Songjun Cao
MPE-TTS: Customized Emotion Zero-Shot Text-To-Speech Using Multi-Modal Prompt
May 24, 2025Abstract:Most existing Zero-Shot Text-To-Speech(ZS-TTS) systems generate the unseen speech based on single prompt, such as reference speech or text descriptions, which limits their flexibility. We propose a customized emotion ZS-TTS system based on multi-modal prompt. The system disentangles speech into the content, timbre, emotion and prosody, allowing emotion prompts to be provided as text, image or speech. To extract emotion information from different prompts, we propose a multi-modal prompt emotion encoder. Additionally, we introduce an prosody predictor to fit the distribution of prosody and propose an emotion consistency loss to preserve emotion information in the predicted prosody. A diffusion-based acoustic model is employed to generate the target mel-spectrogram. Both objective and subjective experiments demonstrate that our system outperforms existing systems in terms of naturalness and similarity. The samples are available at https://mpetts-demo.github.io/mpetts_demo/.
Detect All-Type Deepfake Audio: Wavelet Prompt Tuning for Enhanced Auditory Perception
Apr 09, 2025



Abstract:The rapid advancement of audio generation technologies has escalated the risks of malicious deepfake audio across speech, sound, singing voice, and music, threatening multimedia security and trust. While existing countermeasures (CMs) perform well in single-type audio deepfake detection (ADD), their performance declines in cross-type scenarios. This paper is dedicated to studying the alltype ADD task. We are the first to comprehensively establish an all-type ADD benchmark to evaluate current CMs, incorporating cross-type deepfake detection across speech, sound, singing voice, and music. Then, we introduce the prompt tuning self-supervised learning (PT-SSL) training paradigm, which optimizes SSL frontend by learning specialized prompt tokens for ADD, requiring 458x fewer trainable parameters than fine-tuning (FT). Considering the auditory perception of different audio types,we propose the wavelet prompt tuning (WPT)-SSL method to capture type-invariant auditory deepfake information from the frequency domain without requiring additional training parameters, thereby enhancing performance over FT in the all-type ADD task. To achieve an universally CM, we utilize all types of deepfake audio for co-training. Experimental results demonstrate that WPT-XLSR-AASIST achieved the best performance, with an average EER of 3.58% across all evaluation sets. The code is available online.
DiffCSS: Diverse and Expressive Conversational Speech Synthesis with Diffusion Models
Feb 27, 2025


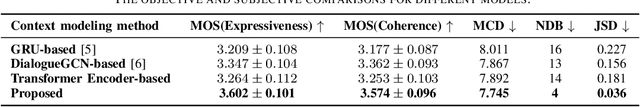
Abstract:Conversational speech synthesis (CSS) aims to synthesize both contextually appropriate and expressive speech, and considerable efforts have been made to enhance the understanding of conversational context. However, existing CSS systems are limited to deterministic prediction, overlooking the diversity of potential responses. Moreover, they rarely employ language model (LM)-based TTS backbones, limiting the naturalness and quality of synthesized speech. To address these issues, in this paper, we propose DiffCSS, an innovative CSS framework that leverages diffusion models and an LM-based TTS backbone to generate diverse, expressive, and contextually coherent speech. A diffusion-based context-aware prosody predictor is proposed to sample diverse prosody embeddings conditioned on multimodal conversational context. Then a prosody-controllable LM-based TTS backbone is developed to synthesize high-quality speech with sampled prosody embeddings. Experimental results demonstrate that the synthesized speech from DiffCSS is more diverse, contextually coherent, and expressive than existing CSS systems
Neural Codec Source Tracing: Toward Comprehensive Attribution in Open-Set Condition
Jan 11, 2025



Abstract:Current research in audio deepfake detection is gradually transitioning from binary classification to multi-class tasks, referred as audio deepfake source tracing task. However, existing studies on source tracing consider only closed-set scenarios and have not considered the challenges posed by open-set conditions. In this paper, we define the Neural Codec Source Tracing (NCST) task, which is capable of performing open-set neural codec classification and interpretable ALM detection. Specifically, we constructed the ST-Codecfake dataset for the NCST task, which includes bilingual audio samples generated by 11 state-of-the-art neural codec methods and ALM-based out-ofdistribution (OOD) test samples. Furthermore, we establish a comprehensive source tracing benchmark to assess NCST models in open-set conditions. The experimental results reveal that although the NCST models perform well in in-distribution (ID) classification and OOD detection, they lack robustness in classifying unseen real audio. The ST-codecfake dataset and code are available.
A Transcription Prompt-based Efficient Audio Large Language Model for Robust Speech Recognition
Aug 18, 2024Abstract:Audio-LLM introduces audio modality into a large language model (LLM) to enable a powerful LLM to recognize, understand, and generate audio. However, during speech recognition in noisy environments, we observed the presence of illusions and repetition issues in audio-LLM, leading to substitution and insertion errors. This paper proposes a transcription prompt-based audio-LLM by introducing an ASR expert as a transcription tokenizer and a hybrid Autoregressive (AR) Non-autoregressive (NAR) decoding approach to solve the above problems. Experiments on 10k-hour WenetSpeech Mandarin corpus show that our approach decreases 12.2% and 9.6% CER relatively on Test_Net and Test_Meeting evaluation sets compared with baseline. Notably, we reduce the decoding repetition rate on the evaluation set to zero, showing that the decoding repetition problem has been solved fundamentally.
DistillW2V2: A Small and Streaming Wav2vec 2.0 Based ASR Model
Mar 16, 2023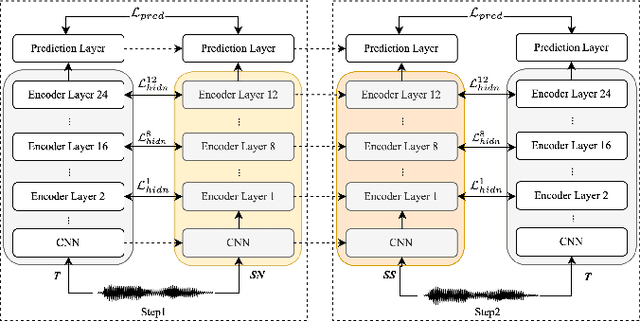
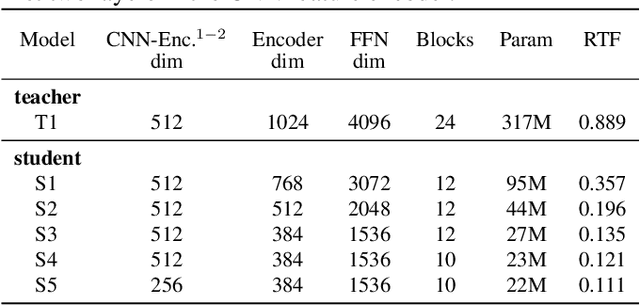
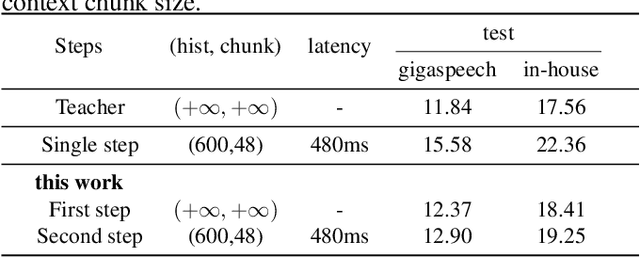
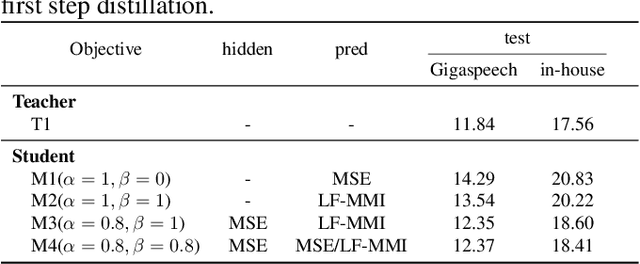
Abstract:Wav2vec 2.0 (W2V2) has shown impressive performance in automatic speech recognition (ASR). However, the large model size and the non-streaming architecture make it hard to be used under low-resource or streaming scenarios. In this work, we propose a two-stage knowledge distillation method to solve these two problems: the first step is to make the big and non-streaming teacher model smaller, and the second step is to make it streaming. Specially, we adopt the MSE loss for the distillation of hidden layers and the modified LF-MMI loss for the distillation of the prediction layer. Experiments are conducted on Gigaspeech, Librispeech, and an in-house dataset. The results show that the distilled student model (DistillW2V2) we finally get is 8x faster and 12x smaller than the original teacher model. For the 480ms latency setup, the DistillW2V2's relative word error rate (WER) degradation varies from 9% to 23.4% on test sets, which reveals a promising way to extend the W2V2's application scope.
Censer: Curriculum Semi-supervised Learning for Speech Recognition Based on Self-supervised Pre-training
Jun 27, 2022



Abstract:Recent studies have shown that the benefits provided by self-supervised pre-training and self-training (pseudo-labeling) are complementary. Semi-supervised fine-tuning strategies under the pre-training framework, however, remain insufficiently studied. Besides, modern semi-supervised speech recognition algorithms either treat unlabeled data indiscriminately or filter out noisy samples with a confidence threshold. The dissimilarities among different unlabeled data are often ignored. In this paper, we propose Censer, a semi-supervised speech recognition algorithm based on self-supervised pre-training to maximize the utilization of unlabeled data. The pre-training stage of Censer adopts wav2vec2.0 and the fine-tuning stage employs an improved semi-supervised learning algorithm from slimIPL, which leverages unlabeled data progressively according to their pseudo labels' qualities. We also incorporate a temporal pseudo label pool and an exponential moving average to control the pseudo labels' update frequency and to avoid model divergence. Experimental results on Libri-Light and LibriSpeech datasets manifest our proposed method achieves better performance compared to existing approaches while being more unified.
A practical framework for multi-domain speech recognition and an instance sampling method to neural language modeling
Mar 09, 2022



Abstract:Automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems used on smart phones or vehicles are usually required to process speech queries from very different domains. In such situations, a vanilla ASR system usually fails to perform well on every domain. This paper proposes a multi-domain ASR framework for Tencent Map, a navigation app used on smart phones and in-vehicle infotainment systems. The proposed framework consists of three core parts: a basic ASR module to generate n-best lists of a speech query, a text classification module to determine which domain the speech query belongs to, and a reranking module to rescore n-best lists using domain-specific language models. In addition, an instance sampling based method to training neural network language models (NNLMs) is proposed to address the data imbalance problem in multi-domain ASR. In experiments, the proposed framework was evaluated on navigation domain and music domain, since navigating and playing music are two main features of Tencent Map. Compared to a general ASR system, the proposed framework achieves a relative 13% $\sim$ 22% character error rate reduction on several test sets collected from Tencent Map and our in-car voice assistant.
Improving CTC-based speech recognition via knowledge transferring from pre-trained language models
Feb 22, 2022



Abstract:Recently, end-to-end automatic speech recognition models based on connectionist temporal classification (CTC) have achieved impressive results, especially when fine-tuned from wav2vec2.0 models. Due to the conditional independence assumption, CTC-based models are always weaker than attention-based encoder-decoder models and require the assistance of external language models (LMs). To solve this issue, we propose two knowledge transferring methods that leverage pre-trained LMs, such as BERT and GPT2, to improve CTC-based models. The first method is based on representation learning, in which the CTC-based models use the representation produced by BERT as an auxiliary learning target. The second method is based on joint classification learning, which combines GPT2 for text modeling with a hybrid CTC/attention architecture. Experiment on AISHELL-1 corpus yields a character error rate (CER) of 4.2% on the test set. When compared to the vanilla CTC-based models fine-tuned from the wav2vec2.0 models, our knowledge transferring method reduces CER by 16.1% relatively without external LMs.
Improving Hybrid CTC/Attention End-to-end Speech Recognition with Pretrained Acoustic and Language Model
Dec 14, 2021



Abstract:Recently, self-supervised pretraining has achieved impressive results in end-to-end (E2E) automatic speech recognition (ASR). However, the dominant sequence-to-sequence (S2S) E2E model is still hard to fully utilize the self-supervised pre-training methods because its decoder is conditioned on acoustic representation thus cannot be pretrained separately. In this paper, we propose a pretrained Transformer (Preformer) S2S ASR architecture based on hybrid CTC/attention E2E models to fully utilize the pretrained acoustic models (AMs) and language models (LMs). In our framework, the encoder is initialized with a pretrained AM (wav2vec2.0). The Preformer leverages CTC as an auxiliary task during training and inference. Furthermore, we design a one-cross decoder (OCD), which relaxes the dependence on acoustic representations so that it can be initialized with pretrained LM (DistilGPT2). Experiments are conducted on the AISHELL-1 corpus and achieve a $4.6\%$ character error rate (CER) on the test set. Compared with our vanilla hybrid CTC/attention Transformer baseline, our proposed CTC/attention-based Preformer yields $27\%$ relative CER reduction. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to utilize both pretrained AM and LM in a S2S ASR system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge