Yihao Zhi
MV-Performer: Taming Video Diffusion Model for Faithful and Synchronized Multi-view Performer Synthesis
Oct 08, 2025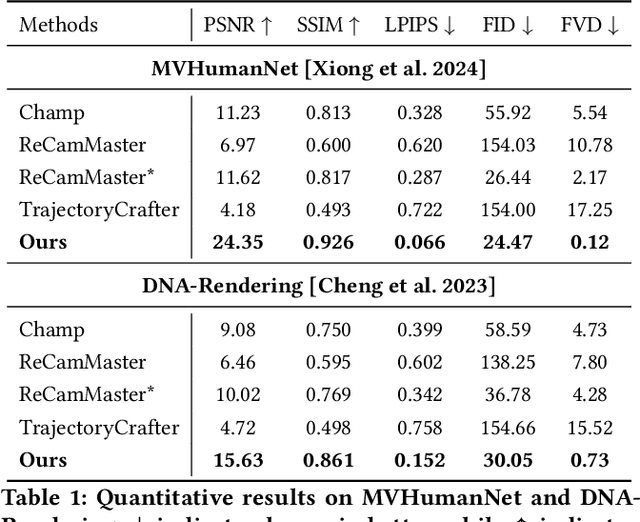
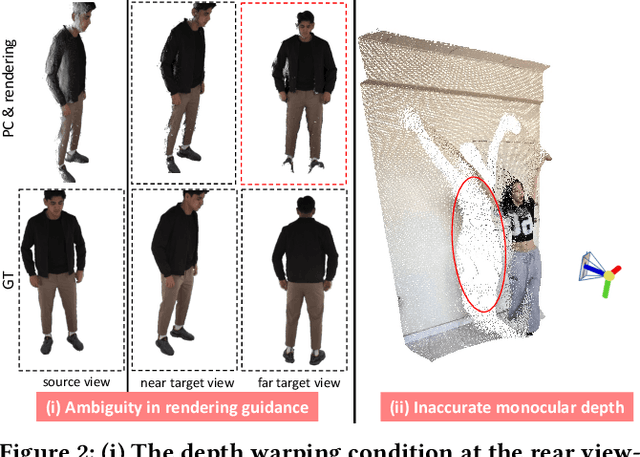

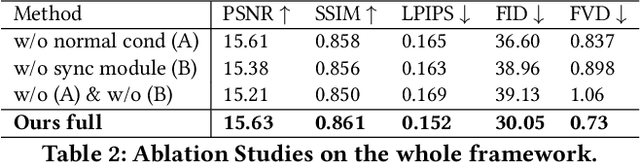
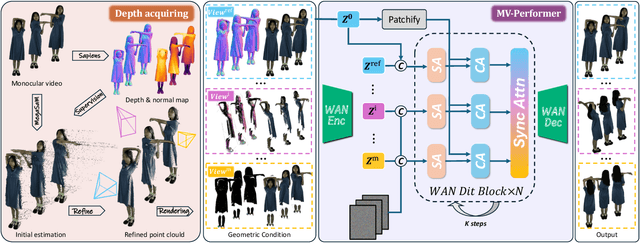
Abstract:Recent breakthroughs in video generation, powered by large-scale datasets and diffusion techniques, have shown that video diffusion models can function as implicit 4D novel view synthesizers. Nevertheless, current methods primarily concentrate on redirecting camera trajectory within the front view while struggling to generate 360-degree viewpoint changes. In this paper, we focus on human-centric subdomain and present MV-Performer, an innovative framework for creating synchronized novel view videos from monocular full-body captures. To achieve a 360-degree synthesis, we extensively leverage the MVHumanNet dataset and incorporate an informative condition signal. Specifically, we use the camera-dependent normal maps rendered from oriented partial point clouds, which effectively alleviate the ambiguity between seen and unseen observations. To maintain synchronization in the generated videos, we propose a multi-view human-centric video diffusion model that fuses information from the reference video, partial rendering, and different viewpoints. Additionally, we provide a robust inference procedure for in-the-wild video cases, which greatly mitigates the artifacts induced by imperfect monocular depth estimation. Extensive experiments on three datasets demonstrate our MV-Performer's state-of-the-art effectiveness and robustness, setting a strong model for human-centric 4D novel view synthesis.
Exploring Disentangled and Controllable Human Image Synthesis: From End-to-End to Stage-by-Stage
Mar 25, 2025



Abstract:Achieving fine-grained controllability in human image synthesis is a long-standing challenge in computer vision. Existing methods primarily focus on either facial synthesis or near-frontal body generation, with limited ability to simultaneously control key factors such as viewpoint, pose, clothing, and identity in a disentangled manner. In this paper, we introduce a new disentangled and controllable human synthesis task, which explicitly separates and manipulates these four factors within a unified framework. We first develop an end-to-end generative model trained on MVHumanNet for factor disentanglement. However, the domain gap between MVHumanNet and in-the-wild data produce unsatisfacotry results, motivating the exploration of virtual try-on (VTON) dataset as a potential solution. Through experiments, we observe that simply incorporating the VTON dataset as additional data to train the end-to-end model degrades performance, primarily due to the inconsistency in data forms between the two datasets, which disrupts the disentanglement process. To better leverage both datasets, we propose a stage-by-stage framework that decomposes human image generation into three sequential steps: clothed A-pose generation, back-view synthesis, and pose and view control. This structured pipeline enables better dataset utilization at different stages, significantly improving controllability and generalization, especially for in-the-wild scenarios. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our stage-by-stage approach outperforms end-to-end models in both visual fidelity and disentanglement quality, offering a scalable solution for real-world tasks. Additional demos are available on the project page: https://taited.github.io/discohuman-project/.
MAG: Multi-Modal Aligned Autoregressive Co-Speech Gesture Generation without Vector Quantization
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:This work focuses on full-body co-speech gesture generation. Existing methods typically employ an autoregressive model accompanied by vector-quantized tokens for gesture generation, which results in information loss and compromises the realism of the generated gestures. To address this, inspired by the natural continuity of real-world human motion, we propose MAG, a novel multi-modal aligned framework for high-quality and diverse co-speech gesture synthesis without relying on discrete tokenization. Specifically, (1) we introduce a motion-text-audio-aligned variational autoencoder (MTA-VAE), which leverages pre-trained WavCaps' text and audio embeddings to enhance both semantic and rhythmic alignment with motion, ultimately producing more realistic gestures. (2) Building on this, we propose a multimodal masked autoregressive model (MMAG) that enables autoregressive modeling in continuous motion embeddings through diffusion without vector quantization. To further ensure multi-modal consistency, MMAG incorporates a hybrid granularity audio-text fusion block, which serves as conditioning for diffusion process. Extensive experiments on two benchmark datasets demonstrate that MAG achieves stateof-the-art performance both quantitatively and qualitatively, producing highly realistic and diverse co-speech gestures.The code will be released to facilitate future research.
Surfel-based Gaussian Inverse Rendering for Fast and Relightable Dynamic Human Reconstruction from Monocular Video
Jul 23, 2024



Abstract:Efficient and accurate reconstruction of a relightable, dynamic clothed human avatar from a monocular video is crucial for the entertainment industry. This paper introduces the Surfel-based Gaussian Inverse Avatar (SGIA) method, which introduces efficient training and rendering for relightable dynamic human reconstruction. SGIA advances previous Gaussian Avatar methods by comprehensively modeling Physically-Based Rendering (PBR) properties for clothed human avatars, allowing for the manipulation of avatars into novel poses under diverse lighting conditions. Specifically, our approach integrates pre-integration and image-based lighting for fast light calculations that surpass the performance of existing implicit-based techniques. To address challenges related to material lighting disentanglement and accurate geometry reconstruction, we propose an innovative occlusion approximation strategy and a progressive training approach. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SGIA not only achieves highly accurate physical properties but also significantly enhances the realistic relighting of dynamic human avatars, providing a substantial speed advantage. We exhibit more results in our project page: https://GS-IA.github.io.
GauStudio: A Modular Framework for 3D Gaussian Splatting and Beyond
Mar 28, 2024Abstract:We present GauStudio, a novel modular framework for modeling 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) to provide standardized, plug-and-play components for users to easily customize and implement a 3DGS pipeline. Supported by our framework, we propose a hybrid Gaussian representation with foreground and skyball background models. Experiments demonstrate this representation reduces artifacts in unbounded outdoor scenes and improves novel view synthesis. Finally, we propose Gaussian Splatting Surface Reconstruction (GauS), a novel render-then-fuse approach for high-fidelity mesh reconstruction from 3DGS inputs without fine-tuning. Overall, our GauStudio framework, hybrid representation, and GauS approach enhance 3DGS modeling and rendering capabilities, enabling higher-quality novel view synthesis and surface reconstruction.
LivelySpeaker: Towards Semantic-Aware Co-Speech Gesture Generation
Sep 17, 2023



Abstract:Gestures are non-verbal but important behaviors accompanying people's speech. While previous methods are able to generate speech rhythm-synchronized gestures, the semantic context of the speech is generally lacking in the gesticulations. Although semantic gestures do not occur very regularly in human speech, they are indeed the key for the audience to understand the speech context in a more immersive environment. Hence, we introduce LivelySpeaker, a framework that realizes semantics-aware co-speech gesture generation and offers several control handles. In particular, our method decouples the task into two stages: script-based gesture generation and audio-guided rhythm refinement. Specifically, the script-based gesture generation leverages the pre-trained CLIP text embeddings as the guidance for generating gestures that are highly semantically aligned with the script. Then, we devise a simple but effective diffusion-based gesture generation backbone simply using pure MLPs, that is conditioned on only audio signals and learns to gesticulate with realistic motions. We utilize such powerful prior to rhyme the script-guided gestures with the audio signals, notably in a zero-shot setting. Our novel two-stage generation framework also enables several applications, such as changing the gesticulation style, editing the co-speech gestures via textual prompting, and controlling the semantic awareness and rhythm alignment with guided diffusion. Extensive experiments demonstrate the advantages of the proposed framework over competing methods. In addition, our core diffusion-based generative model also achieves state-of-the-art performance on two benchmarks. The code and model will be released to facilitate future research.
Dual-Space NeRF: Learning Animatable Avatars and Scene Lighting in Separate Spaces
Aug 31, 2022

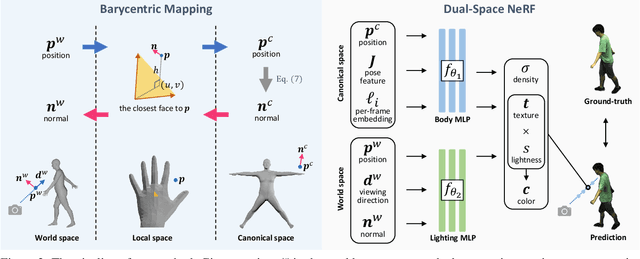

Abstract:Modeling the human body in a canonical space is a common practice for capturing and animation. But when involving the neural radiance field (NeRF), learning a static NeRF in the canonical space is not enough because the lighting of the body changes when the person moves even though the scene lighting is constant. Previous methods alleviate the inconsistency of lighting by learning a per-frame embedding, but this operation does not generalize to unseen poses. Given that the lighting condition is static in the world space while the human body is consistent in the canonical space, we propose a dual-space NeRF that models the scene lighting and the human body with two MLPs in two separate spaces. To bridge these two spaces, previous methods mostly rely on the linear blend skinning (LBS) algorithm. However, the blending weights for LBS of a dynamic neural field are intractable and thus are usually memorized with another MLP, which does not generalize to novel poses. Although it is possible to borrow the blending weights of a parametric mesh such as SMPL, the interpolation operation introduces more artifacts. In this paper, we propose to use the barycentric mapping, which can directly generalize to unseen poses and surprisingly achieves superior results than LBS with neural blending weights. Quantitative and qualitative results on the Human3.6M and the ZJU-MoCap datasets show the effectiveness of our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge