Long Ye
Towards Explicit Acoustic Evidence Perception in Audio LLMs for Speech Deepfake Detection
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Speech deepfake detection (SDD) focuses on identifying whether a given speech signal is genuine or has been synthetically generated. Existing audio large language model (LLM)-based methods excel in content understanding; however, their predictions are often biased toward semantically correlated cues, which results in fine-grained acoustic artifacts being overlooked during the decisionmaking process. Consequently, fake speech with natural semantics can bypass detectors despite harboring subtle acoustic anomalies; this suggests that the challenge stems not from the absence of acoustic data, but from its inadequate accessibility when semantic-dominant reasoning prevails. To address this issue, we investigate SDD within the audio LLM paradigm and introduce SDD with Auditory Perception-enhanced Audio Large Language Model (SDD-APALLM), an acoustically enhanced framework designed to explicitly expose fine-grained time-frequency evidence as accessible acoustic cues. By combining raw audio with structured spectrograms, the proposed framework empowers audio LLMs to more effectively capture subtle acoustic inconsistencies without compromising their semantic understanding. Experimental results indicate consistent gains in detection accuracy and robustness, especially in cases where semantic cues are misleading. Further analysis reveals that these improvements stem from a coordinated utilization of semantic and acoustic information, as opposed to simple modality aggregation.
Interpretable All-Type Audio Deepfake Detection with Audio LLMs via Frequency-Time Reinforcement Learning
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in audio large language models (ALLMs) have made high-quality synthetic audio widely accessible, increasing the risk of malicious audio deepfakes across speech, environmental sounds, singing voice, and music. Real-world audio deepfake detection (ADD) therefore requires all-type detectors that generalize across heterogeneous audio and provide interpretable decisions. Given the strong multi-task generalization ability of ALLMs, we first investigate their performance on all-type ADD under both supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and reinforcement fine-tuning (RFT). However, SFT using only binary real/fake labels tends to reduce the model to a black-box classifier, sacrificing interpretability. Meanwhile, vanilla RFT under sparse supervision is prone to reward hacking and can produce hallucinated, ungrounded rationales. To address this, we propose an automatic annotation and polishing pipeline that constructs Frequency-Time structured chain-of-thought (CoT) rationales, producing ~340K cold-start demonstrations. Building on CoT data, we propose Frequency Time-Group Relative Policy Optimization (FT-GRPO), a two-stage training paradigm that cold-starts ALLMs with SFT and then applies GRPO under rule-based frequency-time constraints. Experiments demonstrate that FT-GRPO achieves state-of-the-art performance on all-type ADD while producing interpretable, FT-grounded rationales. The data and code are available online.
EnvSSLAM-FFN: Lightweight Layer-Fused System for ESDD 2026 Challenge
Dec 23, 2025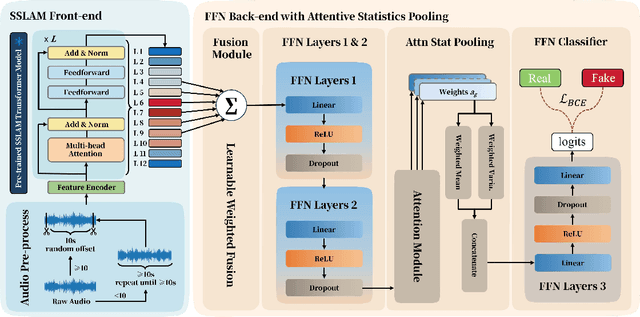
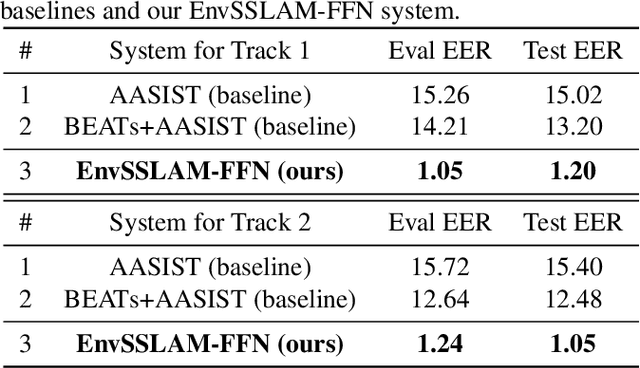
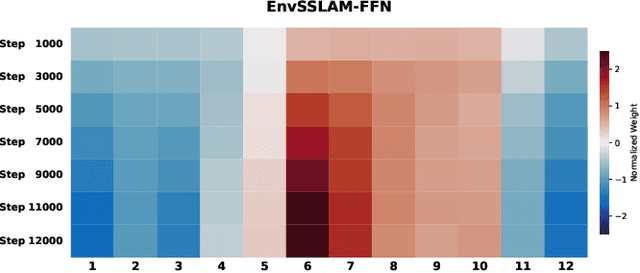
Abstract:Recent advances in generative audio models have enabled high-fidelity environmental sound synthesis, raising serious concerns for audio security. The ESDD 2026 Challenge therefore addresses environmental sound deepfake detection under unseen generators (Track 1) and black-box low-resource detection (Track 2) conditions. We propose EnvSSLAM-FFN, which integrates a frozen SSLAM self-supervised encoder with a lightweight FFN back-end. To effectively capture spoofing artifacts under severe data imbalance, we fuse intermediate SSLAM representations from layers 4-9 and adopt a class-weighted training objective. Experimental results show that the proposed system consistently outperforms the official baselines on both tracks, achieving Test Equal Error Rates (EERs) of 1.20% and 1.05%, respectively.
Depth-Guided Bundle Sampling for Efficient Generalizable Neural Radiance Field Reconstruction
May 26, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in generalizable novel view synthesis have achieved impressive quality through interpolation between nearby views. However, rendering high-resolution images remains computationally intensive due to the need for dense sampling of all rays. Recognizing that natural scenes are typically piecewise smooth and sampling all rays is often redundant, we propose a novel depth-guided bundle sampling strategy to accelerate rendering. By grouping adjacent rays into a bundle and sampling them collectively, a shared representation is generated for decoding all rays within the bundle. To further optimize efficiency, our adaptive sampling strategy dynamically allocates samples based on depth confidence, concentrating more samples in complex regions while reducing them in smoother areas. When applied to ENeRF, our method achieves up to a 1.27 dB PSNR improvement and a 47% increase in FPS on the DTU dataset. Extensive experiments on synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate state-of-the-art rendering quality and up to 2x faster rendering compared to existing generalizable methods. Code is available at https://github.com/KLMAV-CUC/GDB-NeRF.
GoLF-NRT: Integrating Global Context and Local Geometry for Few-Shot View Synthesis
May 26, 2025Abstract:Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have transformed novel view synthesis by modeling scene-specific volumetric representations directly from images. While generalizable NeRF models can generate novel views across unknown scenes by learning latent ray representations, their performance heavily depends on a large number of multi-view observations. However, with limited input views, these methods experience significant degradation in rendering quality. To address this limitation, we propose GoLF-NRT: a Global and Local feature Fusion-based Neural Rendering Transformer. GoLF-NRT enhances generalizable neural rendering from few input views by leveraging a 3D transformer with efficient sparse attention to capture global scene context. In parallel, it integrates local geometric features extracted along the epipolar line, enabling high-quality scene reconstruction from as few as 1 to 3 input views. Furthermore, we introduce an adaptive sampling strategy based on attention weights and kernel regression, improving the accuracy of transformer-based neural rendering. Extensive experiments on public datasets show that GoLF-NRT achieves state-of-the-art performance across varying numbers of input views, highlighting the effectiveness and superiority of our approach. Code is available at https://github.com/KLMAV-CUC/GoLF-NRT.
Detect All-Type Deepfake Audio: Wavelet Prompt Tuning for Enhanced Auditory Perception
Apr 09, 2025



Abstract:The rapid advancement of audio generation technologies has escalated the risks of malicious deepfake audio across speech, sound, singing voice, and music, threatening multimedia security and trust. While existing countermeasures (CMs) perform well in single-type audio deepfake detection (ADD), their performance declines in cross-type scenarios. This paper is dedicated to studying the alltype ADD task. We are the first to comprehensively establish an all-type ADD benchmark to evaluate current CMs, incorporating cross-type deepfake detection across speech, sound, singing voice, and music. Then, we introduce the prompt tuning self-supervised learning (PT-SSL) training paradigm, which optimizes SSL frontend by learning specialized prompt tokens for ADD, requiring 458x fewer trainable parameters than fine-tuning (FT). Considering the auditory perception of different audio types,we propose the wavelet prompt tuning (WPT)-SSL method to capture type-invariant auditory deepfake information from the frequency domain without requiring additional training parameters, thereby enhancing performance over FT in the all-type ADD task. To achieve an universally CM, we utilize all types of deepfake audio for co-training. Experimental results demonstrate that WPT-XLSR-AASIST achieved the best performance, with an average EER of 3.58% across all evaluation sets. The code is available online.
MAG: Multi-Modal Aligned Autoregressive Co-Speech Gesture Generation without Vector Quantization
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:This work focuses on full-body co-speech gesture generation. Existing methods typically employ an autoregressive model accompanied by vector-quantized tokens for gesture generation, which results in information loss and compromises the realism of the generated gestures. To address this, inspired by the natural continuity of real-world human motion, we propose MAG, a novel multi-modal aligned framework for high-quality and diverse co-speech gesture synthesis without relying on discrete tokenization. Specifically, (1) we introduce a motion-text-audio-aligned variational autoencoder (MTA-VAE), which leverages pre-trained WavCaps' text and audio embeddings to enhance both semantic and rhythmic alignment with motion, ultimately producing more realistic gestures. (2) Building on this, we propose a multimodal masked autoregressive model (MMAG) that enables autoregressive modeling in continuous motion embeddings through diffusion without vector quantization. To further ensure multi-modal consistency, MMAG incorporates a hybrid granularity audio-text fusion block, which serves as conditioning for diffusion process. Extensive experiments on two benchmark datasets demonstrate that MAG achieves stateof-the-art performance both quantitatively and qualitatively, producing highly realistic and diverse co-speech gestures.The code will be released to facilitate future research.
Neural Codec Source Tracing: Toward Comprehensive Attribution in Open-Set Condition
Jan 11, 2025



Abstract:Current research in audio deepfake detection is gradually transitioning from binary classification to multi-class tasks, referred as audio deepfake source tracing task. However, existing studies on source tracing consider only closed-set scenarios and have not considered the challenges posed by open-set conditions. In this paper, we define the Neural Codec Source Tracing (NCST) task, which is capable of performing open-set neural codec classification and interpretable ALM detection. Specifically, we constructed the ST-Codecfake dataset for the NCST task, which includes bilingual audio samples generated by 11 state-of-the-art neural codec methods and ALM-based out-ofdistribution (OOD) test samples. Furthermore, we establish a comprehensive source tracing benchmark to assess NCST models in open-set conditions. The experimental results reveal that although the NCST models perform well in in-distribution (ID) classification and OOD detection, they lack robustness in classifying unseen real audio. The ST-codecfake dataset and code are available.
Does Current Deepfake Audio Detection Model Effectively Detect ALM-based Deepfake Audio?
Aug 20, 2024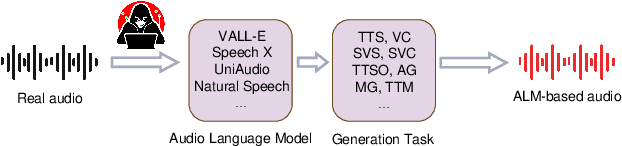
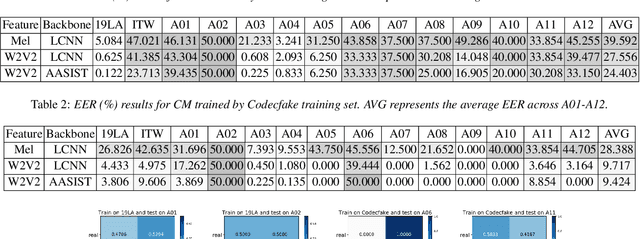
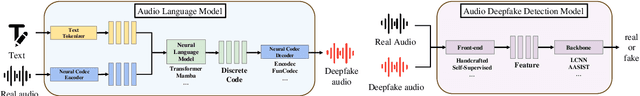
Abstract:Currently, Audio Language Models (ALMs) are rapidly advancing due to the developments in large language models and audio neural codecs. These ALMs have significantly lowered the barrier to creating deepfake audio, generating highly realistic and diverse types of deepfake audio, which pose severe threats to society. Consequently, effective audio deepfake detection technologies to detect ALM-based audio have become increasingly critical. This paper investigate the effectiveness of current countermeasure (CM) against ALM-based audio. Specifically, we collect 12 types of the latest ALM-based deepfake audio and utilizing the latest CMs to evaluate. Our findings reveal that the latest codec-trained CM can effectively detect ALM-based audio, achieving 0% equal error rate under most ALM test conditions, which exceeded our expectations. This indicates promising directions for future research in ALM-based deepfake audio detection.
Temporal Variability and Multi-Viewed Self-Supervised Representations to Tackle the ASVspoof5 Deepfake Challenge
Aug 13, 2024
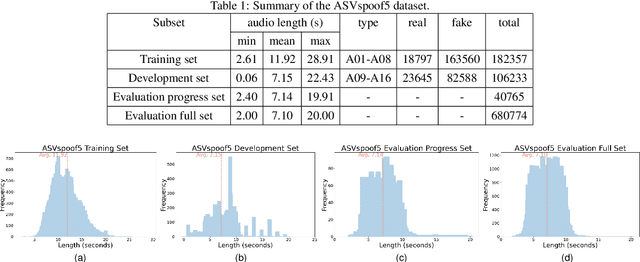
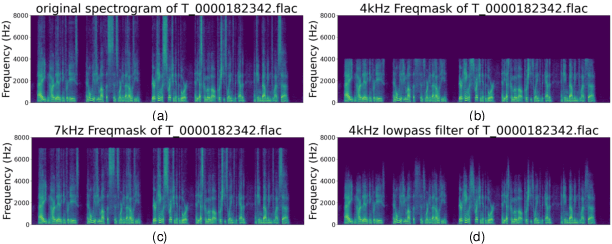
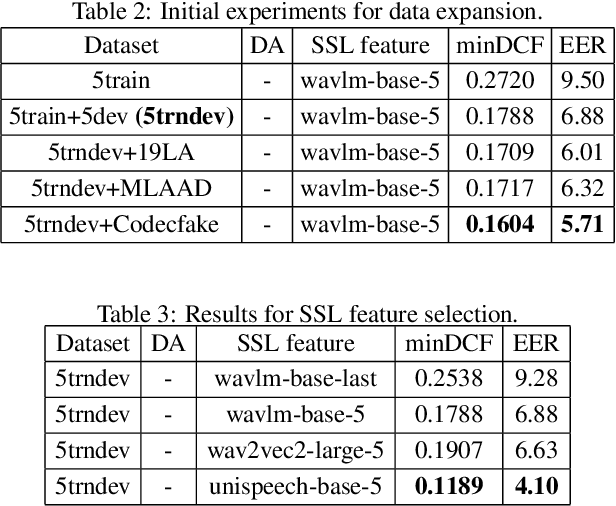
Abstract:ASVspoof5, the fifth edition of the ASVspoof series, is one of the largest global audio security challenges. It aims to advance the development of countermeasure (CM) to discriminate bonafide and spoofed speech utterances. In this paper, we focus on addressing the problem of open-domain audio deepfake detection, which corresponds directly to the ASVspoof5 Track1 open condition. At first, we comprehensively investigate various CM on ASVspoof5, including data expansion, data augmentation, and self-supervised learning (SSL) features. Due to the high-frequency gaps characteristic of the ASVspoof5 dataset, we introduce Frequency Mask, a data augmentation method that masks specific frequency bands to improve CM robustness. Combining various scale of temporal information with multiple SSL features, our experiments achieved a minDCF of 0.0158 and an EER of 0.55% on the ASVspoof 5 Track 1 evaluation progress set.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge