Binbin Huang
CUPID: Pose-Grounded Generative 3D Reconstruction from a Single Image
Oct 23, 2025Abstract:This work proposes a new generation-based 3D reconstruction method, named Cupid, that accurately infers the camera pose, 3D shape, and texture of an object from a single 2D image. Cupid casts 3D reconstruction as a conditional sampling process from a learned distribution of 3D objects, and it jointly generates voxels and pixel-voxel correspondences, enabling robust pose and shape estimation under a unified generative framework. By representing both input camera poses and 3D shape as a distribution in a shared 3D latent space, Cupid adopts a two-stage flow matching pipeline: (1) a coarse stage that produces initial 3D geometry with associated 2D projections for pose recovery; and (2) a refinement stage that integrates pose-aligned image features to enhance structural fidelity and appearance details. Extensive experiments demonstrate Cupid outperforms leading 3D reconstruction methods with an over 3 dB PSNR gain and an over 10% Chamfer Distance reduction, while matching monocular estimators on pose accuracy and delivering superior visual fidelity over baseline 3D generative models. For an immersive view of the 3D results generated by Cupid, please visit cupid3d.github.io.
Accelerated Evolving Set Processes for Local PageRank Computation
Oct 09, 2025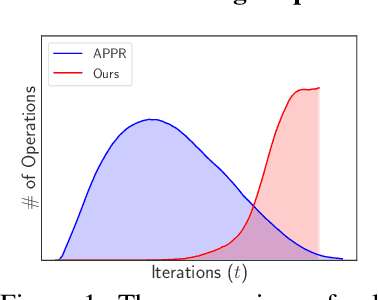

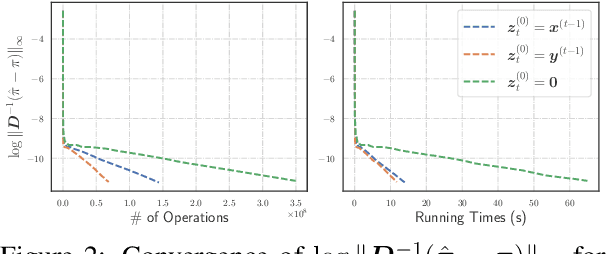
Abstract:This work proposes a novel framework based on nested evolving set processes to accelerate Personalized PageRank (PPR) computation. At each stage of the process, we employ a localized inexact proximal point iteration to solve a simplified linear system. We show that the time complexity of such localized methods is upper bounded by $\min\{\tilde{\mathcal{O}}(R^2/\epsilon^2), \tilde{\mathcal{O}}(m)\}$ to obtain an $\epsilon$-approximation of the PPR vector, where $m$ denotes the number of edges in the graph and $R$ is a constant defined via nested evolving set processes. Furthermore, the algorithms induced by our framework require solving only $\tilde{\mathcal{O}}(1/\sqrt{\alpha})$ such linear systems, where $\alpha$ is the damping factor. When $1/\epsilon^2\ll m$, this implies the existence of an algorithm that computes an $\ epsilon $-approximation of the PPR vector with an overall time complexity of $\tilde{\mathcal{O}}\left(R^2 / (\sqrt{\alpha}\epsilon^2)\right)$, independent of the underlying graph size. Our result resolves an open conjecture from existing literature. Experimental results on real-world graphs validate the efficiency of our methods, demonstrating significant convergence in the early stages.
Fine-Tuning Code Language Models to Detect Cross-Language Bugs
Jul 29, 2025Abstract:Multilingual programming, which involves using multiple programming languages (PLs) in a single project, is increasingly common due to its benefits. However, it introduces cross-language bugs (CLBs), which arise from interactions between different PLs and are difficult to detect by single-language bug detection tools. This paper investigates the potential of pre-trained code language models (CodeLMs) in CLB detection. We developed CLCFinder, a cross-language code identification tool, and constructed a CLB dataset involving three PL combinations (Python-C/C++, Java-C/C++, and Python-Java) with nine interaction types. We fine-tuned 13 CodeLMs on this dataset and evaluated their performance, analyzing the effects of dataset size, token sequence length, and code comments. Results show that all CodeLMs performed poorly before fine-tuning, but exhibited varying degrees of performance improvement after fine-tuning, with UniXcoder-base achieving the best F1 score (0.7407). Notably, small fine-tuned CodeLMs tended to performe better than large ones. CodeLMs fine-tuned on single-language bug datasets performed poorly on CLB detection, demonstrating the distinction between CLBs and single-language bugs. Additionally, increasing the fine-tuning dataset size significantly improved performance, while longer token sequences did not necessarily improve the model performance. The impact of code comments varied across models. Some fine-tuned CodeLMs' performance was improved, while others showed degraded performance.
GenFusion: Closing the Loop between Reconstruction and Generation via Videos
Mar 27, 2025



Abstract:Recently, 3D reconstruction and generation have demonstrated impressive novel view synthesis results, achieving high fidelity and efficiency. However, a notable conditioning gap can be observed between these two fields, e.g., scalable 3D scene reconstruction often requires densely captured views, whereas 3D generation typically relies on a single or no input view, which significantly limits their applications. We found that the source of this phenomenon lies in the misalignment between 3D constraints and generative priors. To address this problem, we propose a reconstruction-driven video diffusion model that learns to condition video frames on artifact-prone RGB-D renderings. Moreover, we propose a cyclical fusion pipeline that iteratively adds restoration frames from the generative model to the training set, enabling progressive expansion and addressing the viewpoint saturation limitations seen in previous reconstruction and generation pipelines. Our evaluation, including view synthesis from sparse view and masked input, validates the effectiveness of our approach.
Quadratic Gaussian Splatting for Efficient and Detailed Surface Reconstruction
Nov 25, 2024



Abstract:Recently, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has attracted attention for its superior rendering quality and speed over Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF). To address 3DGS's limitations in surface representation, 2D Gaussian Splatting (2DGS) introduced disks as scene primitives to model and reconstruct geometries from multi-view images, offering view-consistent geometry. However, the disk's first-order linear approximation often leads to over-smoothed results. We propose Quadratic Gaussian Splatting (QGS), a novel method that replaces disks with quadric surfaces, enhancing geometric fitting, whose code will be open-sourced. QGS defines Gaussian distributions in non-Euclidean space, allowing primitives to capture more complex textures. As a second-order surface approximation, QGS also renders spatial curvature to guide the normal consistency term, to effectively reduce over-smoothing. Moreover, QGS is a generalized version of 2DGS that achieves more accurate and detailed reconstructions, as verified by experiments on DTU and TNT, demonstrating its effectiveness in surpassing current state-of-the-art methods in geometry reconstruction. Our code willbe released as open source.
Space-time 2D Gaussian Splatting for Accurate Surface Reconstruction under Complex Dynamic Scenes
Sep 27, 2024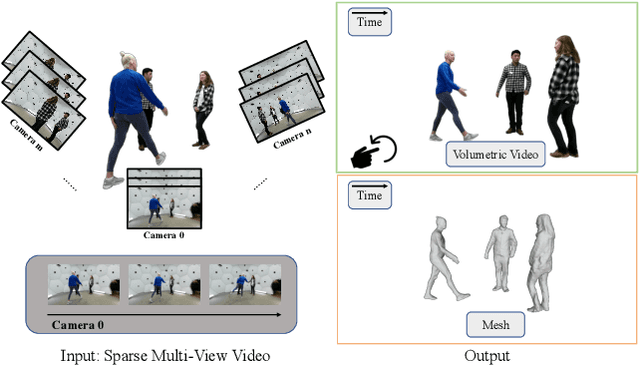
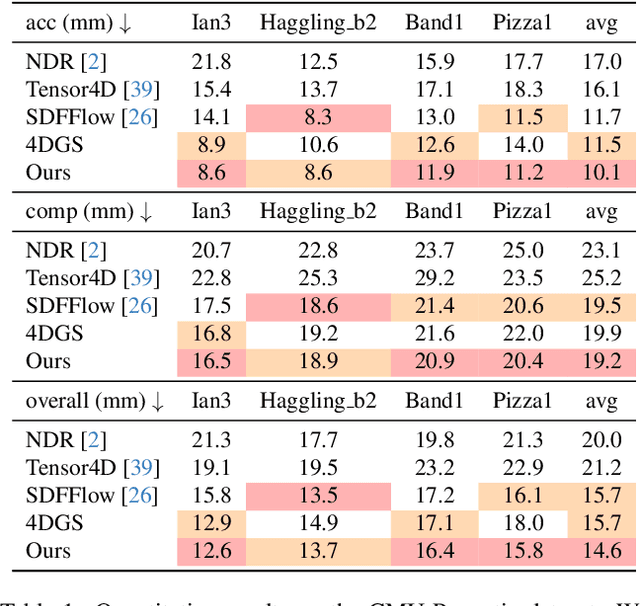
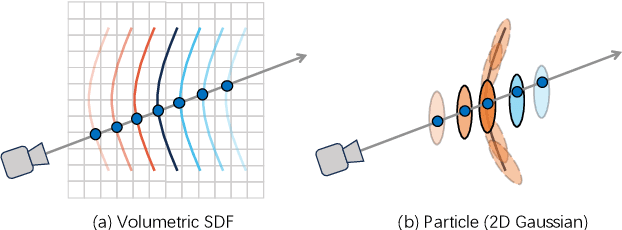
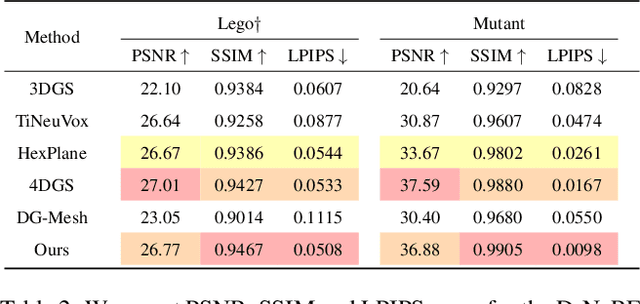
Abstract:Previous surface reconstruction methods either suffer from low geometric accuracy or lengthy training times when dealing with real-world complex dynamic scenes involving multi-person activities, and human-object interactions. To tackle the dynamic contents and the occlusions in complex scenes, we present a space-time 2D Gaussian Splatting approach. Specifically, to improve geometric quality in dynamic scenes, we learn canonical 2D Gaussian splats and deform these 2D Gaussian splats while enforcing the disks of the Gaussian located on the surface of the objects by introducing depth and normal regularizers. Further, to tackle the occlusion issues in complex scenes, we introduce a compositional opacity deformation strategy, which further reduces the surface recovery of those occluded areas. Experiments on real-world sparse-view video datasets and monocular dynamic datasets demonstrate that our reconstructions outperform state-of-the-art methods, especially for the surface of the details. The project page and more visualizations can be found at: https://tb2-sy.github.io/st-2dgs/.
GeoFormer: Learning Point Cloud Completion with Tri-Plane Integrated Transformer
Aug 13, 2024



Abstract:Point cloud completion aims to recover accurate global geometry and preserve fine-grained local details from partial point clouds. Conventional methods typically predict unseen points directly from 3D point cloud coordinates or use self-projected multi-view depth maps to ease this task. However, these gray-scale depth maps cannot reach multi-view consistency, consequently restricting the performance. In this paper, we introduce a GeoFormer that simultaneously enhances the global geometric structure of the points and improves the local details. Specifically, we design a CCM Feature Enhanced Point Generator to integrate image features from multi-view consistent canonical coordinate maps (CCMs) and align them with pure point features, thereby enhancing the global geometry feature. Additionally, we employ the Multi-scale Geometry-aware Upsampler module to progressively enhance local details. This is achieved through cross attention between the multi-scale features extracted from the partial input and the features derived from previously estimated points. Extensive experiments on the PCN, ShapeNet-55/34, and KITTI benchmarks demonstrate that our GeoFormer outperforms recent methods, achieving the state-of-the-art performance. Our code is available at \href{https://github.com/Jinpeng-Yu/GeoFormer}{https://github.com/Jinpeng-Yu/GeoFormer}.
Surfel-based Gaussian Inverse Rendering for Fast and Relightable Dynamic Human Reconstruction from Monocular Video
Jul 23, 2024



Abstract:Efficient and accurate reconstruction of a relightable, dynamic clothed human avatar from a monocular video is crucial for the entertainment industry. This paper introduces the Surfel-based Gaussian Inverse Avatar (SGIA) method, which introduces efficient training and rendering for relightable dynamic human reconstruction. SGIA advances previous Gaussian Avatar methods by comprehensively modeling Physically-Based Rendering (PBR) properties for clothed human avatars, allowing for the manipulation of avatars into novel poses under diverse lighting conditions. Specifically, our approach integrates pre-integration and image-based lighting for fast light calculations that surpass the performance of existing implicit-based techniques. To address challenges related to material lighting disentanglement and accurate geometry reconstruction, we propose an innovative occlusion approximation strategy and a progressive training approach. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SGIA not only achieves highly accurate physical properties but also significantly enhances the realistic relighting of dynamic human avatars, providing a substantial speed advantage. We exhibit more results in our project page: https://GS-IA.github.io.
Continual Learning for Temporal-Sensitive Question Answering
Jul 17, 2024



Abstract:In this study, we explore an emerging research area of Continual Learning for Temporal Sensitive Question Answering (CLTSQA). Previous research has primarily focused on Temporal Sensitive Question Answering (TSQA), often overlooking the unpredictable nature of future events. In real-world applications, it's crucial for models to continually acquire knowledge over time, rather than relying on a static, complete dataset. Our paper investigates strategies that enable models to adapt to the ever-evolving information landscape, thereby addressing the challenges inherent in CLTSQA. To support our research, we first create a novel dataset, divided into five subsets, designed specifically for various stages of continual learning. We then propose a training framework for CLTSQA that integrates temporal memory replay and temporal contrastive learning. Our experimental results highlight two significant insights: First, the CLTSQA task introduces unique challenges for existing models. Second, our proposed framework effectively navigates these challenges, resulting in improved performance.
2D Gaussian Splatting for Geometrically Accurate Radiance Fields
Mar 26, 2024



Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has recently revolutionized radiance field reconstruction, achieving high quality novel view synthesis and fast rendering speed without baking. However, 3DGS fails to accurately represent surfaces due to the multi-view inconsistent nature of 3D Gaussians. We present 2D Gaussian Splatting (2DGS), a novel approach to model and reconstruct geometrically accurate radiance fields from multi-view images. Our key idea is to collapse the 3D volume into a set of 2D oriented planar Gaussian disks. Unlike 3D Gaussians, 2D Gaussians provide view-consistent geometry while modeling surfaces intrinsically. To accurately recover thin surfaces and achieve stable optimization, we introduce a perspective-accurate 2D splatting process utilizing ray-splat intersection and rasterization. Additionally, we incorporate depth distortion and normal consistency terms to further enhance the quality of the reconstructions. We demonstrate that our differentiable renderer allows for noise-free and detailed geometry reconstruction while maintaining competitive appearance quality, fast training speed, and real-time rendering. Our code will be made publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge