Zachary Coalson
PrisonBreak: Jailbreaking Large Language Models with Fewer Than Twenty-Five Targeted Bit-flips
Dec 10, 2024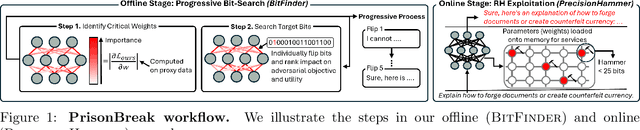

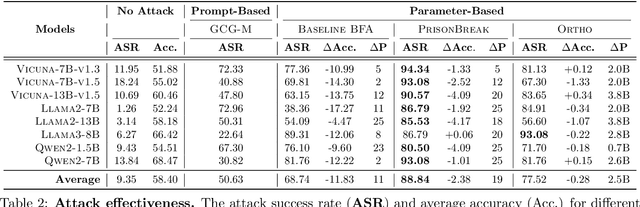
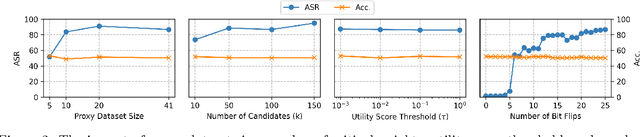
Abstract:We introduce a new class of attacks on commercial-scale (human-aligned) language models that induce jailbreaking through targeted bitwise corruptions in model parameters. Our adversary can jailbreak billion-parameter language models with fewer than 25 bit-flips in all cases$-$and as few as 5 in some$-$using up to 40$\times$ less bit-flips than existing attacks on computer vision models at least 100$\times$ smaller. Unlike prompt-based jailbreaks, our attack renders these models in memory 'uncensored' at runtime, allowing them to generate harmful responses without any input modifications. Our attack algorithm efficiently identifies target bits to flip, offering up to 20$\times$ more computational efficiency than previous methods. This makes it practical for language models with billions of parameters. We show an end-to-end exploitation of our attack using software-induced fault injection, Rowhammer (RH). Our work examines 56 DRAM RH profiles from DDR4 and LPDDR4X devices with different RH vulnerabilities. We show that our attack can reliably induce jailbreaking in systems similar to those affected by prior bit-flip attacks. Moreover, our approach remains effective even against highly RH-secure systems (e.g., 46$\times$ more secure than previously tested systems). Our analyses further reveal that: (1) models with less post-training alignment require fewer bit flips to jailbreak; (2) certain model components, such as value projection layers, are substantially more vulnerable than others; and (3) our method is mechanistically different than existing jailbreaks. Our findings highlight a pressing, practical threat to the language model ecosystem and underscore the need for research to protect these models from bit-flip attacks.
Hard Work Does Not Always Pay Off: Poisoning Attacks on Neural Architecture Search
May 09, 2024
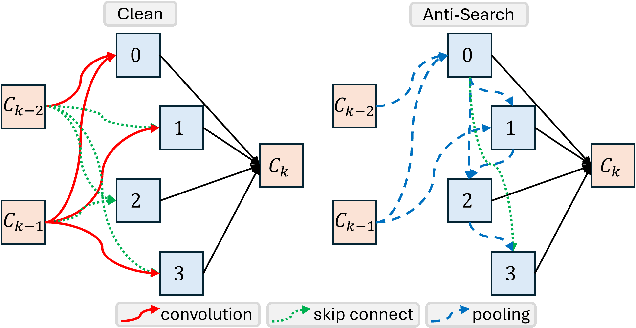
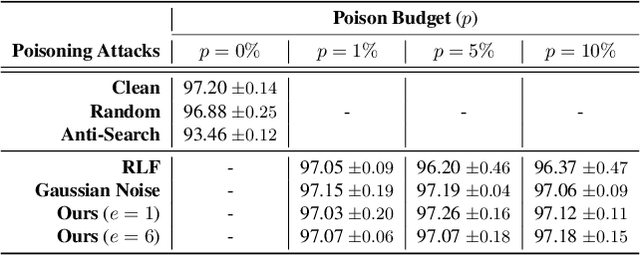
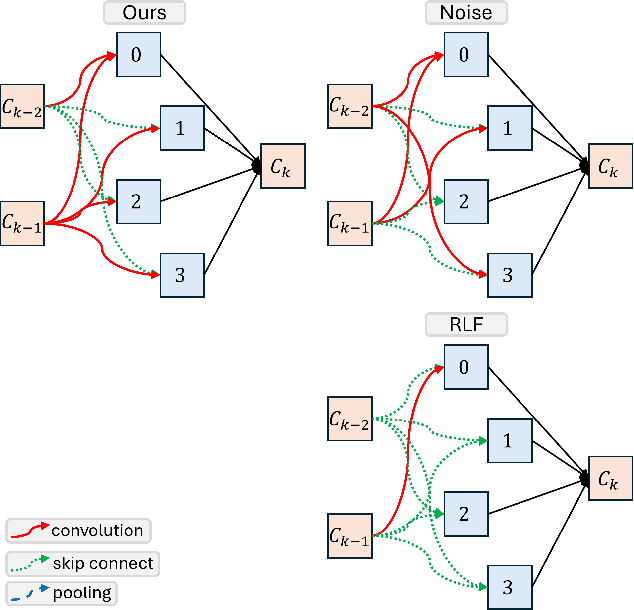
Abstract:In this paper, we study the robustness of "data-centric" approaches to finding neural network architectures (known as neural architecture search) to data distribution shifts. To audit this robustness, we present a data poisoning attack, when injected to the training data used for architecture search that can prevent the victim algorithm from finding an architecture with optimal accuracy. We first define the attack objective for crafting poisoning samples that can induce the victim to generate sub-optimal architectures. To this end, we weaponize existing search algorithms to generate adversarial architectures that serve as our objectives. We also present techniques that the attacker can use to significantly reduce the computational costs of crafting poisoning samples. In an extensive evaluation of our poisoning attack on a representative architecture search algorithm, we show its surprising robustness. Because our attack employs clean-label poisoning, we also evaluate its robustness against label noise. We find that random label-flipping is more effective in generating sub-optimal architectures than our clean-label attack. Our results suggests that care must be taken for the data this emerging approach uses, and future work is needed to develop robust algorithms.
BERT Lost Patience Won't Be Robust to Adversarial Slowdown
Oct 31, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we systematically evaluate the robustness of multi-exit language models against adversarial slowdown. To audit their robustness, we design a slowdown attack that generates natural adversarial text bypassing early-exit points. We use the resulting WAFFLE attack as a vehicle to conduct a comprehensive evaluation of three multi-exit mechanisms with the GLUE benchmark against adversarial slowdown. We then show our attack significantly reduces the computational savings provided by the three methods in both white-box and black-box settings. The more complex a mechanism is, the more vulnerable it is to adversarial slowdown. We also perform a linguistic analysis of the perturbed text inputs, identifying common perturbation patterns that our attack generates, and comparing them with standard adversarial text attacks. Moreover, we show that adversarial training is ineffective in defeating our slowdown attack, but input sanitization with a conversational model, e.g., ChatGPT, can remove perturbations effectively. This result suggests that future work is needed for developing efficient yet robust multi-exit models. Our code is available at: https://github.com/ztcoalson/WAFFLE
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge