense strategies.
Emu3: Next-Token Prediction is All You Need
Sep 27, 2024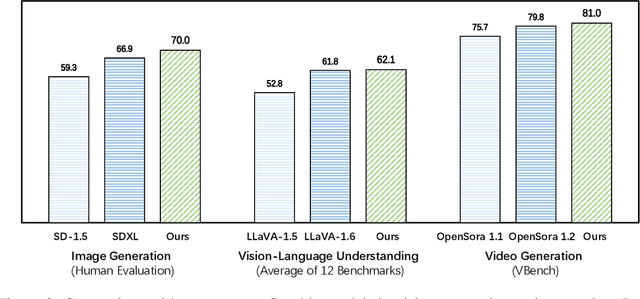


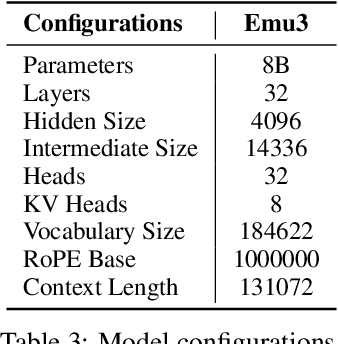
Abstract:While next-token prediction is considered a promising path towards artificial general intelligence, it has struggled to excel in multimodal tasks, which are still dominated by diffusion models (e.g., Stable Diffusion) and compositional approaches (e.g., CLIP combined with LLMs). In this paper, we introduce Emu3, a new suite of state-of-the-art multimodal models trained solely with next-token prediction. By tokenizing images, text, and videos into a discrete space, we train a single transformer from scratch on a mixture of multimodal sequences. Emu3 outperforms several well-established task-specific models in both generation and perception tasks, surpassing flagship models such as SDXL and LLaVA-1.6, while eliminating the need for diffusion or compositional architectures. Emu3 is also capable of generating high-fidelity video via predicting the next token in a video sequence. We simplify complex multimodal model designs by converging on a singular focus: tokens, unlocking great potential for scaling both during training and inference. Our results demonstrate that next-token prediction is a promising path towards building general multimodal intelligence beyond language. We open-source key techniques and models to support further research in this direction.
Evaluating Attribute Comprehension in Large Vision-Language Models
Aug 25, 2024



Abstract:Currently, large vision-language models have gained promising progress on many downstream tasks. However, they still suffer many challenges in fine-grained visual understanding tasks, such as object attribute comprehension. Besides, there have been growing efforts on the evaluations of large vision-language models, but lack of in-depth study of attribute comprehension and the visual language fine-tuning process. In this paper, we propose to evaluate the attribute comprehension ability of large vision-language models from two perspectives: attribute recognition and attribute hierarchy understanding. We evaluate three vision-language interactions, including visual question answering, image-text matching, and image-text cosine similarity. Furthermore, we explore the factors affecting attribute comprehension during fine-tuning. Through a series of quantitative and qualitative experiments, we introduce three main findings: (1) Large vision-language models possess good attribute recognition ability, but their hierarchical understanding ability is relatively limited. (2) Compared to ITC, ITM exhibits superior capability in capturing finer details, making it more suitable for attribute understanding tasks. (3) The attribute information in the captions used for fine-tuning plays a crucial role in attribute understanding. We hope this work can help guide future progress in fine-grained visual understanding of large vision-language models.
CMMU: A Benchmark for Chinese Multi-modal Multi-type Question Understanding and Reasoning
Jan 26, 2024



Abstract:Multi-modal large language models(MLLMs) have achieved remarkable progress and demonstrated powerful knowledge comprehension and reasoning abilities. However, the mastery of domain-specific knowledge, which is essential for evaluating the intelligence of MLLMs, continues to be a challenge. Current multi-modal benchmarks for domain-specific knowledge concentrate on multiple-choice questions and are predominantly available in English, which imposes limitations on the comprehensiveness of the evaluation. To this end, we introduce CMMU, a novel benchmark for multi-modal and multi-type question understanding and reasoning in Chinese. CMMU consists of 3,603 questions in 7 subjects, covering knowledge from primary to high school. The questions can be categorized into 3 types: multiple-choice, multiple-response, and fill-in-the-blank, bringing greater challenges to MLLMs. In addition, we propose a rigorous evaluation strategy called ShiftCheck for assessing multiple-choice questions. The strategy aims to reduce position bias, minimize the influence of randomness on correctness, and perform a quantitative analysis of position bias. We evaluate seven open-source MLLMs along with GPT4-V, Gemini-Pro, and Qwen-VL-Plus. The results demonstrate that CMMU poses a significant challenge to the recent MLLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge