Yuqin Cao
Audio-Assisted Face Video Restoration with Temporal and Identity Complementary Learning
Aug 06, 2025
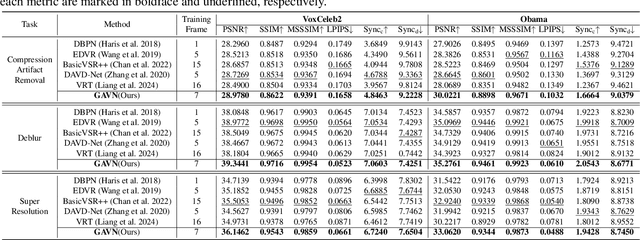
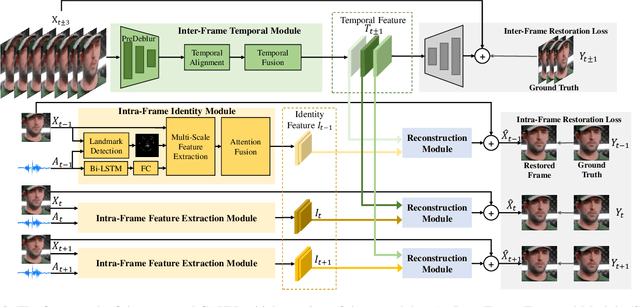
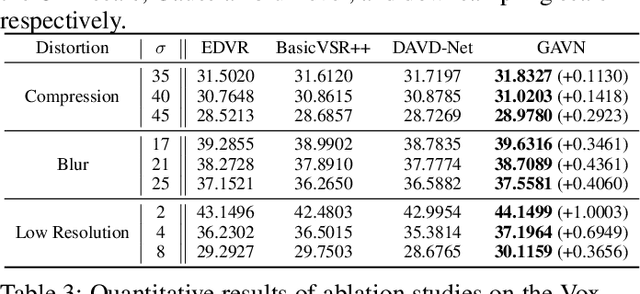
Abstract:Face videos accompanied by audio have become integral to our daily lives, while they often suffer from complex degradations. Most face video restoration methods neglect the intrinsic correlations between the visual and audio features, especially in mouth regions. A few audio-aided face video restoration methods have been proposed, but they only focus on compression artifact removal. In this paper, we propose a General Audio-assisted face Video restoration Network (GAVN) to address various types of streaming video distortions via identity and temporal complementary learning. Specifically, GAVN first captures inter-frame temporal features in the low-resolution space to restore frames coarsely and save computational cost. Then, GAVN extracts intra-frame identity features in the high-resolution space with the assistance of audio signals and face landmarks to restore more facial details. Finally, the reconstruction module integrates temporal features and identity features to generate high-quality face videos. Experimental results demonstrate that GAVN outperforms the existing state-of-the-art methods on face video compression artifact removal, deblurring, and super-resolution. Codes will be released upon publication.
Mitigating Low-Level Visual Hallucinations Requires Self-Awareness: Database, Model and Training Strategy
Mar 27, 2025



Abstract:The rapid development of multimodal large language models has resulted in remarkable advancements in visual perception and understanding, consolidating several tasks into a single visual question-answering framework. However, these models are prone to hallucinations, which limit their reliability as artificial intelligence systems. While this issue is extensively researched in natural language processing and image captioning, there remains a lack of investigation of hallucinations in Low-level Visual Perception and Understanding (HLPU), especially in the context of image quality assessment tasks. We consider that these hallucinations arise from an absence of clear self-awareness within the models. To address this issue, we first introduce the HLPU instruction database, the first instruction database specifically focused on hallucinations in low-level vision tasks. This database contains approximately 200K question-answer pairs and comprises four subsets, each covering different types of instructions. Subsequently, we propose the Self-Awareness Failure Elimination (SAFEQA) model, which utilizes image features, salient region features and quality features to improve the perception and comprehension abilities of the model in low-level vision tasks. Furthermore, we propose the Enhancing Self-Awareness Preference Optimization (ESA-PO) framework to increase the model's awareness of knowledge boundaries, thereby mitigating the incidence of hallucination. Finally, we conduct comprehensive experiments on low-level vision tasks, with the results demonstrating that our proposed method significantly enhances self-awareness of the model in these tasks and reduces hallucinations. Notably, our proposed method improves both accuracy and self-awareness of the proposed model and outperforms close-source models in terms of various evaluation metrics.
AGAV-Rater: Adapting Large Multimodal Model for AI-Generated Audio-Visual Quality Assessment
Jan 30, 2025



Abstract:Many video-to-audio (VTA) methods have been proposed for dubbing silent AI-generated videos. An efficient quality assessment method for AI-generated audio-visual content (AGAV) is crucial for ensuring audio-visual quality. Existing audio-visual quality assessment methods struggle with unique distortions in AGAVs, such as unrealistic and inconsistent elements. To address this, we introduce AGAVQA, the first large-scale AGAV quality assessment dataset, comprising 3,382 AGAVs from 16 VTA methods. AGAVQA includes two subsets: AGAVQA-MOS, which provides multi-dimensional scores for audio quality, content consistency, and overall quality, and AGAVQA-Pair, designed for optimal AGAV pair selection. We further propose AGAV-Rater, a LMM-based model that can score AGAVs, as well as audio and music generated from text, across multiple dimensions, and selects the best AGAV generated by VTA methods to present to the user. AGAV-Rater achieves state-of-the-art performance on AGAVQA, Text-to-Audio, and Text-to-Music datasets. Subjective tests also confirm that AGAV-Rater enhances VTA performance and user experience. The project page is available at https://agav-rater.github.io.
AIM 2024 Challenge on Video Super-Resolution Quality Assessment: Methods and Results
Oct 05, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents the Video Super-Resolution (SR) Quality Assessment (QA) Challenge that was part of the Advances in Image Manipulation (AIM) workshop, held in conjunction with ECCV 2024. The task of this challenge was to develop an objective QA method for videos upscaled 2x and 4x by modern image- and video-SR algorithms. QA methods were evaluated by comparing their output with aggregate subjective scores collected from >150,000 pairwise votes obtained through crowd-sourced comparisons across 52 SR methods and 1124 upscaled videos. The goal was to advance the state-of-the-art in SR QA, which had proven to be a challenging problem with limited applicability of traditional QA methods. The challenge had 29 registered participants, and 5 teams had submitted their final results, all outperforming the current state-of-the-art. All data, including the private test subset, has been made publicly available on the challenge homepage at https://challenges.videoprocessing.ai/challenges/super-resolution-metrics-challenge.html
Exploring Rich Subjective Quality Information for Image Quality Assessment in the Wild
Sep 09, 2024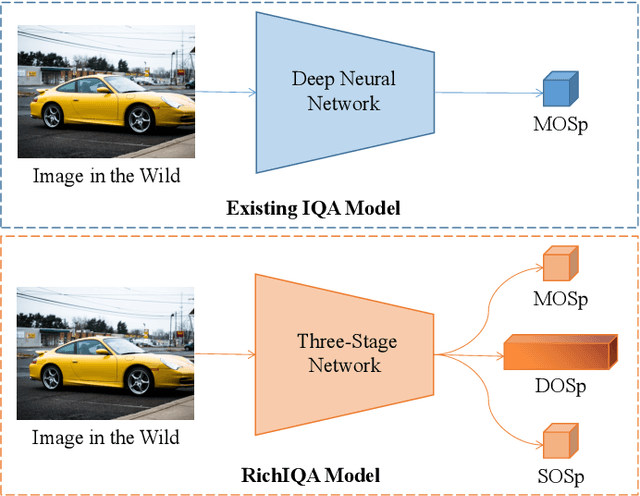


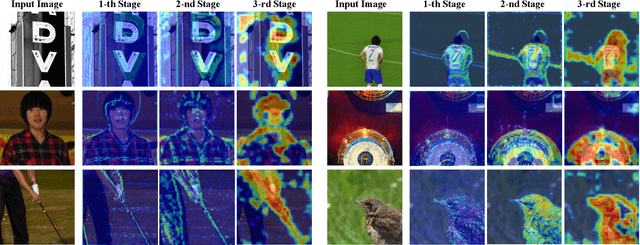
Abstract:Traditional in the wild image quality assessment (IQA) models are generally trained with the quality labels of mean opinion score (MOS), while missing the rich subjective quality information contained in the quality ratings, for example, the standard deviation of opinion scores (SOS) or even distribution of opinion scores (DOS). In this paper, we propose a novel IQA method named RichIQA to explore the rich subjective rating information beyond MOS to predict image quality in the wild. RichIQA is characterized by two key novel designs: (1) a three-stage image quality prediction network which exploits the powerful feature representation capability of the Convolutional vision Transformer (CvT) and mimics the short-term and long-term memory mechanisms of human brain; (2) a multi-label training strategy in which rich subjective quality information like MOS, SOS and DOS are concurrently used to train the quality prediction network. Powered by these two novel designs, RichIQA is able to predict the image quality in terms of a distribution, from which the mean image quality can be subsequently obtained. Extensive experimental results verify that the three-stage network is tailored to predict rich quality information, while the multi-label training strategy can fully exploit the potentials within subjective quality rating and enhance the prediction performance and generalizability of the network. RichIQA outperforms state-of-the-art competitors on multiple large-scale in the wild IQA databases with rich subjective rating labels. The code of RichIQA will be made publicly available on GitHub.
Assessing UHD Image Quality from Aesthetics, Distortions, and Saliency
Sep 01, 2024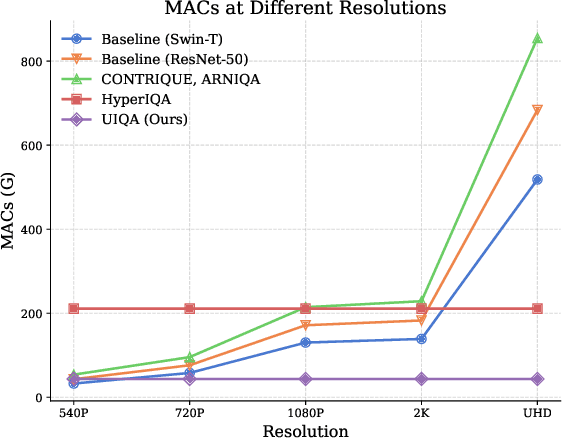
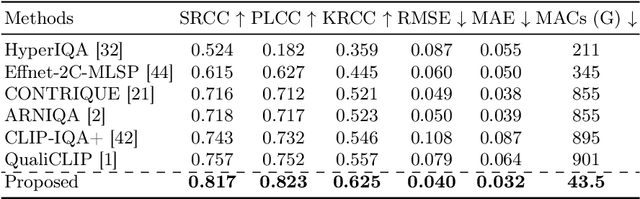

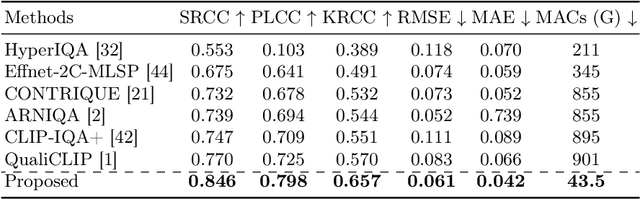
Abstract:UHD images, typically with resolutions equal to or higher than 4K, pose a significant challenge for efficient image quality assessment (IQA) algorithms, as adopting full-resolution images as inputs leads to overwhelming computational complexity and commonly used pre-processing methods like resizing or cropping may cause substantial loss of detail. To address this problem, we design a multi-branch deep neural network (DNN) to assess the quality of UHD images from three perspectives: global aesthetic characteristics, local technical distortions, and salient content perception. Specifically, aesthetic features are extracted from low-resolution images downsampled from the UHD ones, which lose high-frequency texture information but still preserve the global aesthetics characteristics. Technical distortions are measured using a fragment image composed of mini-patches cropped from UHD images based on the grid mini-patch sampling strategy. The salient content of UHD images is detected and cropped to extract quality-aware features from the salient regions. We adopt the Swin Transformer Tiny as the backbone networks to extract features from these three perspectives. The extracted features are concatenated and regressed into quality scores by a two-layer multi-layer perceptron (MLP) network. We employ the mean square error (MSE) loss to optimize prediction accuracy and the fidelity loss to optimize prediction monotonicity. Experimental results show that the proposed model achieves the best performance on the UHD-IQA dataset while maintaining the lowest computational complexity, demonstrating its effectiveness and efficiency. Moreover, the proposed model won first prize in ECCV AIM 2024 UHD-IQA Challenge. The code is available at https://github.com/sunwei925/UIQA.
AIM 2024 Challenge on Compressed Video Quality Assessment: Methods and Results
Aug 21, 2024
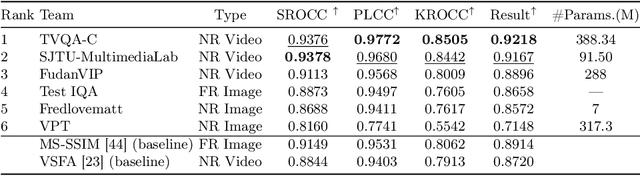
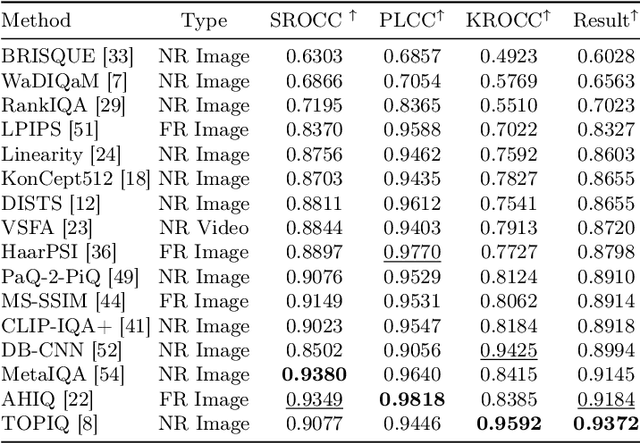
Abstract:Video quality assessment (VQA) is a crucial task in the development of video compression standards, as it directly impacts the viewer experience. This paper presents the results of the Compressed Video Quality Assessment challenge, held in conjunction with the Advances in Image Manipulation (AIM) workshop at ECCV 2024. The challenge aimed to evaluate the performance of VQA methods on a diverse dataset of 459 videos, encoded with 14 codecs of various compression standards (AVC/H.264, HEVC/H.265, AV1, and VVC/H.266) and containing a comprehensive collection of compression artifacts. To measure the methods performance, we employed traditional correlation coefficients between their predictions and subjective scores, which were collected via large-scale crowdsourced pairwise human comparisons. For training purposes, participants were provided with the Compressed Video Quality Assessment Dataset (CVQAD), a previously developed dataset of 1022 videos. Up to 30 participating teams registered for the challenge, while we report the results of 6 teams, which submitted valid final solutions and code for reproducing the results. Moreover, we calculated and present the performance of state-of-the-art VQA methods on the developed dataset, providing a comprehensive benchmark for future research. The dataset, results, and online leaderboard are publicly available at https://challenges.videoprocessing.ai/challenges/compressed-video-quality-assessment.html.
UNQA: Unified No-Reference Quality Assessment for Audio, Image, Video, and Audio-Visual Content
Jul 29, 2024



Abstract:As multimedia data flourishes on the Internet, quality assessment (QA) of multimedia data becomes paramount for digital media applications. Since multimedia data includes multiple modalities including audio, image, video, and audio-visual (A/V) content, researchers have developed a range of QA methods to evaluate the quality of different modality data. While they exclusively focus on addressing the single modality QA issues, a unified QA model that can handle diverse media across multiple modalities is still missing, whereas the latter can better resemble human perception behaviour and also have a wider range of applications. In this paper, we propose the Unified No-reference Quality Assessment model (UNQA) for audio, image, video, and A/V content, which tries to train a single QA model across different media modalities. To tackle the issue of inconsistent quality scales among different QA databases, we develop a multi-modality strategy to jointly train UNQA on multiple QA databases. Based on the input modality, UNQA selectively extracts the spatial features, motion features, and audio features, and calculates a final quality score via the four corresponding modality regression modules. Compared with existing QA methods, UNQA has two advantages: 1) the multi-modality training strategy makes the QA model learn more general and robust quality-aware feature representation as evidenced by the superior performance of UNQA compared to state-of-the-art QA methods. 2) UNQA reduces the number of models required to assess multimedia data across different modalities. and is friendly to deploy to practical applications.
NTIRE 2024 Quality Assessment of AI-Generated Content Challenge
Apr 25, 2024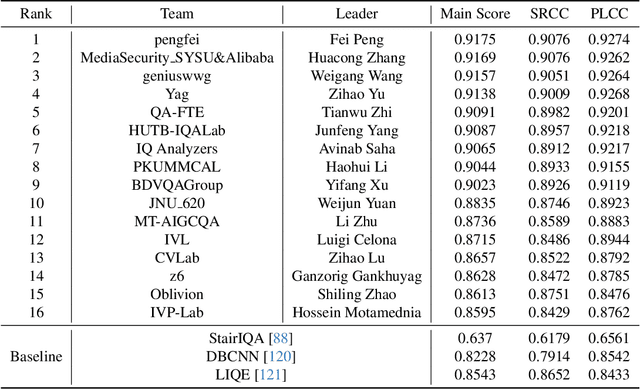
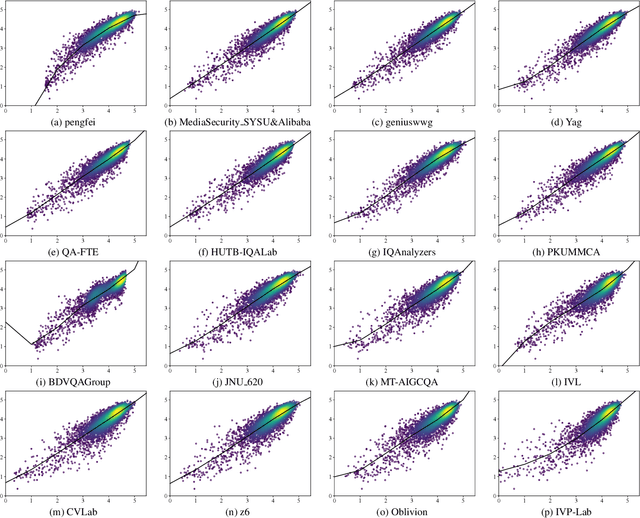
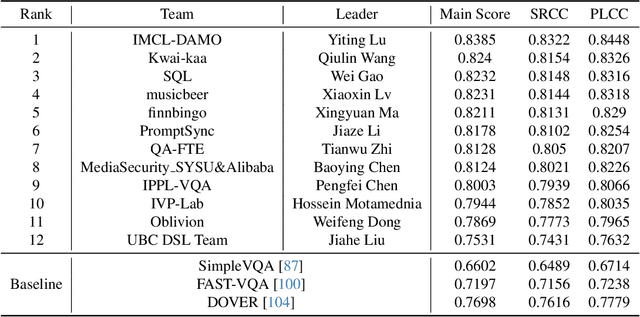
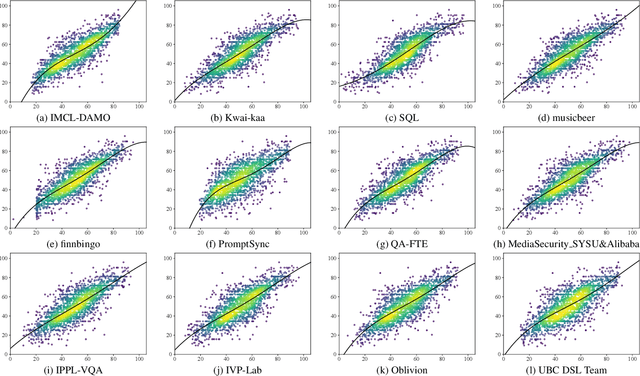
Abstract:This paper reports on the NTIRE 2024 Quality Assessment of AI-Generated Content Challenge, which will be held in conjunction with the New Trends in Image Restoration and Enhancement Workshop (NTIRE) at CVPR 2024. This challenge is to address a major challenge in the field of image and video processing, namely, Image Quality Assessment (IQA) and Video Quality Assessment (VQA) for AI-Generated Content (AIGC). The challenge is divided into the image track and the video track. The image track uses the AIGIQA-20K, which contains 20,000 AI-Generated Images (AIGIs) generated by 15 popular generative models. The image track has a total of 318 registered participants. A total of 1,646 submissions are received in the development phase, and 221 submissions are received in the test phase. Finally, 16 participating teams submitted their models and fact sheets. The video track uses the T2VQA-DB, which contains 10,000 AI-Generated Videos (AIGVs) generated by 9 popular Text-to-Video (T2V) models. A total of 196 participants have registered in the video track. A total of 991 submissions are received in the development phase, and 185 submissions are received in the test phase. Finally, 12 participating teams submitted their models and fact sheets. Some methods have achieved better results than baseline methods, and the winning methods in both tracks have demonstrated superior prediction performance on AIGC.
AIS 2024 Challenge on Video Quality Assessment of User-Generated Content: Methods and Results
Apr 24, 2024



Abstract:This paper reviews the AIS 2024 Video Quality Assessment (VQA) Challenge, focused on User-Generated Content (UGC). The aim of this challenge is to gather deep learning-based methods capable of estimating the perceptual quality of UGC videos. The user-generated videos from the YouTube UGC Dataset include diverse content (sports, games, lyrics, anime, etc.), quality and resolutions. The proposed methods must process 30 FHD frames under 1 second. In the challenge, a total of 102 participants registered, and 15 submitted code and models. The performance of the top-5 submissions is reviewed and provided here as a survey of diverse deep models for efficient video quality assessment of user-generated content.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge