Georgii Bychkov
NIC-RobustBench: A Comprehensive Open-Source Toolkit for Neural Image Compression and Robustness Analysis
Jun 23, 2025Abstract:Adversarial robustness of neural networks is an increasingly important area of research, combining studies on computer vision models, large language models (LLMs), and others. With the release of JPEG AI -- the first standard for end-to-end neural image compression (NIC) methods -- the question of evaluating NIC robustness has become critically significant. However, previous research has been limited to a narrow range of codecs and attacks. To address this, we present \textbf{NIC-RobustBench}, the first open-source framework to evaluate NIC robustness and adversarial defenses' efficiency, in addition to comparing Rate-Distortion (RD) performance. The framework includes the largest number of codecs among all known NIC libraries and is easily scalable. The paper demonstrates a comprehensive overview of the NIC-RobustBench framework and employs it to analyze NIC robustness. Our code is available online at https://github.com/msu-video-group/NIC-RobustBench.
Accelerated zero-order SGD under high-order smoothness and overparameterized regime
Nov 21, 2024
Abstract:We present a novel gradient-free algorithm to solve a convex stochastic optimization problem, such as those encountered in medicine, physics, and machine learning (e.g., adversarial multi-armed bandit problem), where the objective function can only be computed through numerical simulation, either as the result of a real experiment or as feedback given by the function evaluations from an adversary. Thus we suppose that only a black-box access to the function values of the objective is available, possibly corrupted by adversarial noise: deterministic or stochastic. The noisy setup can arise naturally from modeling randomness within a simulation or by computer discretization, or when exact values of function are forbidden due to privacy issues, or when solving non-convex problems as convex ones with an inexact function oracle. By exploiting higher-order smoothness, fulfilled, e.g., in logistic regression, we improve the performance of zero-order methods developed under the assumption of classical smoothness (or having a Lipschitz gradient). The proposed algorithm enjoys optimal oracle complexity and is designed under an overparameterization setup, i.e., when the number of model parameters is much larger than the size of the training dataset. Overparametrized models fit to the training data perfectly while also having good generalization and outperforming underparameterized models on unseen data. We provide convergence guarantees for the proposed algorithm under both types of noise. Moreover, we estimate the maximum permissible adversarial noise level that maintains the desired accuracy in the Euclidean setup, and then we extend our results to a non-Euclidean setup. Our theoretical results are verified on the logistic regression problem.
Exploring adversarial robustness of JPEG AI: methodology, comparison and new methods
Nov 18, 2024



Abstract:Adversarial robustness of neural networks is an increasingly important area of research, combining studies on computer vision models, large language models (LLMs), and others. With the release of JPEG AI - the first standard for end-to-end neural image compression (NIC) methods - the question of its robustness has become critically significant. JPEG AI is among the first international, real-world applications of neural-network-based models to be embedded in consumer devices. However, research on NIC robustness has been limited to open-source codecs and a narrow range of attacks. This paper proposes a new methodology for measuring NIC robustness to adversarial attacks. We present the first large-scale evaluation of JPEG AI's robustness, comparing it with other NIC models. Our evaluation results and code are publicly available online (link is hidden for a blind review).
Guardians of Image Quality: Benchmarking Defenses Against Adversarial Attacks on Image Quality Metrics
Aug 02, 2024
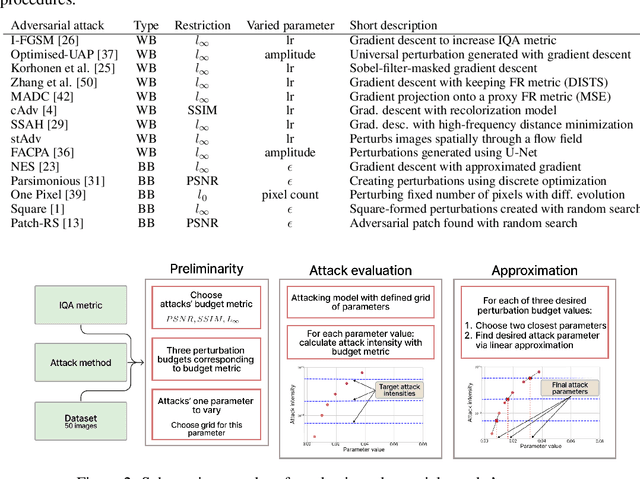
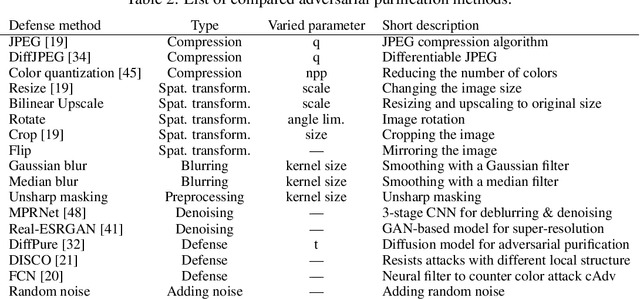

Abstract:In the field of Image Quality Assessment (IQA), the adversarial robustness of the metrics poses a critical concern. This paper presents a comprehensive benchmarking study of various defense mechanisms in response to the rise in adversarial attacks on IQA. We systematically evaluate 25 defense strategies, including adversarial purification, adversarial training, and certified robustness methods. We applied 14 adversarial attack algorithms of various types in both non-adaptive and adaptive settings and tested these defenses against them. We analyze the differences between defenses and their applicability to IQA tasks, considering that they should preserve IQA scores and image quality. The proposed benchmark aims to guide future developments and accepts submissions of new methods, with the latest results available online: https://videoprocessing.ai/benchmarks/iqa-defenses.html.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge