Wanlong Li
Geo-ConvGRU: Geographically Masked Convolutional Gated Recurrent Unit for Bird-Eye View Segmentation
Dec 28, 2024Abstract:Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have significantly impacted various computer vision tasks, however, they inherently struggle to model long-range dependencies explicitly due to the localized nature of convolution operations. Although Transformers have addressed limitations in long-range dependencies for the spatial dimension, the temporal dimension remains underexplored. In this paper, we first highlight that 3D CNNs exhibit limitations in capturing long-range temporal dependencies. Though Transformers mitigate spatial dimension issues, they result in a considerable increase in parameter and processing speed reduction. To overcome these challenges, we introduce a simple yet effective module, Geographically Masked Convolutional Gated Recurrent Unit (Geo-ConvGRU), tailored for Bird's-Eye View segmentation. Specifically, we substitute the 3D CNN layers with ConvGRU in the temporal module to bolster the capacity of networks for handling temporal dependencies. Additionally, we integrate a geographical mask into the Convolutional Gated Recurrent Unit to suppress noise introduced by the temporal module. Comprehensive experiments conducted on the NuScenes dataset substantiate the merits of the proposed Geo-ConvGRU, revealing that our approach attains state-of-the-art performance in Bird's-Eye View segmentation.
Self-supervised Event-based Monocular Depth Estimation using Cross-modal Consistency
Jan 14, 2024Abstract:An event camera is a novel vision sensor that can capture per-pixel brightness changes and output a stream of asynchronous ``events''. It has advantages over conventional cameras in those scenes with high-speed motions and challenging lighting conditions because of the high temporal resolution, high dynamic range, low bandwidth, low power consumption, and no motion blur. Therefore, several supervised monocular depth estimation from events is proposed to address scenes difficult for conventional cameras. However, depth annotation is costly and time-consuming. In this paper, to lower the annotation cost, we propose a self-supervised event-based monocular depth estimation framework named EMoDepth. EMoDepth constrains the training process using the cross-modal consistency from intensity frames that are aligned with events in the pixel coordinate. Moreover, in inference, only events are used for monocular depth prediction. Additionally, we design a multi-scale skip-connection architecture to effectively fuse features for depth estimation while maintaining high inference speed. Experiments on MVSEC and DSEC datasets demonstrate that our contributions are effective and that the accuracy can outperform existing supervised event-based and unsupervised frame-based methods.
Semi-Supervised Learning for Visual Bird's Eye View Semantic Segmentation
Aug 28, 2023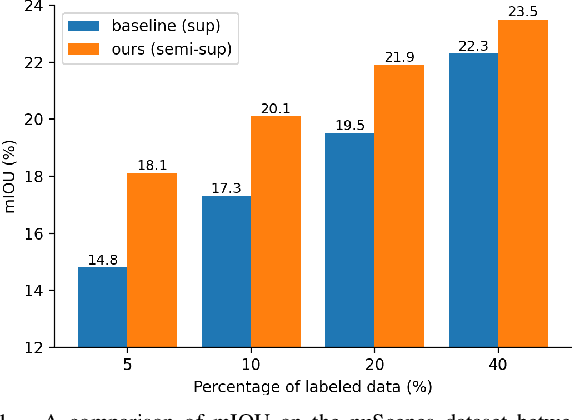
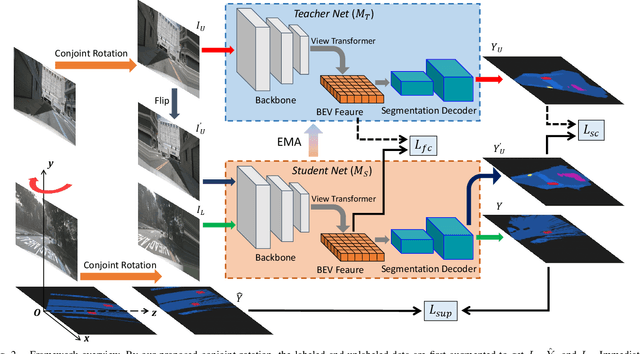
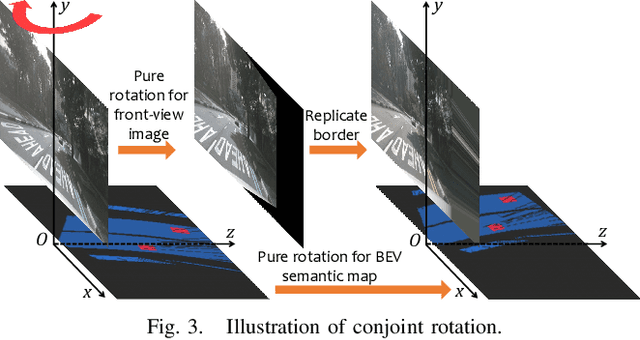
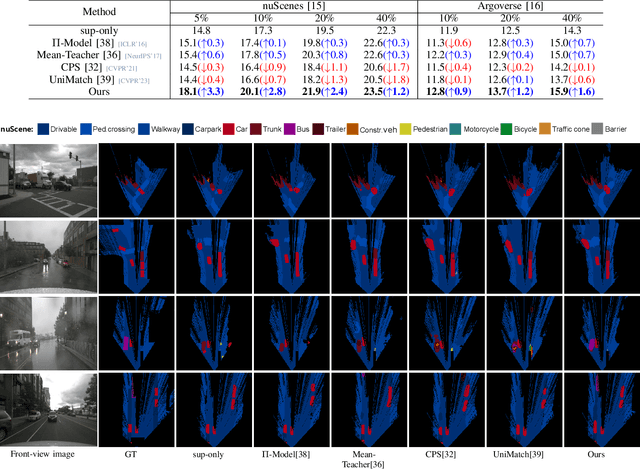
Abstract:Visual bird's eye view (BEV) semantic segmentation helps autonomous vehicles understand the surrounding environment only from images, including static elements (e.g., roads) and dynamic elements (e.g., vehicles, pedestrians). However, the high cost of annotation procedures of full-supervised methods limits the capability of the visual BEV semantic segmentation, which usually needs HD maps, 3D object bounding boxes, and camera extrinsic matrixes. In this paper, we present a novel semi-supervised framework for visual BEV semantic segmentation to boost performance by exploiting unlabeled images during the training. A consistency loss that makes full use of unlabeled data is then proposed to constrain the model on not only semantic prediction but also the BEV feature. Furthermore, we propose a novel and effective data augmentation method named conjoint rotation which reasonably augments the dataset while maintaining the geometric relationship between the front-view images and the BEV semantic segmentation. Extensive experiments on the nuScenes and Argoverse datasets show that our semi-supervised framework can effectively improve prediction accuracy. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work that explores improving visual BEV semantic segmentation performance using unlabeled data. The code will be publicly available.
FG-Depth: Flow-Guided Unsupervised Monocular Depth Estimation
Jan 20, 2023



Abstract:The great potential of unsupervised monocular depth estimation has been demonstrated by many works due to low annotation cost and impressive accuracy comparable to supervised methods. To further improve the performance, recent works mainly focus on designing more complex network structures and exploiting extra supervised information, e.g., semantic segmentation. These methods optimize the models by exploiting the reconstructed relationship between the target and reference images in varying degrees. However, previous methods prove that this image reconstruction optimization is prone to get trapped in local minima. In this paper, our core idea is to guide the optimization with prior knowledge from pretrained Flow-Net. And we show that the bottleneck of unsupervised monocular depth estimation can be broken with our simple but effective framework named FG-Depth. In particular, we propose (i) a flow distillation loss to replace the typical photometric loss that limits the capacity of the model and (ii) a prior flow based mask to remove invalid pixels that bring the noise in training loss. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of each component, and our approach achieves state-of-the-art results on both KITTI and NYU-Depth-v2 datasets.
Semantic Segmentation-assisted Scene Completion for LiDAR Point Clouds
Sep 23, 2021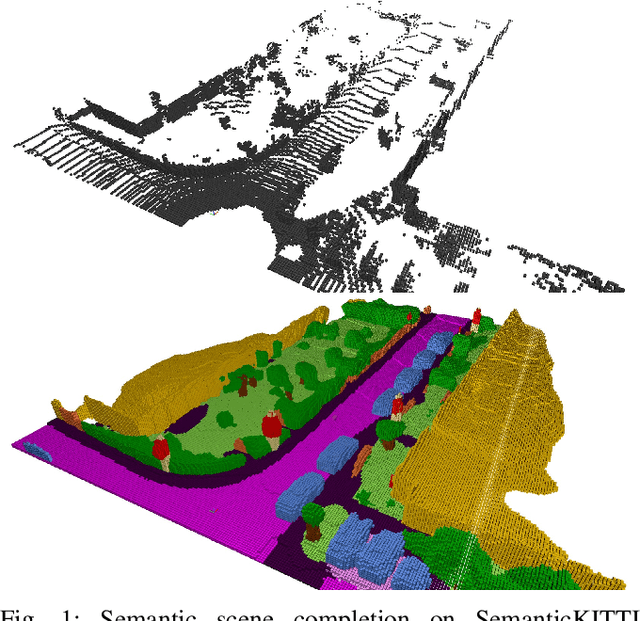
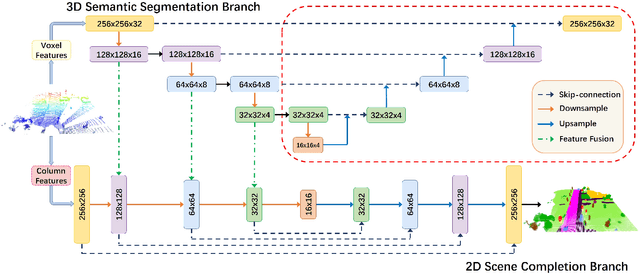
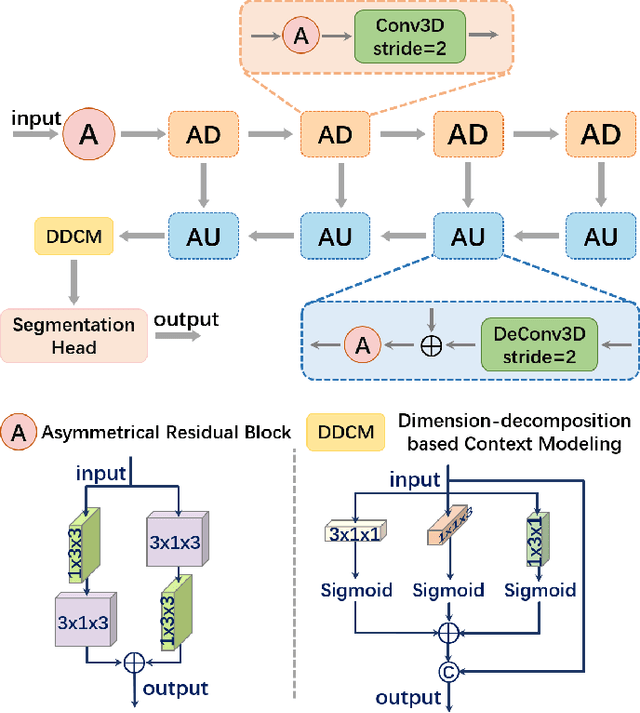
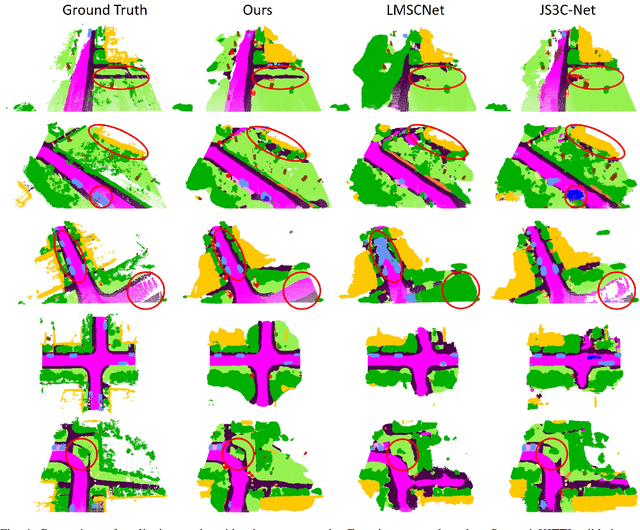
Abstract:Outdoor scene completion is a challenging issue in 3D scene understanding, which plays an important role in intelligent robotics and autonomous driving. Due to the sparsity of LiDAR acquisition, it is far more complex for 3D scene completion and semantic segmentation. Since semantic features can provide constraints and semantic priors for completion tasks, the relationship between them is worth exploring. Therefore, we propose an end-to-end semantic segmentation-assisted scene completion network, including a 2D completion branch and a 3D semantic segmentation branch. Specifically, the network takes a raw point cloud as input, and merges the features from the segmentation branch into the completion branch hierarchically to provide semantic information. By adopting BEV representation and 3D sparse convolution, we can benefit from the lower operand while maintaining effective expression. Besides, the decoder of the segmentation branch is used as an auxiliary, which can be discarded in the inference stage to save computational consumption. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves competitive performance on SemanticKITTI dataset with low latency. Code and models will be released at https://github.com/jokester-zzz/SSA-SC.
SA-LOAM: Semantic-aided LiDAR SLAM with Loop Closure
Jul 01, 2021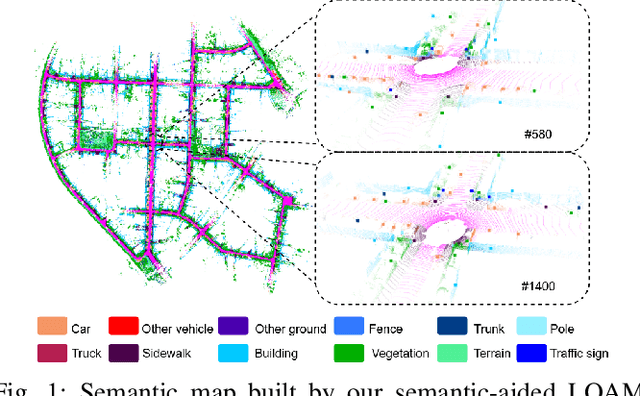
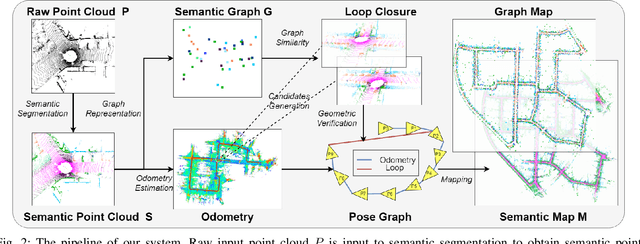
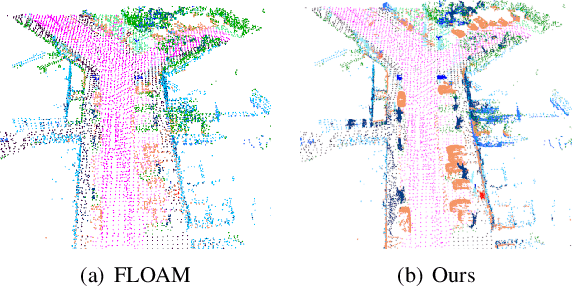
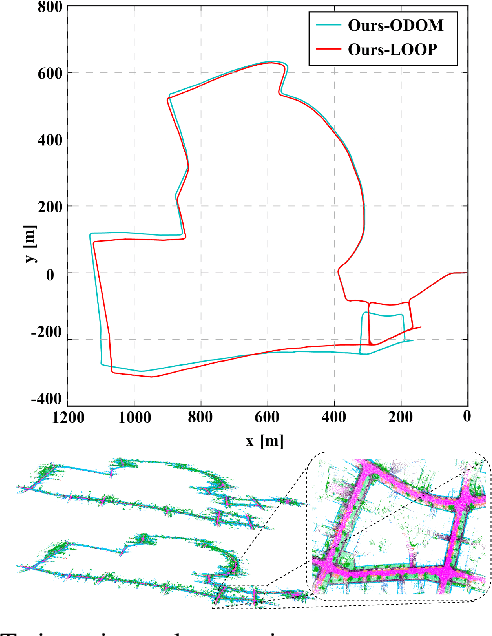
Abstract:LiDAR-based SLAM system is admittedly more accurate and stable than others, while its loop closure detection is still an open issue. With the development of 3D semantic segmentation for point cloud, semantic information can be obtained conveniently and steadily, essential for high-level intelligence and conductive to SLAM. In this paper, we present a novel semantic-aided LiDAR SLAM with loop closure based on LOAM, named SA-LOAM, which leverages semantics in odometry as well as loop closure detection. Specifically, we propose a semantic-assisted ICP, including semantically matching, downsampling and plane constraint, and integrates a semantic graph-based place recognition method in our loop closure detection module. Benefitting from semantics, we can improve the localization accuracy, detect loop closures effectively, and construct a global consistent semantic map even in large-scale scenes. Extensive experiments on KITTI and Ford Campus dataset show that our system significantly improves baseline performance, has generalization ability to unseen data and achieves competitive results compared with state-of-the-art methods.
F-Siamese Tracker: A Frustum-based Double Siamese Network for 3D Single Object Tracking
Oct 22, 2020
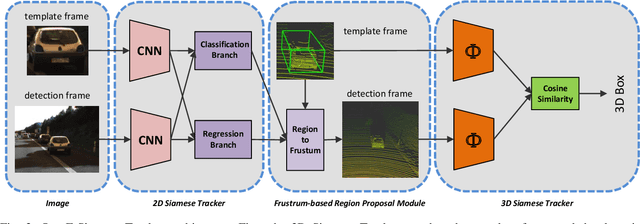
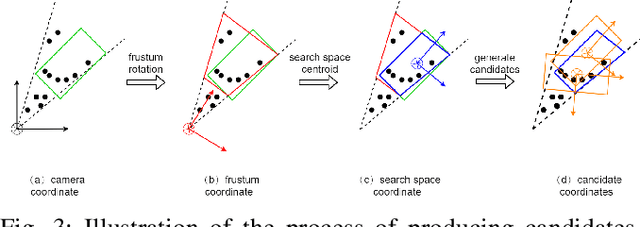

Abstract:This paper presents F-Siamese Tracker, a novel approach for single object tracking prominently characterized by more robustly integrating 2D and 3D information to reduce redundant search space. A main challenge in 3D single object tracking is how to reduce search space for generating appropriate 3D candidates. Instead of solely relying on 3D proposals, firstly, our method leverages the Siamese network applied on RGB images to produce 2D region proposals which are then extruded into 3D viewing frustums. Besides, we perform an online accuracy validation on the 3D frustum to generate refined point cloud searching space, which can be embedded directly into the existing 3D tracking backbone. For efficiency, our approach gains better performance with fewer candidates by reducing search space. In addition, benefited from introducing the online accuracy validation, for occasional cases with strong occlusions or very sparse points, our approach can still achieve high precision, even when the 2D Siamese tracker loses the target. This approach allows us to set a new state-of-the-art in 3D single object tracking by a significant margin on a sparse outdoor dataset (KITTI tracking). Moreover, experiments on 2D single object tracking show that our framework boosts 2D tracking performance as well.
Semantic Graph Based Place Recognition for 3D Point Clouds
Aug 26, 2020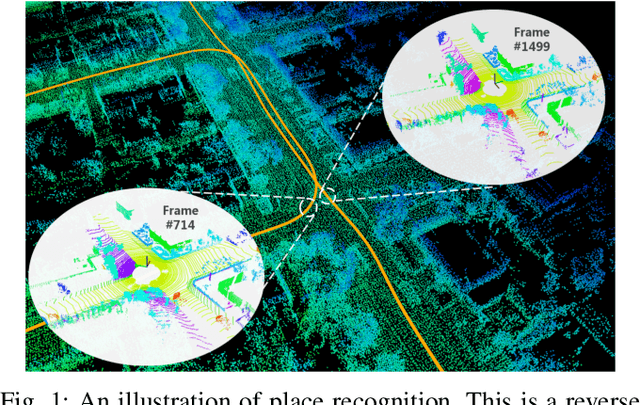
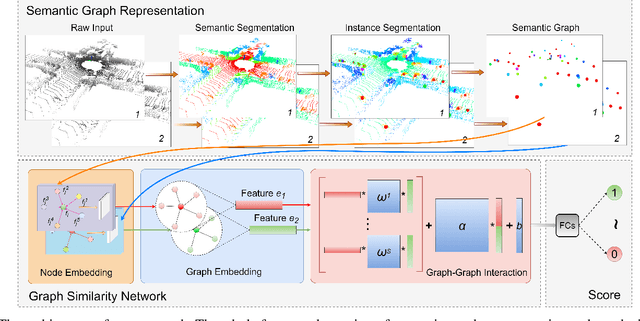
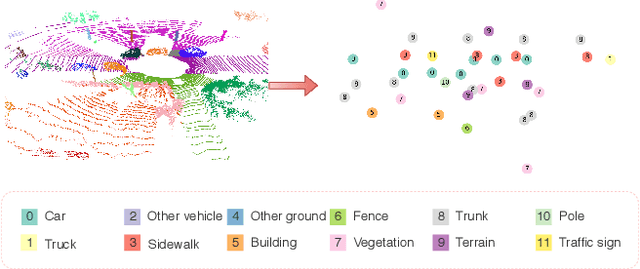
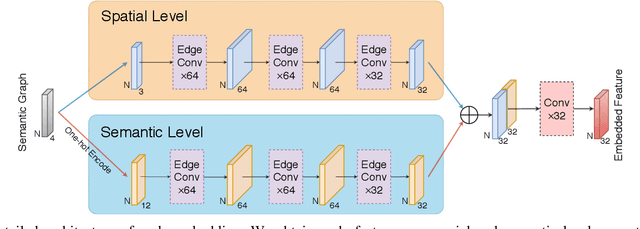
Abstract:Due to the difficulty in generating the effective descriptors which are robust to occlusion and viewpoint changes, place recognition for 3D point cloud remains an open issue. Unlike most of the existing methods that focus on extracting local, global, and statistical features of raw point clouds, our method aims at the semantic level that can be superior in terms of robustness to environmental changes. Inspired by the perspective of humans, who recognize scenes through identifying semantic objects and capturing their relations, this paper presents a novel semantic graph based approach for place recognition. First, we propose a novel semantic graph representation for the point cloud scenes by reserving the semantic and topological information of the raw point cloud. Thus, place recognition is modeled as a graph matching problem. Then we design a fast and effective graph similarity network to compute the similarity. Exhaustive evaluations on the KITTI dataset show that our approach is robust to the occlusion as well as viewpoint changes and outperforms the state-of-the-art methods with a large margin. Our code is available at: \url{https://github.com/kxhit/SG_PR}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge