Wenhua Wu
DNA: Uncovering Universal Latent Forgery Knowledge
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:As generative AI achieves hyper-realism, superficial artifact detection has become obsolete. While prevailing methods rely on resource-intensive fine-tuning of black-box backbones, we propose that forgery detection capability is already encoded within pre-trained models rather than requiring end-to-end retraining. To elicit this intrinsic capability, we propose the discriminative neural anchors (DNA) framework, which employs a coarse-to-fine excavation mechanism. First, by analyzing feature decoupling and attention distribution shifts, we pinpoint critical intermediate layers where the focus of the model logically transitions from global semantics to local anomalies. Subsequently, we introduce a triadic fusion scoring metric paired with a curvature-truncation strategy to strip away semantic redundancy, precisely isolating the forgery-discriminative units (FDUs) inherently imprinted with sensitivity to forgery traces. Moreover, we introduce HIFI-Gen, a high-fidelity synthetic benchmark built upon the very latest models, to address the lag in existing datasets. Experiments demonstrate that by solely relying on these anchors, DNA achieves superior detection performance even under few-shot conditions. Furthermore, it exhibits remarkable robustness across diverse architectures and against unseen generative models, validating that waking up latent neurons is more effective than extensive fine-tuning.
TraceRouter: Robust Safety for Large Foundation Models via Path-Level Intervention
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Despite their capabilities, large foundation models (LFMs) remain susceptible to adversarial manipulation. Current defenses predominantly rely on the "locality hypothesis", suppressing isolated neurons or features. However, harmful semantics act as distributed, cross-layer circuits, rendering such localized interventions brittle and detrimental to utility. To bridge this gap, we propose \textbf{TraceRouter}, a path-level framework that traces and disconnects the causal propagation circuits of illicit semantics. TraceRouter operates in three stages: (1) it pinpoints a sensitive onset layer by analyzing attention divergence; (2) it leverages sparse autoencoders (SAEs) and differential activation analysis to disentangle and isolate malicious features; and (3) it maps these features to downstream causal pathways via feature influence scores (FIS) derived from zero-out interventions. By selectively suppressing these causal chains, TraceRouter physically severs the flow of harmful information while leaving orthogonal computation routes intact. Extensive experiments demonstrate that TraceRouter significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, achieving a superior trade-off between adversarial robustness and general utility. Our code will be publicly released. WARNING: This paper contains unsafe model responses.
HarmoniAD: Harmonizing Local Structures and Global Semantics for Anomaly Detection
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:Anomaly detection is crucial in industrial product quality inspection. Failing to detect tiny defects often leads to serious consequences. Existing methods face a structure-semantics trade-off: structure-oriented models (such as frequency-based filters) are noise-sensitive, while semantics-oriented models (such as CLIP-based encoders) often miss fine details. To address this, we propose HarmoniAD, a frequency-guided dual-branch framework. Features are first extracted by the CLIP image encoder, then transformed into the frequency domain, and finally decoupled into high- and low-frequency paths for complementary modeling of structure and semantics. The high-frequency branch is equipped with a fine-grained structural attention module (FSAM) to enhance textures and edges for detecting small anomalies, while the low-frequency branch uses a global structural context module (GSCM) to capture long-range dependencies and preserve semantic consistency. Together, these branches balance fine detail and global semantics. HarmoniAD further adopts a multi-class joint training strategy, and experiments on MVTec-AD, VisA, and BTAD show state-of-the-art performance with both sensitivity and robustness.
Reloc-VGGT: Visual Re-localization with Geometry Grounded Transformer
Dec 26, 2025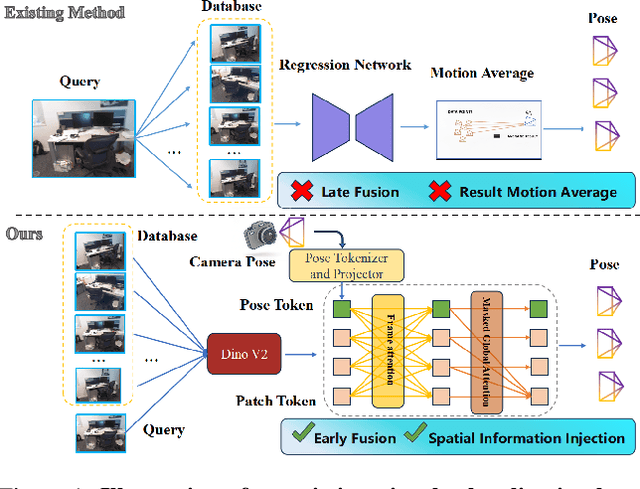
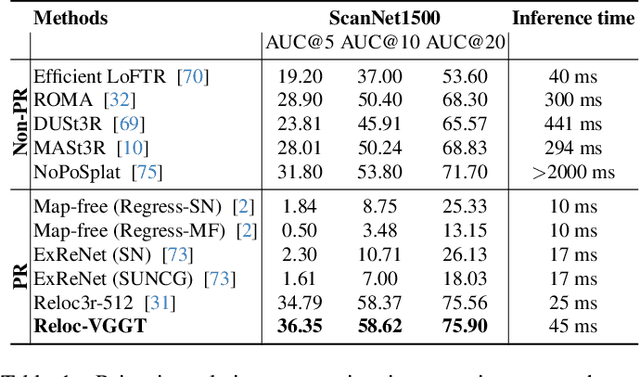
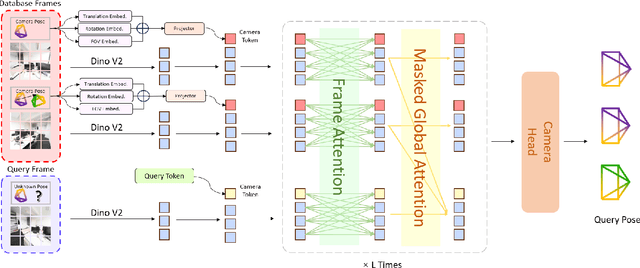
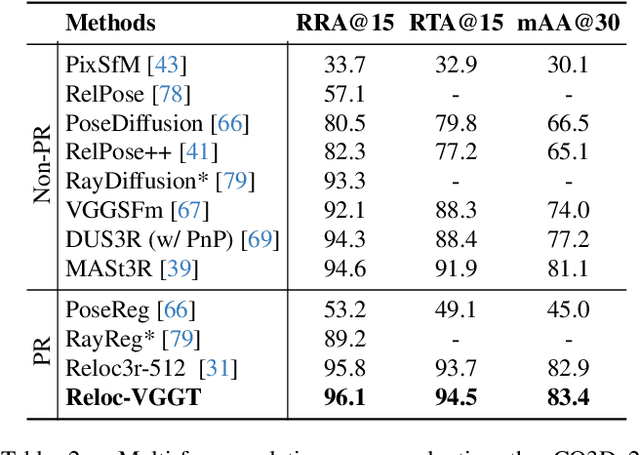
Abstract:Visual localization has traditionally been formulated as a pair-wise pose regression problem. Existing approaches mainly estimate relative poses between two images and employ a late-fusion strategy to obtain absolute pose estimates. However, the late motion average is often insufficient for effectively integrating spatial information, and its accuracy degrades in complex environments. In this paper, we present the first visual localization framework that performs multi-view spatial integration through an early-fusion mechanism, enabling robust operation in both structured and unstructured environments. Our framework is built upon the VGGT backbone, which encodes multi-view 3D geometry, and we introduce a pose tokenizer and projection module to more effectively exploit spatial relationships from multiple database views. Furthermore, we propose a novel sparse mask attention strategy that reduces computational cost by avoiding the quadratic complexity of global attention, thereby enabling real-time performance at scale. Trained on approximately eight million posed image pairs, Reloc-VGGT demonstrates strong accuracy and remarkable generalization ability. Extensive experiments across diverse public datasets consistently validate the effectiveness and efficiency of our approach, delivering high-quality camera pose estimates in real time while maintaining robustness to unseen environments. Our code and models will be publicly released upon acceptance.https://github.com/dtc111111/Reloc-VGGT.
D$^2$GSLAM: 4D Dynamic Gaussian Splatting SLAM
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in Dense Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) have demonstrated remarkable performance in static environments. However, dense SLAM in dynamic environments remains challenging. Most methods directly remove dynamic objects and focus solely on static scene reconstruction, which ignores the motion information contained in these dynamic objects. In this paper, we present D$^2$GSLAM, a novel dynamic SLAM system utilizing Gaussian representation, which simultaneously performs accurate dynamic reconstruction and robust tracking within dynamic environments. Our system is composed of four key components: (i) We propose a geometric-prompt dynamic separation method to distinguish between static and dynamic elements of the scene. This approach leverages the geometric consistency of Gaussian representation and scene geometry to obtain coarse dynamic regions. The regions then serve as prompts to guide the refinement of the coarse mask for achieving accurate motion mask. (ii) To facilitate accurate and efficient mapping of the dynamic scene, we introduce dynamic-static composite representation that integrates static 3D Gaussians with dynamic 4D Gaussians. This representation allows for modeling the transitions between static and dynamic states of objects in the scene for composite mapping and optimization. (iii) We employ a progressive pose refinement strategy that leverages both the multi-view consistency of static scene geometry and motion information from dynamic objects to achieve accurate camera tracking. (iv) We introduce a motion consistency loss, which leverages the temporal continuity in object motions for accurate dynamic modeling. Our D$^2$GSLAM demonstrates superior performance on dynamic scenes in terms of mapping and tracking accuracy, while also showing capability in accurate dynamic modeling.
DIAL-GS: Dynamic Instance Aware Reconstruction for Label-free Street Scenes with 4D Gaussian Splatting
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Urban scene reconstruction is critical for autonomous driving, enabling structured 3D representations for data synthesis and closed-loop testing. Supervised approaches rely on costly human annotations and lack scalability, while current self-supervised methods often confuse static and dynamic elements and fail to distinguish individual dynamic objects, limiting fine-grained editing. We propose DIAL-GS, a novel dynamic instance-aware reconstruction method for label-free street scenes with 4D Gaussian Splatting. We first accurately identify dynamic instances by exploiting appearance-position inconsistency between warped rendering and actual observation. Guided by instance-level dynamic perception, we employ instance-aware 4D Gaussians as the unified volumetric representation, realizing dynamic-adaptive and instance-aware reconstruction. Furthermore, we introduce a reciprocal mechanism through which identity and dynamics reinforce each other, enhancing both integrity and consistency. Experiments on urban driving scenarios show that DIAL-GS surpasses existing self-supervised baselines in reconstruction quality and instance-level editing, offering a concise yet powerful solution for urban scene modeling.
F2Net: A Frequency-Fused Network for Ultra-High Resolution Remote Sensing Segmentation
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Semantic segmentation of ultra-high-resolution (UHR) remote sensing imagery is critical for applications like environmental monitoring and urban planning but faces computational and optimization challenges. Conventional methods either lose fine details through downsampling or fragment global context via patch processing. While multi-branch networks address this trade-off, they suffer from computational inefficiency and conflicting gradient dynamics during training. We propose F2Net, a frequency-aware framework that decomposes UHR images into high- and low-frequency components for specialized processing. The high-frequency branch preserves full-resolution structural details, while the low-frequency branch processes downsampled inputs through dual sub-branches capturing short- and long-range dependencies. A Hybrid-Frequency Fusion module integrates these observations, guided by two novel objectives: Cross-Frequency Alignment Loss ensures semantic consistency between frequency components, and Cross-Frequency Balance Loss regulates gradient magnitudes across branches to stabilize training. Evaluated on DeepGlobe and Inria Aerial benchmarks, F2Net achieves state-of-the-art performance with mIoU of 80.22 and 83.39, respectively. Our code will be publicly available.
ADD-SLAM: Adaptive Dynamic Dense SLAM with Gaussian Splatting
May 26, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian-based Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) methods have demonstrated exceptional localization precision and remarkable dense mapping performance. However, dynamic objects introduce critical challenges by disrupting scene consistency, leading to tracking drift and mapping artifacts. Existing methods that employ semantic segmentation or object detection for dynamic identification and filtering typically rely on predefined categorical priors, while discarding dynamic scene information crucial for robotic applications such as dynamic obstacle avoidance and environmental interaction. To overcome these challenges, we propose ADD-SLAM: an Adaptive Dynamic Dense SLAM framework based on Gaussian splitting. We design an adaptive dynamic identification mechanism grounded in scene consistency analysis, comparing geometric and textural discrepancies between real-time observations and historical maps. Ours requires no predefined semantic category priors and adaptively discovers scene dynamics. Precise dynamic object recognition effectively mitigates interference from moving targets during localization. Furthermore, we propose a dynamic-static separation mapping strategy that constructs a temporal Gaussian model to achieve online incremental dynamic modeling. Experiments conducted on multiple dynamic datasets demonstrate our method's flexible and accurate dynamic segmentation capabilities, along with state-of-the-art performance in both localization and mapping.
VPGS-SLAM: Voxel-based Progressive 3D Gaussian SLAM in Large-Scale Scenes
May 25, 2025



Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting has recently shown promising results in dense visual SLAM. However, existing 3DGS-based SLAM methods are all constrained to small-room scenarios and struggle with memory explosion in large-scale scenes and long sequences. To this end, we propose VPGS-SLAM, the first 3DGS-based large-scale RGBD SLAM framework for both indoor and outdoor scenarios. We design a novel voxel-based progressive 3D Gaussian mapping method with multiple submaps for compact and accurate scene representation in large-scale and long-sequence scenes. This allows us to scale up to arbitrary scenes and improves robustness (even under pose drifts). In addition, we propose a 2D-3D fusion camera tracking method to achieve robust and accurate camera tracking in both indoor and outdoor large-scale scenes. Furthermore, we design a 2D-3D Gaussian loop closure method to eliminate pose drift. We further propose a submap fusion method with online distillation to achieve global consistency in large-scale scenes when detecting a loop. Experiments on various indoor and outdoor datasets demonstrate the superiority and generalizability of the proposed framework. The code will be open source on https://github.com/dtc111111/vpgs-slam.
BEV-GS: Feed-forward Gaussian Splatting in Bird's-Eye-View for Road Reconstruction
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Road surface is the sole contact medium for wheels or robot feet. Reconstructing road surface is crucial for unmanned vehicles and mobile robots. Recent studies on Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and Gaussian Splatting (GS) have achieved remarkable results in scene reconstruction. However, they typically rely on multi-view image inputs and require prolonged optimization times. In this paper, we propose BEV-GS, a real-time single-frame road surface reconstruction method based on feed-forward Gaussian splatting. BEV-GS consists of a prediction module and a rendering module. The prediction module introduces separate geometry and texture networks following Bird's-Eye-View paradigm. Geometric and texture parameters are directly estimated from a single frame, avoiding per-scene optimization. In the rendering module, we utilize grid Gaussian for road surface representation and novel view synthesis, which better aligns with road surface characteristics. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on the real-world dataset RSRD. The road elevation error reduces to 1.73 cm, and the PSNR of novel view synthesis reaches 28.36 dB. The prediction and rendering FPS is 26, and 2061, respectively, enabling high-accuracy and real-time applications. The code will be available at: \href{https://github.com/cat-wwh/BEV-GS}{\texttt{https://github.com/cat-wwh/BEV-GS}}
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge