Wenjian Sun
Trajectory Entropy: Modeling Game State Stability from Multimodality Trajectory Prediction
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Complex interactions among agents present a significant challenge for autonomous driving in real-world scenarios. Recently, a promising approach has emerged, which formulates the interactions of agents as a level-k game framework. It effectively decouples agent policies by hierarchical game levels. However, this framework ignores both the varying driving complexities among agents and the dynamic changes in agent states across game levels, instead treating them uniformly. Consequently, redundant and error-prone computations are introduced into this framework. To tackle the issue, this paper proposes a metric, termed as Trajectory Entropy, to reveal the game status of agents within the level-k game framework. The key insight stems from recognizing the inherit relationship between agent policy uncertainty and the associated driving complexity. Specifically, Trajectory Entropy extracts statistical signals representing uncertainty from the multimodality trajectory prediction results of agents in the game. Then, the signal-to-noise ratio of this signal is utilized to quantify the game status of agents. Based on the proposed Trajectory Entropy, we refine the current level-k game framework through a simple gating mechanism, significantly improving overall accuracy while reducing computational costs. Our method is evaluated on the Waymo and nuPlan datasets, in terms of trajectory prediction, open-loop and closed-loop planning tasks. The results demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of our method, with precision improved by up to 19.89% for prediction and up to 16.48% for planning.
IMAGINE-E: Image Generation Intelligence Evaluation of State-of-the-art Text-to-Image Models
Jan 23, 2025



Abstract:With the rapid development of diffusion models, text-to-image(T2I) models have made significant progress, showcasing impressive abilities in prompt following and image generation. Recently launched models such as FLUX.1 and Ideogram2.0, along with others like Dall-E3 and Stable Diffusion 3, have demonstrated exceptional performance across various complex tasks, raising questions about whether T2I models are moving towards general-purpose applicability. Beyond traditional image generation, these models exhibit capabilities across a range of fields, including controllable generation, image editing, video, audio, 3D, and motion generation, as well as computer vision tasks like semantic segmentation and depth estimation. However, current evaluation frameworks are insufficient to comprehensively assess these models' performance across expanding domains. To thoroughly evaluate these models, we developed the IMAGINE-E and tested six prominent models: FLUX.1, Ideogram2.0, Midjourney, Dall-E3, Stable Diffusion 3, and Jimeng. Our evaluation is divided into five key domains: structured output generation, realism, and physical consistency, specific domain generation, challenging scenario generation, and multi-style creation tasks. This comprehensive assessment highlights each model's strengths and limitations, particularly the outstanding performance of FLUX.1 and Ideogram2.0 in structured and specific domain tasks, underscoring the expanding applications and potential of T2I models as foundational AI tools. This study provides valuable insights into the current state and future trajectory of T2I models as they evolve towards general-purpose usability. Evaluation scripts will be released at https://github.com/jylei16/Imagine-e.
Automatic driving lane change safety prediction model based on LSTM
Feb 28, 2024



Abstract:Autonomous driving technology can improve traffic safety and reduce traffic accidents. In addition, it improves traffic flow, reduces congestion, saves energy and increases travel efficiency. In the relatively mature automatic driving technology, the automatic driving function is divided into several modules: perception, decision-making, planning and control, and a reasonable division of labor can improve the stability of the system. Therefore, autonomous vehicles need to have the ability to predict the trajectory of surrounding vehicles in order to make reasonable decision planning and safety measures to improve driving safety. By using deep learning method, a safety-sensitive deep learning model based on short term memory (LSTM) network is proposed. This model can alleviate the shortcomings of current automatic driving trajectory planning, and the output trajectory not only ensures high accuracy but also improves safety. The cell state simulation algorithm simulates the trackability of the trajectory generated by this model. The research results show that compared with the traditional model-based method, the trajectory prediction method based on LSTM network has obvious advantages in predicting the trajectory in the long time domain. The intention recognition module considering interactive information has higher prediction and accuracy, and the algorithm results show that the trajectory is very smooth based on the premise of safe prediction and efficient lane change. And autonomous vehicles can efficiently and safely complete lane changes.
The Fusion of Deep Reinforcement Learning and Edge Computing for Real-time Monitoring and Control Optimization in IoT Environments
Feb 28, 2024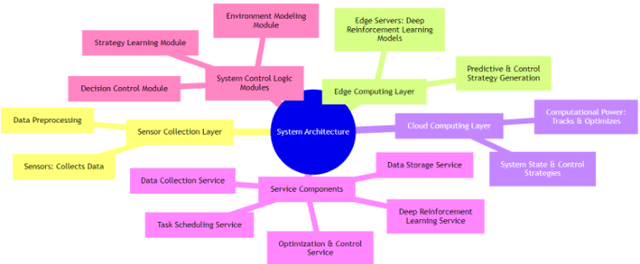
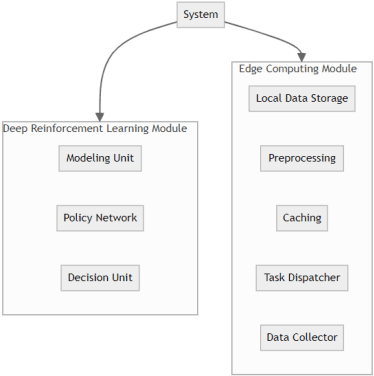
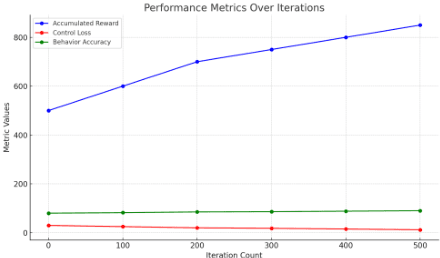
Abstract:In response to the demand for real-time performance and control quality in industrial Internet of Things (IoT) environments, this paper proposes an optimization control system based on deep reinforcement learning and edge computing. The system leverages cloud-edge collaboration, deploys lightweight policy networks at the edge, predicts system states, and outputs controls at a high frequency, enabling monitoring and optimization of industrial objectives. Additionally, a dynamic resource allocation mechanism is designed to ensure rational scheduling of edge computing resources, achieving global optimization. Results demonstrate that this approach reduces cloud-edge communication latency, accelerates response to abnormal situations, reduces system failure rates, extends average equipment operating time, and saves costs for manual maintenance and replacement. This ensures real-time and stable control.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge