Mingli Ding
Geo-ConvGRU: Geographically Masked Convolutional Gated Recurrent Unit for Bird-Eye View Segmentation
Dec 28, 2024Abstract:Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have significantly impacted various computer vision tasks, however, they inherently struggle to model long-range dependencies explicitly due to the localized nature of convolution operations. Although Transformers have addressed limitations in long-range dependencies for the spatial dimension, the temporal dimension remains underexplored. In this paper, we first highlight that 3D CNNs exhibit limitations in capturing long-range temporal dependencies. Though Transformers mitigate spatial dimension issues, they result in a considerable increase in parameter and processing speed reduction. To overcome these challenges, we introduce a simple yet effective module, Geographically Masked Convolutional Gated Recurrent Unit (Geo-ConvGRU), tailored for Bird's-Eye View segmentation. Specifically, we substitute the 3D CNN layers with ConvGRU in the temporal module to bolster the capacity of networks for handling temporal dependencies. Additionally, we integrate a geographical mask into the Convolutional Gated Recurrent Unit to suppress noise introduced by the temporal module. Comprehensive experiments conducted on the NuScenes dataset substantiate the merits of the proposed Geo-ConvGRU, revealing that our approach attains state-of-the-art performance in Bird's-Eye View segmentation.
Boosting Long-tailed Object Detection via Step-wise Learning on Smooth-tail Data
May 22, 2023


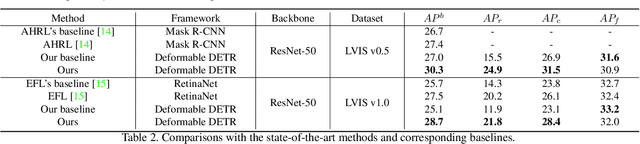
Abstract:Real-world data tends to follow a long-tailed distribution, where the class imbalance results in dominance of the head classes during training. In this paper, we propose a frustratingly simple but effective step-wise learning framework to gradually enhance the capability of the model in detecting all categories of long-tailed datasets. Specifically, we build smooth-tail data where the long-tailed distribution of categories decays smoothly to correct the bias towards head classes. We pre-train a model on the whole long-tailed data to preserve discriminability between all categories. We then fine-tune the class-agnostic modules of the pre-trained model on the head class dominant replay data to get a head class expert model with improved decision boundaries from all categories. Finally, we train a unified model on the tail class dominant replay data while transferring knowledge from the head class expert model to ensure accurate detection of all categories. Extensive experiments on long-tailed datasets LVIS v0.5 and LVIS v1.0 demonstrate the superior performance of our method, where we can improve the AP with ResNet-50 backbone from 27.0% to 30.3% AP, and especially for the rare categories from 15.5% to 24.9% AP. Our best model using ResNet-101 backbone can achieve 30.7% AP, which suppresses all existing detectors using the same backbone.
Open World DETR: Transformer based Open World Object Detection
Dec 06, 2022


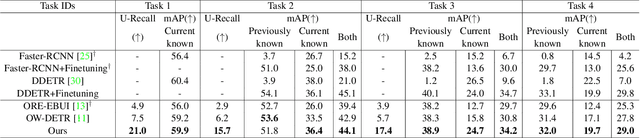
Abstract:Open world object detection aims at detecting objects that are absent in the object classes of the training data as unknown objects without explicit supervision. Furthermore, the exact classes of the unknown objects must be identified without catastrophic forgetting of the previous known classes when the corresponding annotations of unknown objects are given incrementally. In this paper, we propose a two-stage training approach named Open World DETR for open world object detection based on Deformable DETR. In the first stage, we pre-train a model on the current annotated data to detect objects from the current known classes, and concurrently train an additional binary classifier to classify predictions into foreground or background classes. This helps the model to build an unbiased feature representations that can facilitate the detection of unknown classes in subsequent process. In the second stage, we fine-tune the class-specific components of the model with a multi-view self-labeling strategy and a consistency constraint. Furthermore, we alleviate catastrophic forgetting when the annotations of the unknown classes becomes available incrementally by using knowledge distillation and exemplar replay. Experimental results on PASCAL VOC and MS-COCO show that our proposed method outperforms other state-of-the-art open world object detection methods by a large margin.
Incremental-DETR: Incremental Few-Shot Object Detection via Self-Supervised Learning
May 19, 2022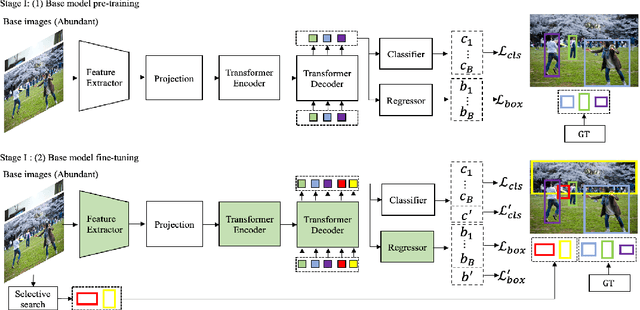
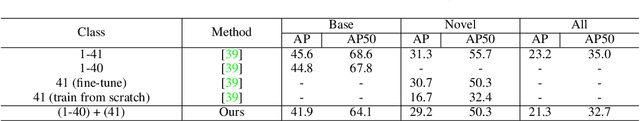
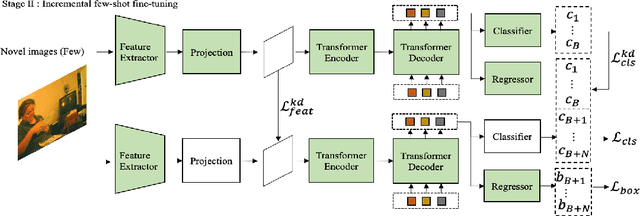
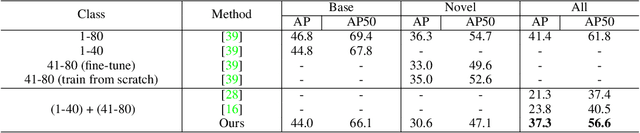
Abstract:Incremental few-shot object detection aims at detecting novel classes without forgetting knowledge of the base classes with only a few labeled training data from the novel classes. Most related prior works are on incremental object detection that rely on the availability of abundant training samples per novel class that substantially limits the scalability to real-world setting where novel data can be scarce. In this paper, we propose the Incremental-DETR that does incremental few-shot object detection via fine-tuning and self-supervised learning on the DETR object detector. To alleviate severe over-fitting with few novel class data, we first fine-tune the class-specific components of DETR with self-supervision from additional object proposals generated using Selective Search as pseudo labels. We further introduce a incremental few-shot fine-tuning strategy with knowledge distillation on the class-specific components of DETR to encourage the network in detecting novel classes without catastrophic forgetting. Extensive experiments conducted on standard incremental object detection and incremental few-shot object detection settings show that our approach significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods by a large margin.
Uncertainty-aware Contrastive Distillation for Incremental Semantic Segmentation
Mar 26, 2022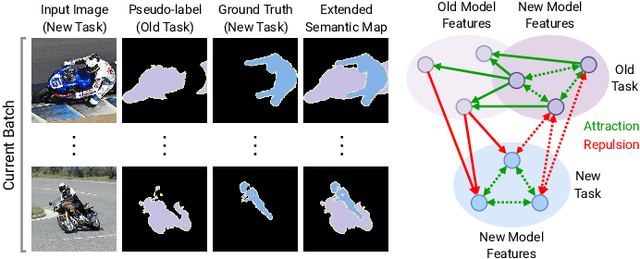

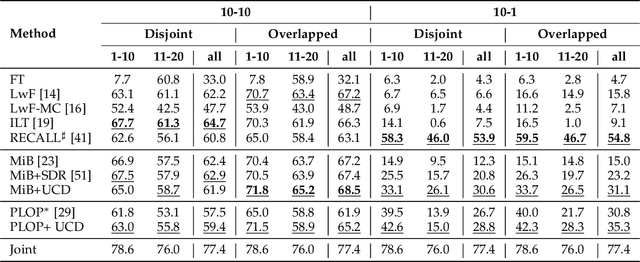
Abstract:A fundamental and challenging problem in deep learning is catastrophic forgetting, i.e. the tendency of neural networks to fail to preserve the knowledge acquired from old tasks when learning new tasks. This problem has been widely investigated in the research community and several Incremental Learning (IL) approaches have been proposed in the past years. While earlier works in computer vision have mostly focused on image classification and object detection, more recently some IL approaches for semantic segmentation have been introduced. These previous works showed that, despite its simplicity, knowledge distillation can be effectively employed to alleviate catastrophic forgetting. In this paper, we follow this research direction and, inspired by recent literature on contrastive learning, we propose a novel distillation framework, Uncertainty-aware Contrastive Distillation (\method). In a nutshell, \method~is operated by introducing a novel distillation loss that takes into account all the images in a mini-batch, enforcing similarity between features associated to all the pixels from the same classes, and pulling apart those corresponding to pixels from different classes. In order to mitigate catastrophic forgetting, we contrast features of the new model with features extracted by a frozen model learned at the previous incremental step. Our experimental results demonstrate the advantage of the proposed distillation technique, which can be used in synergy with previous IL approaches, and leads to state-of-art performance on three commonly adopted benchmarks for incremental semantic segmentation. The code is available at \url{https://github.com/ygjwd12345/UCD}.
Continual Attentive Fusion for Incremental Learning in Semantic Segmentation
Feb 01, 2022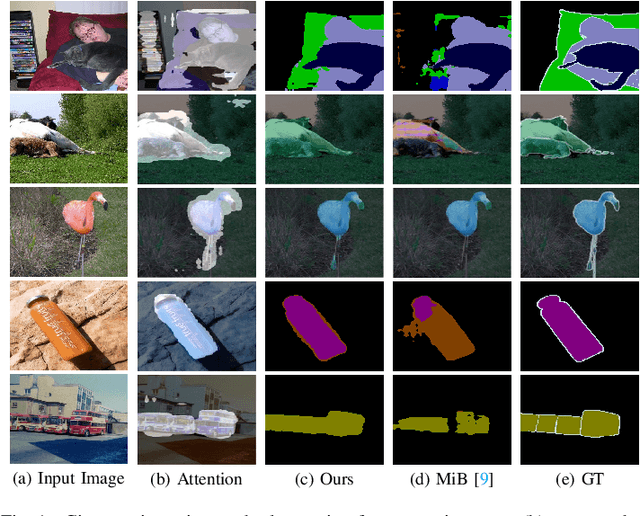


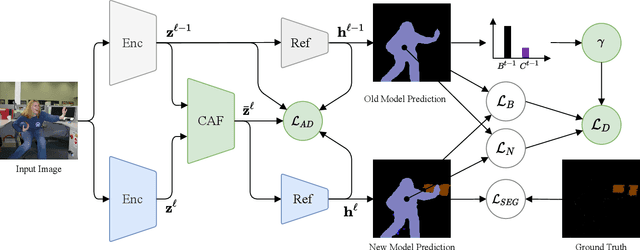
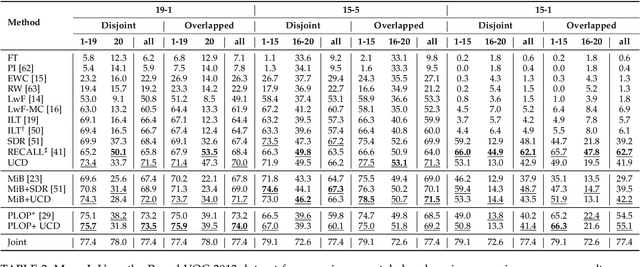
Abstract:Over the past years, semantic segmentation, as many other tasks in computer vision, benefited from the progress in deep neural networks, resulting in significantly improved performance. However, deep architectures trained with gradient-based techniques suffer from catastrophic forgetting, which is the tendency to forget previously learned knowledge while learning new tasks. Aiming at devising strategies to counteract this effect, incremental learning approaches have gained popularity over the past years. However, the first incremental learning methods for semantic segmentation appeared only recently. While effective, these approaches do not account for a crucial aspect in pixel-level dense prediction problems, i.e. the role of attention mechanisms. To fill this gap, in this paper we introduce a novel attentive feature distillation approach to mitigate catastrophic forgetting while accounting for semantic spatial- and channel-level dependencies. Furthermore, we propose a {continual attentive fusion} structure, which takes advantage of the attention learned from the new and the old tasks while learning features for the new task. Finally, we also introduce a novel strategy to account for the background class in the distillation loss, thus preventing biased predictions. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach with an extensive evaluation on Pascal-VOC 2012 and ADE20K, setting a new state of the art.
Global and Local Alignment Networks for Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation
Nov 19, 2021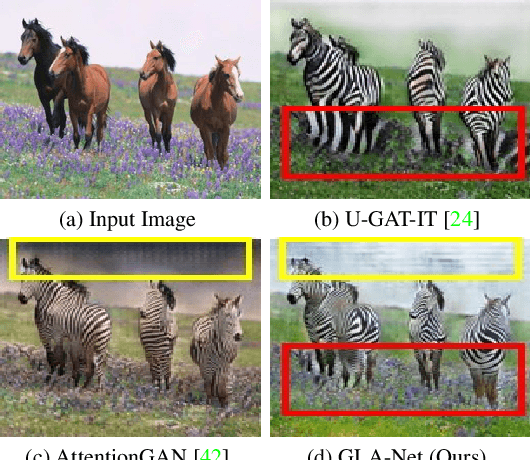
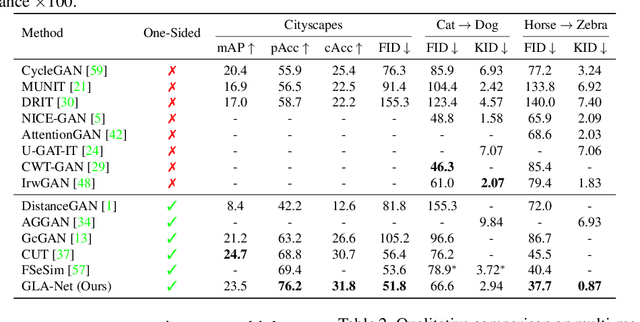
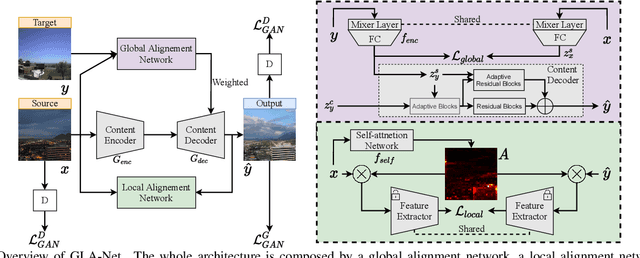
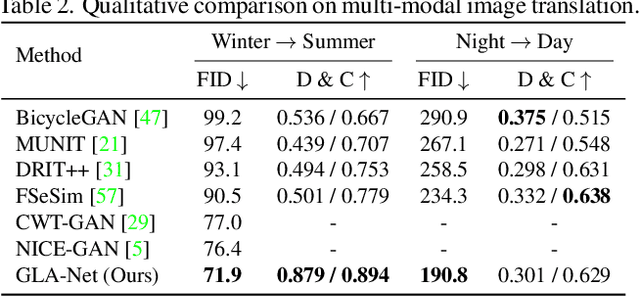
Abstract:The goal of unpaired image-to-image translation is to produce an output image reflecting the target domain's style while keeping unrelated contents of the input source image unchanged. However, due to the lack of attention to the content change in existing methods, the semantic information from source images suffers from degradation during translation. In the paper, to address this issue, we introduce a novel approach, Global and Local Alignment Networks (GLA-Net). The global alignment network aims to transfer the input image from the source domain to the target domain. To effectively do so, we learn the parameters (mean and standard deviation) of multivariate Gaussian distributions as style features by using an MLP-Mixer based style encoder. To transfer the style more accurately, we employ an adaptive instance normalization layer in the encoder, with the parameters of the target multivariate Gaussian distribution as input. We also adopt regularization and likelihood losses to further reduce the domain gap and produce high-quality outputs. Additionally, we introduce a local alignment network, which employs a pretrained self-supervised model to produce an attention map via a novel local alignment loss, ensuring that the translation network focuses on relevant pixels. Extensive experiments conducted on five public datasets demonstrate that our method effectively generates sharper and more realistic images than existing approaches. Our code is available at https://github.com/ygjwd12345/GLANet.
Bi-Mix: Bidirectional Mixing for Domain Adaptive Nighttime Semantic Segmentation
Nov 19, 2021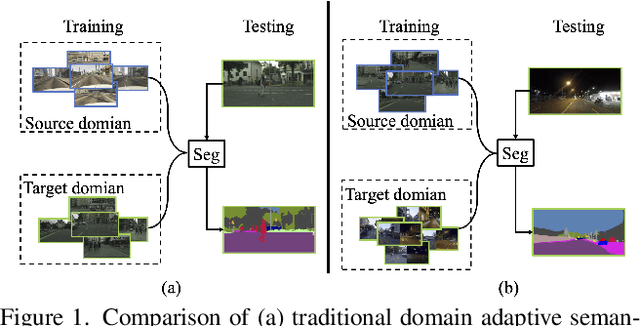
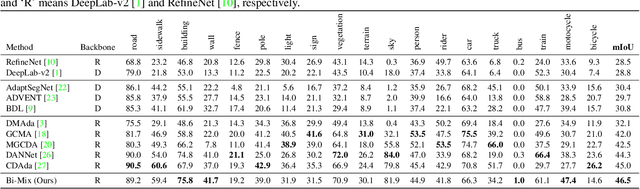
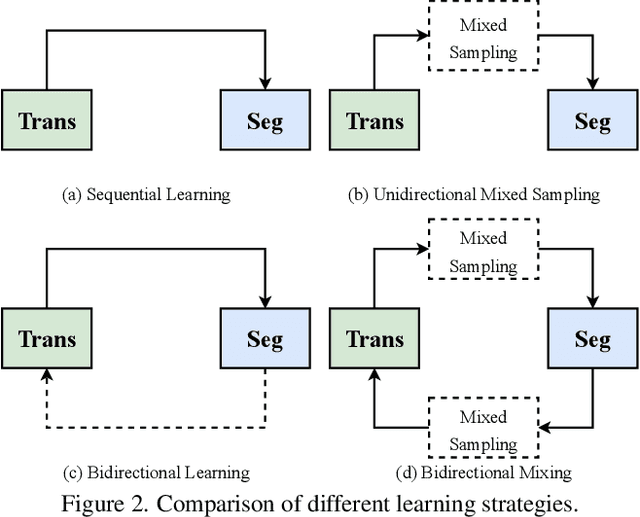
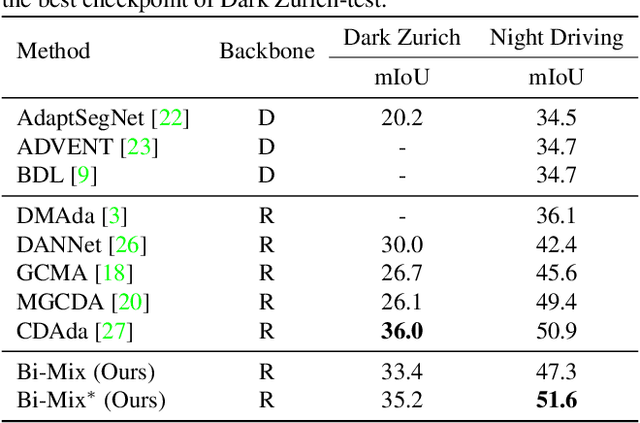
Abstract:In autonomous driving, learning a segmentation model that can adapt to various environmental conditions is crucial. In particular, copying with severe illumination changes is an impelling need, as models trained on daylight data will perform poorly at nighttime. In this paper, we study the problem of Domain Adaptive Nighttime Semantic Segmentation (DANSS), which aims to learn a discriminative nighttime model with a labeled daytime dataset and an unlabeled dataset, including coarsely aligned day-night image pairs. To this end, we propose a novel Bidirectional Mixing (Bi-Mix) framework for DANSS, which can contribute to both image translation and segmentation adaptation processes. Specifically, in the image translation stage, Bi-Mix leverages the knowledge of day-night image pairs to improve the quality of nighttime image relighting. On the other hand, in the segmentation adaptation stage, Bi-Mix effectively bridges the distribution gap between day and night domains for adapting the model to the night domain. In both processes, Bi-Mix simply operates by mixing two samples without extra hyper-parameters, thus it is easy to implement. Extensive experiments on Dark Zurich and Nighttime Driving datasets demonstrate the advantage of the proposed Bi-Mix and show that our approach obtains state-of-the-art performance in DANSS. Our code is available at https://github.com/ygjwd12345/BiMix.
Bridging Non Co-occurrence with Unlabeled In-the-wild Data for Incremental Object Detection
Oct 28, 2021
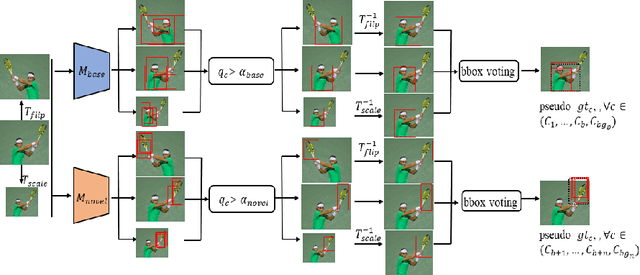
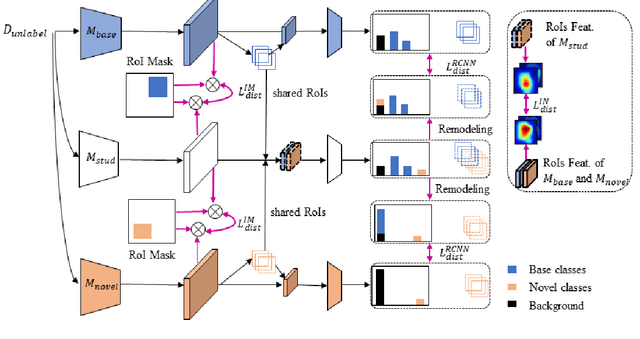
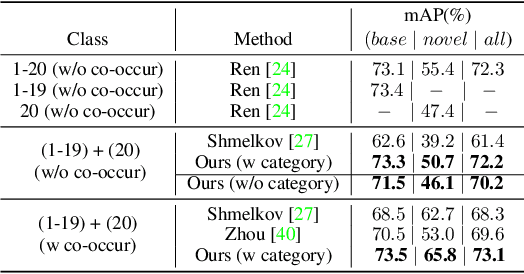
Abstract:Deep networks have shown remarkable results in the task of object detection. However, their performance suffers critical drops when they are subsequently trained on novel classes without any sample from the base classes originally used to train the model. This phenomenon is known as catastrophic forgetting. Recently, several incremental learning methods are proposed to mitigate catastrophic forgetting for object detection. Despite the effectiveness, these methods require co-occurrence of the unlabeled base classes in the training data of the novel classes. This requirement is impractical in many real-world settings since the base classes do not necessarily co-occur with the novel classes. In view of this limitation, we consider a more practical setting of complete absence of co-occurrence of the base and novel classes for the object detection task. We propose the use of unlabeled in-the-wild data to bridge the non co-occurrence caused by the missing base classes during the training of additional novel classes. To this end, we introduce a blind sampling strategy based on the responses of the base-class model and pre-trained novel-class model to select a smaller relevant dataset from the large in-the-wild dataset for incremental learning. We then design a dual-teacher distillation framework to transfer the knowledge distilled from the base- and novel-class teacher models to the student model using the sampled in-the-wild data. Experimental results on the PASCAL VOC and MS COCO datasets show that our proposed method significantly outperforms other state-of-the-art class-incremental object detection methods when there is no co-occurrence between the base and novel classes during training.
Transformer-Based Source-Free Domain Adaptation
May 28, 2021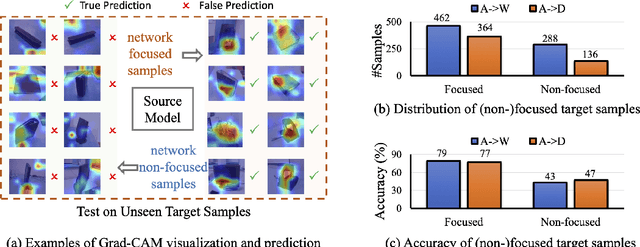
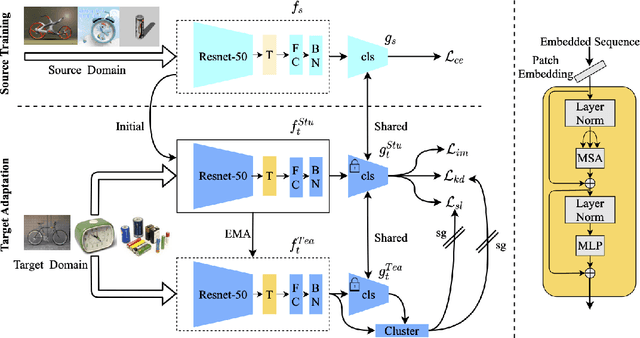
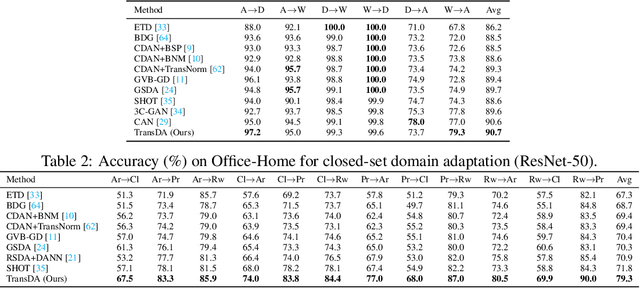
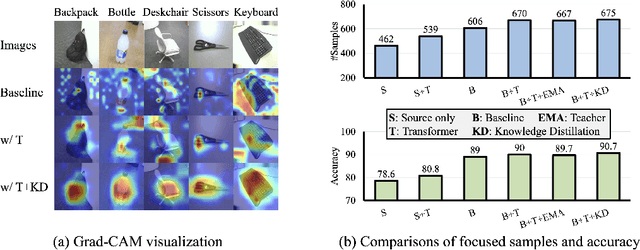
Abstract:In this paper, we study the task of source-free domain adaptation (SFDA), where the source data are not available during target adaptation. Previous works on SFDA mainly focus on aligning the cross-domain distributions. However, they ignore the generalization ability of the pretrained source model, which largely influences the initial target outputs that are vital to the target adaptation stage. To address this, we make the interesting observation that the model accuracy is highly correlated with whether or not attention is focused on the objects in an image. To this end, we propose a generic and effective framework based on Transformer, named TransDA, for learning a generalized model for SFDA. Specifically, we apply the Transformer as the attention module and inject it into a convolutional network. By doing so, the model is encouraged to turn attention towards the object regions, which can effectively improve the model's generalization ability on the target domains. Moreover, a novel self-supervised knowledge distillation approach is proposed to adapt the Transformer with target pseudo-labels, thus further encouraging the network to focus on the object regions. Experiments on three domain adaptation tasks, including closed-set, partial-set, and open-set adaption, demonstrate that TransDA can greatly improve the adaptation accuracy and produce state-of-the-art results. The source code and trained models are available at https://github.com/ygjwd12345/TransDA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge