Xiaomei Wang
Ming-Omni: A Unified Multimodal Model for Perception and Generation
Jun 11, 2025


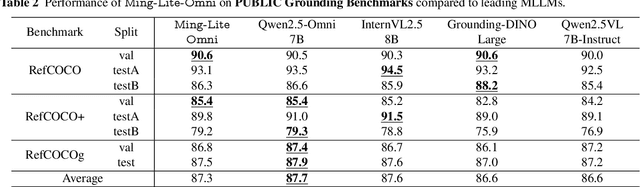
Abstract:We propose Ming-Omni, a unified multimodal model capable of processing images, text, audio, and video, while demonstrating strong proficiency in both speech and image generation. Ming-Omni employs dedicated encoders to extract tokens from different modalities, which are then processed by Ling, an MoE architecture equipped with newly proposed modality-specific routers. This design enables a single model to efficiently process and fuse multimodal inputs within a unified framework, thereby facilitating diverse tasks without requiring separate models, task-specific fine-tuning, or structural redesign. Importantly, Ming-Omni extends beyond conventional multimodal models by supporting audio and image generation. This is achieved through the integration of an advanced audio decoder for natural-sounding speech and Ming-Lite-Uni for high-quality image generation, which also allow the model to engage in context-aware chatting, perform text-to-speech conversion, and conduct versatile image editing. Our experimental results showcase Ming-Omni offers a powerful solution for unified perception and generation across all modalities. Notably, our proposed Ming-Omni is the first open-source model we are aware of to match GPT-4o in modality support, and we release all code and model weights to encourage further research and development in the community.
Towards Human-AI Mutual Learning: A New Research Paradigm
May 07, 2024
Abstract:This paper describes a new research paradigm for studying human-AI collaboration, named "human-AI mutual learning", defined as the process where humans and AI agents preserve, exchange, and improve knowledge during human-AI collaboration. We describe relevant methodologies, motivations, domain examples, benefits, challenges, and future research agenda under this paradigm.
TSP-Transformer: Task-Specific Prompts Boosted Transformer for Holistic Scene Understanding
Nov 06, 2023Abstract:Holistic scene understanding includes semantic segmentation, surface normal estimation, object boundary detection, depth estimation, etc. The key aspect of this problem is to learn representation effectively, as each subtask builds upon not only correlated but also distinct attributes. Inspired by visual-prompt tuning, we propose a Task-Specific Prompts Transformer, dubbed TSP-Transformer, for holistic scene understanding. It features a vanilla transformer in the early stage and tasks-specific prompts transformer encoder in the lateral stage, where tasks-specific prompts are augmented. By doing so, the transformer layer learns the generic information from the shared parts and is endowed with task-specific capacity. First, the tasks-specific prompts serve as induced priors for each task effectively. Moreover, the task-specific prompts can be seen as switches to favor task-specific representation learning for different tasks. Extensive experiments on NYUD-v2 and PASCAL-Context show that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance, validating the effectiveness of our method for holistic scene understanding. We also provide our code in the following link https://github.com/tb2-sy/TSP-Transformer.
Vocabulary-informed Zero-shot and Open-set Learning
Jan 04, 2023Abstract:Despite significant progress in object categorization, in recent years, a number of important challenges remain; mainly, the ability to learn from limited labeled data and to recognize object classes within large, potentially open, set of labels. Zero-shot learning is one way of addressing these challenges, but it has only been shown to work with limited sized class vocabularies and typically requires separation between supervised and unsupervised classes, allowing former to inform the latter but not vice versa. We propose the notion of vocabulary-informed learning to alleviate the above mentioned challenges and address problems of supervised, zero-shot, generalized zero-shot and open set recognition using a unified framework. Specifically, we propose a weighted maximum margin framework for semantic manifold-based recognition that incorporates distance constraints from (both supervised and unsupervised) vocabulary atoms. Distance constraints ensure that labeled samples are projected closer to their correct prototypes, in the embedding space, than to others. We illustrate that resulting model shows improvements in supervised, zero-shot, generalized zero-shot, and large open set recognition, with up to 310K class vocabulary on Animal with Attributes and ImageNet datasets.
* 17 pages, 8 figures. TPAMI 2019 extended from CVPR 2016 (arXiv:1604.07093)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge