Anastasia Antsiferova
BiRQA: Bidirectional Robust Quality Assessment for Images
Feb 23, 2026Abstract:Full-Reference image quality assessment (FR IQA) is important for image compression, restoration and generative modeling, yet current neural metrics remain slow and vulnerable to adversarial perturbations. We present BiRQA, a compact FR IQA metric model that processes four fast complementary features within a bidirectional multiscale pyramid. A bottom-up attention module injects fine-scale cues into coarse levels through an uncertainty-aware gate, while a top-down cross-gating block routes semantic context back to high resolution. To enhance robustness, we introduce Anchored Adversarial Training, a theoretically grounded strategy that uses clean "anchor" samples and a ranking loss to bound pointwise prediction error under attacks. On five public FR IQA benchmarks BiRQA outperforms or matches the previous state of the art (SOTA) while running ~3x faster than previous SOTA models. Under unseen white-box attacks it lifts SROCC from 0.30-0.57 to 0.60-0.84 on KADID-10k, demonstrating substantial robustness gains. To our knowledge, BiRQA is the only FR IQA model combining competitive accuracy with real-time throughput and strong adversarial resilience.
Universal Anti-forensics Attack against Image Forgery Detection via Multi-modal Guidance
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:The rapid advancement of AI-Generated Content (AIGC) technologies poses significant challenges for authenticity assessment. However, existing evaluation protocols largely overlook anti-forensics attack, failing to ensure the comprehensive robustness of state-of-the-art AIGC detectors in real-world applications. To bridge this gap, we propose ForgeryEraser, a framework designed to execute universal anti-forensics attack without access to the target AIGC detectors. We reveal an adversarial vulnerability stemming from the systemic reliance on Vision-Language Models (VLMs) as shared backbones (e.g., CLIP), where downstream AIGC detectors inherit the feature space of these publicly accessible models. Instead of traditional logit-based optimization, we design a multi-modal guidance loss to drive forged image embeddings within the VLM feature space toward text-derived authentic anchors to erase forgery traces, while repelling them from forgery anchors. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ForgeryEraser causes substantial performance degradation to advanced AIGC detectors on both global synthesis and local editing benchmarks. Moreover, ForgeryEraser induces explainable forensic models to generate explanations consistent with authentic images for forged images. Our code will be made publicly available.
FS-IQA: Certified Feature Smoothing for Robust Image Quality Assessment
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:We propose a novel certified defense method for Image Quality Assessment (IQA) models based on randomized smoothing with noise applied in the feature space rather than the input space. Unlike prior approaches that inject Gaussian noise directly into input images, often degrading visual quality, our method preserves image fidelity while providing robustness guarantees. To formally connect noise levels in the feature space with corresponding input-space perturbations, we analyze the maximum singular value of the backbone network's Jacobian. Our approach supports both full-reference (FR) and no-reference (NR) IQA models without requiring any architectural modifications, suitable for various scenarios. It is also computationally efficient, requiring a single backbone forward pass per image. Compared to previous methods, it reduces inference time by 99.5% without certification and by 20.6% when certification is applied. We validate our method with extensive experiments on two benchmark datasets, involving six widely-used FR and NR IQA models and comparisons against five state-of-the-art certified defenses. Our results demonstrate consistent improvements in correlation with subjective quality scores by up to 30.9%.
NIC-RobustBench: A Comprehensive Open-Source Toolkit for Neural Image Compression and Robustness Analysis
Jun 23, 2025Abstract:Adversarial robustness of neural networks is an increasingly important area of research, combining studies on computer vision models, large language models (LLMs), and others. With the release of JPEG AI -- the first standard for end-to-end neural image compression (NIC) methods -- the question of evaluating NIC robustness has become critically significant. However, previous research has been limited to a narrow range of codecs and attacks. To address this, we present \textbf{NIC-RobustBench}, the first open-source framework to evaluate NIC robustness and adversarial defenses' efficiency, in addition to comparing Rate-Distortion (RD) performance. The framework includes the largest number of codecs among all known NIC libraries and is easily scalable. The paper demonstrates a comprehensive overview of the NIC-RobustBench framework and employs it to analyze NIC robustness. Our code is available online at https://github.com/msu-video-group/NIC-RobustBench.
Robustness as Architecture: Designing IQA Models to Withstand Adversarial Perturbations
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Image Quality Assessment (IQA) models are increasingly relied upon to evaluate image quality in real-world systems -- from compression and enhancement to generation and streaming. Yet their adoption brings a fundamental risk: these models are inherently unstable. Adversarial manipulations can easily fool them, inflating scores and undermining trust. Traditionally, such vulnerabilities are addressed through data-driven defenses -- adversarial retraining, regularization, or input purification. But what if this is the wrong lens? What if robustness in perceptual models is not something to learn but something to design? In this work, we propose a provocative idea: robustness as an architectural prior. Rather than training models to resist perturbations, we reshape their internal structure to suppress sensitivity from the ground up. We achieve this by enforcing orthogonal information flow, constraining the network to norm-preserving operations -- and further stabilizing the system through pruning and fine-tuning. The result is a robust IQA architecture that withstands adversarial attacks without requiring adversarial training or significant changes to the original model. This approach suggests a shift in perspective: from optimizing robustness through data to engineering it through design.
Cross-Modal Transferable Image-to-Video Attack on Video Quality Metrics
Jan 14, 2025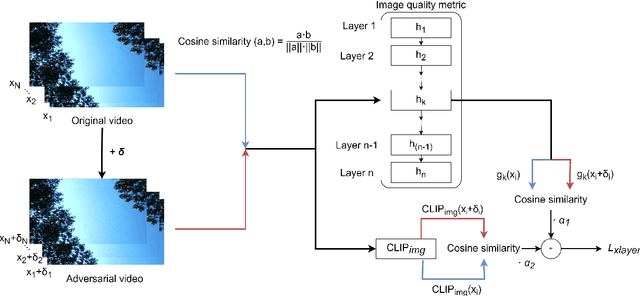
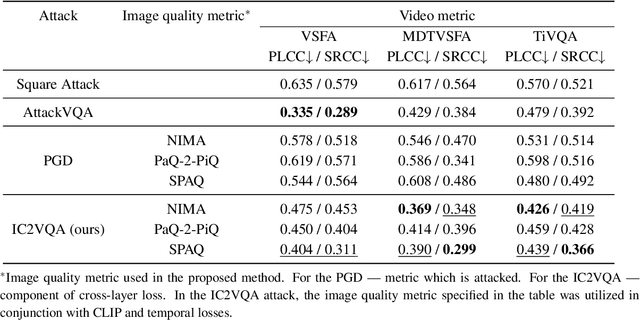
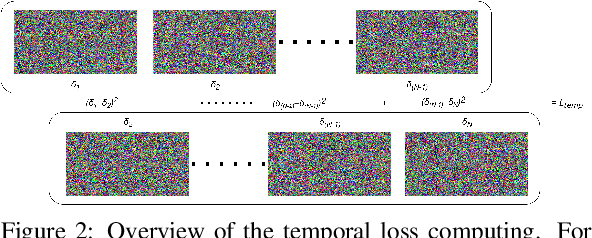
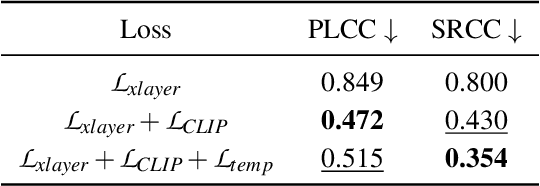
Abstract:Recent studies have revealed that modern image and video quality assessment (IQA/VQA) metrics are vulnerable to adversarial attacks. An attacker can manipulate a video through preprocessing to artificially increase its quality score according to a certain metric, despite no actual improvement in visual quality. Most of the attacks studied in the literature are white-box attacks, while black-box attacks in the context of VQA have received less attention. Moreover, some research indicates a lack of transferability of adversarial examples generated for one model to another when applied to VQA. In this paper, we propose a cross-modal attack method, IC2VQA, aimed at exploring the vulnerabilities of modern VQA models. This approach is motivated by the observation that the low-level feature spaces of images and videos are similar. We investigate the transferability of adversarial perturbations across different modalities; specifically, we analyze how adversarial perturbations generated on a white-box IQA model with an additional CLIP module can effectively target a VQA model. The addition of the CLIP module serves as a valuable aid in increasing transferability, as the CLIP model is known for its effective capture of low-level semantics. Extensive experiments demonstrate that IC2VQA achieves a high success rate in attacking three black-box VQA models. We compare our method with existing black-box attack strategies, highlighting its superiority in terms of attack success within the same number of iterations and levels of attack strength. We believe that the proposed method will contribute to the deeper analysis of robust VQA metrics.
Accelerated zero-order SGD under high-order smoothness and overparameterized regime
Nov 21, 2024
Abstract:We present a novel gradient-free algorithm to solve a convex stochastic optimization problem, such as those encountered in medicine, physics, and machine learning (e.g., adversarial multi-armed bandit problem), where the objective function can only be computed through numerical simulation, either as the result of a real experiment or as feedback given by the function evaluations from an adversary. Thus we suppose that only a black-box access to the function values of the objective is available, possibly corrupted by adversarial noise: deterministic or stochastic. The noisy setup can arise naturally from modeling randomness within a simulation or by computer discretization, or when exact values of function are forbidden due to privacy issues, or when solving non-convex problems as convex ones with an inexact function oracle. By exploiting higher-order smoothness, fulfilled, e.g., in logistic regression, we improve the performance of zero-order methods developed under the assumption of classical smoothness (or having a Lipschitz gradient). The proposed algorithm enjoys optimal oracle complexity and is designed under an overparameterization setup, i.e., when the number of model parameters is much larger than the size of the training dataset. Overparametrized models fit to the training data perfectly while also having good generalization and outperforming underparameterized models on unseen data. We provide convergence guarantees for the proposed algorithm under both types of noise. Moreover, we estimate the maximum permissible adversarial noise level that maintains the desired accuracy in the Euclidean setup, and then we extend our results to a non-Euclidean setup. Our theoretical results are verified on the logistic regression problem.
Stochastic BIQA: Median Randomized Smoothing for Certified Blind Image Quality Assessment
Nov 19, 2024



Abstract:Most modern No-Reference Image-Quality Assessment (NR-IQA) metrics are based on neural networks vulnerable to adversarial attacks. Attacks on such metrics lead to incorrect image/video quality predictions, which poses significant risks, especially in public benchmarks. Developers of image processing algorithms may unfairly increase the score of a target IQA metric without improving the actual quality of the adversarial image. Although some empirical defenses for IQA metrics were proposed, they do not provide theoretical guarantees and may be vulnerable to adaptive attacks. This work focuses on developing a provably robust no-reference IQA metric. Our method is based on Median Smoothing (MS) combined with an additional convolution denoiser with ranking loss to improve the SROCC and PLCC scores of the defended IQA metric. Compared with two prior methods on three datasets, our method exhibited superior SROCC and PLCC scores while maintaining comparable certified guarantees.
Exploring adversarial robustness of JPEG AI: methodology, comparison and new methods
Nov 18, 2024



Abstract:Adversarial robustness of neural networks is an increasingly important area of research, combining studies on computer vision models, large language models (LLMs), and others. With the release of JPEG AI - the first standard for end-to-end neural image compression (NIC) methods - the question of its robustness has become critically significant. JPEG AI is among the first international, real-world applications of neural-network-based models to be embedded in consumer devices. However, research on NIC robustness has been limited to open-source codecs and a narrow range of attacks. This paper proposes a new methodology for measuring NIC robustness to adversarial attacks. We present the first large-scale evaluation of JPEG AI's robustness, comparing it with other NIC models. Our evaluation results and code are publicly available online (link is hidden for a blind review).
AIM 2024 Challenge on Compressed Video Quality Assessment: Methods and Results
Aug 21, 2024
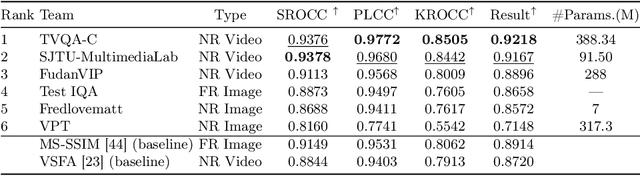
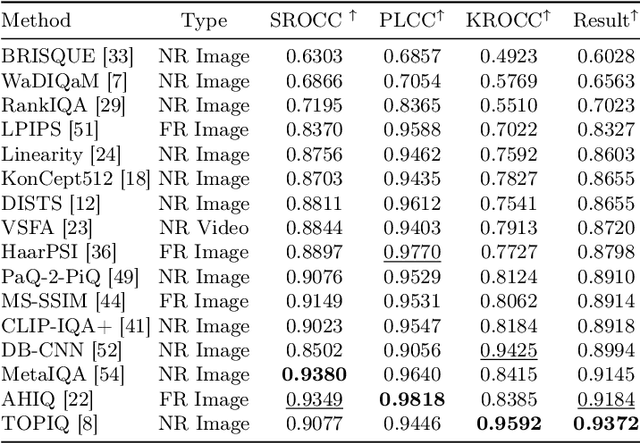
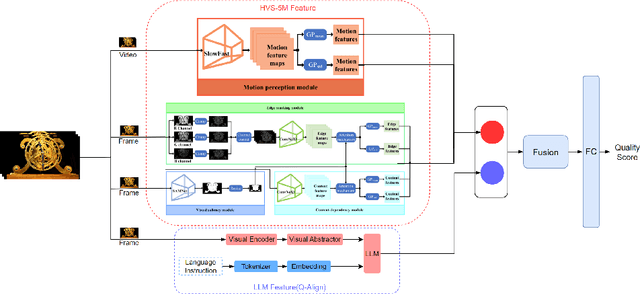
Abstract:Video quality assessment (VQA) is a crucial task in the development of video compression standards, as it directly impacts the viewer experience. This paper presents the results of the Compressed Video Quality Assessment challenge, held in conjunction with the Advances in Image Manipulation (AIM) workshop at ECCV 2024. The challenge aimed to evaluate the performance of VQA methods on a diverse dataset of 459 videos, encoded with 14 codecs of various compression standards (AVC/H.264, HEVC/H.265, AV1, and VVC/H.266) and containing a comprehensive collection of compression artifacts. To measure the methods performance, we employed traditional correlation coefficients between their predictions and subjective scores, which were collected via large-scale crowdsourced pairwise human comparisons. For training purposes, participants were provided with the Compressed Video Quality Assessment Dataset (CVQAD), a previously developed dataset of 1022 videos. Up to 30 participating teams registered for the challenge, while we report the results of 6 teams, which submitted valid final solutions and code for reproducing the results. Moreover, we calculated and present the performance of state-of-the-art VQA methods on the developed dataset, providing a comprehensive benchmark for future research. The dataset, results, and online leaderboard are publicly available at https://challenges.videoprocessing.ai/challenges/compressed-video-quality-assessment.html.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge