Elisa Ricci
Linear Model Merging Unlocks Simple and Scalable Multimodal Data Mixture Optimization
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Selecting the best data mixture is critical for successful Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) of Multimodal Large Language Models. However, determining the optimal mixture weights across multiple domain-specific datasets remains a significant bottleneck due to the combinatorial search space and the high cost associated with even a single training run. This is the so-called Data Mixture Optimization (DMO) problem. On the other hand, model merging unifies domain-specific experts through parameter interpolation. This strategy is efficient, as it only requires a single training run per domain, yet oftentimes leads to suboptimal models. In this work, we take the best of both worlds, studying model merging as an efficient strategy for estimating the performance of different data mixtures. We train domain-specific multimodal experts and evaluate their weighted parameter-space combinations to estimate the efficacy of corresponding data mixtures. We conduct extensive experiments on 14 multimodal benchmarks, and empirically demonstrate that the merged proxy models exhibit a high rank correlation with models trained on actual data mixtures. This decouples the search for optimal mixtures from the resource-intensive training process, thereby providing a scalable and efficient strategy for navigating the complex landscape of mixture weights. Code is publicly available at https://github.com/BerasiDavide/mLLMs_merging_4_DMO.
LT-Soups: Bridging Head and Tail Classes via Subsampled Model Soups
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:Real-world datasets typically exhibit long-tailed (LT) distributions, where a few head classes dominate and many tail classes are severely underrepresented. While recent work shows that parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods like LoRA and AdaptFormer preserve tail-class performance on foundation models such as CLIP, we find that they do so at the cost of head-class accuracy. We identify the head-tail ratio, the proportion of head to tail classes, as a crucial but overlooked factor influencing this trade-off. Through controlled experiments on CIFAR100 with varying imbalance ratio ($ρ$) and head-tail ratio ($η$), we show that PEFT excels in tail-heavy scenarios but degrades in more balanced and head-heavy distributions. To overcome these limitations, we propose LT-Soups, a two-stage model soups framework designed to generalize across diverse LT regimes. In the first stage, LT-Soups averages models fine-tuned on balanced subsets to reduce head-class bias; in the second, it fine-tunes only the classifier on the full dataset to restore head-class accuracy. Experiments across six benchmark datasets show that LT-Soups achieves superior trade-offs compared to both PEFT and traditional model soups across a wide range of imbalance regimes.
Dynamic Scoring with Enhanced Semantics for Training-Free Human-Object Interaction Detection
Jul 23, 2025



Abstract:Human-Object Interaction (HOI) detection aims to identify humans and objects within images and interpret their interactions. Existing HOI methods rely heavily on large datasets with manual annotations to learn interactions from visual cues. These annotations are labor-intensive to create, prone to inconsistency, and limit scalability to new domains and rare interactions. We argue that recent advances in Vision-Language Models (VLMs) offer untapped potential, particularly in enhancing interaction representation. While prior work has injected such potential and even proposed training-free methods, there remain key gaps. Consequently, we propose a novel training-free HOI detection framework for Dynamic Scoring with enhanced semantics (DYSCO) that effectively utilizes textual and visual interaction representations within a multimodal registry, enabling robust and nuanced interaction understanding. This registry incorporates a small set of visual cues and uses innovative interaction signatures to improve the semantic alignment of verbs, facilitating effective generalization to rare interactions. Additionally, we propose a unique multi-head attention mechanism that adaptively weights the contributions of the visual and textual features. Experimental results demonstrate that our DYSCO surpasses training-free state-of-the-art models and is competitive with training-based approaches, particularly excelling in rare interactions. Code is available at https://github.com/francescotonini/dysco.
MAMBO: High-Resolution Generative Approach for Mammography Images
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Mammography is the gold standard for the detection and diagnosis of breast cancer. This procedure can be significantly enhanced with Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based software, which assists radiologists in identifying abnormalities. However, training AI systems requires large and diverse datasets, which are often difficult to obtain due to privacy and ethical constraints. To address this issue, the paper introduces MAMmography ensemBle mOdel (MAMBO), a novel patch-based diffusion approach designed to generate full-resolution mammograms. Diffusion models have shown breakthrough results in realistic image generation, yet few studies have focused on mammograms, and none have successfully generated high-resolution outputs required to capture fine-grained features of small lesions. To achieve this, MAMBO integrates separate diffusion models to capture both local and global (image-level) contexts. The contextual information is then fed into the final patch-based model, significantly aiding the noise removal process. This thoughtful design enables MAMBO to generate highly realistic mammograms of up to 3840x3840 pixels. Importantly, this approach can be used to enhance the training of classification models and extended to anomaly detection. Experiments, both numerical and radiologist validation, assess MAMBO's capabilities in image generation, super-resolution, and anomaly detection, highlighting its potential to enhance mammography analysis for more accurate diagnoses and earlier lesion detection.
FedMVP: Federated Multi-modal Visual Prompt Tuning for Vision-Language Models
Apr 29, 2025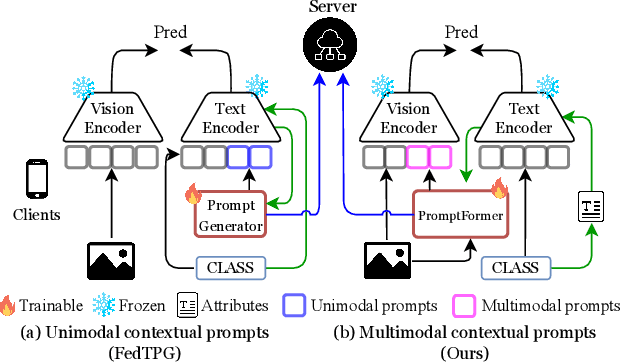
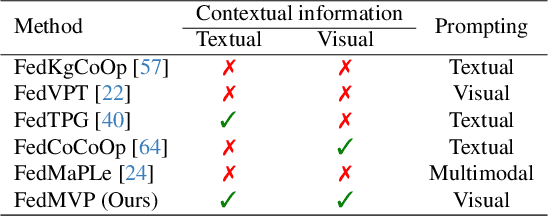
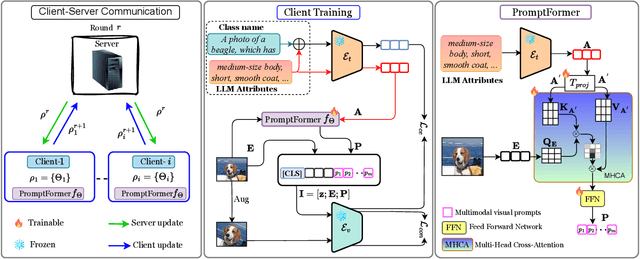
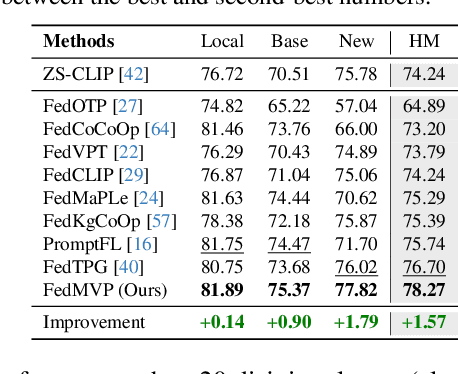
Abstract:Textual prompt tuning adapts Vision-Language Models (e.g., CLIP) in federated learning by tuning lightweight input tokens (or prompts) on local client data, while keeping network weights frozen. Post training, only the prompts are shared by the clients with the central server for aggregation. However, textual prompt tuning often struggles with overfitting to known concepts and may be overly reliant on memorized text features, limiting its adaptability to unseen concepts. To address this limitation, we propose Federated Multimodal Visual Prompt Tuning (FedMVP) that conditions the prompts on comprehensive contextual information -- image-conditioned features and textual attribute features of a class -- that is multimodal in nature. At the core of FedMVP is a PromptFormer module that synergistically aligns textual and visual features through cross-attention, enabling richer contexual integration. The dynamically generated multimodal visual prompts are then input to the frozen vision encoder of CLIP, and trained with a combination of CLIP similarity loss and a consistency loss. Extensive evaluation on 20 datasets spanning three generalization settings demonstrates that FedMVP not only preserves performance on in-distribution classes and domains, but also displays higher generalizability to unseen classes and domains when compared to state-of-the-art methods. Codes will be released upon acceptance.
Classifier-to-Bias: Toward Unsupervised Automatic Bias Detection for Visual Classifiers
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:A person downloading a pre-trained model from the web should be aware of its biases. Existing approaches for bias identification rely on datasets containing labels for the task of interest, something that a non-expert may not have access to, or may not have the necessary resources to collect: this greatly limits the number of tasks where model biases can be identified. In this work, we present Classifier-to-Bias (C2B), the first bias discovery framework that works without access to any labeled data: it only relies on a textual description of the classification task to identify biases in the target classification model. This description is fed to a large language model to generate bias proposals and corresponding captions depicting biases together with task-specific target labels. A retrieval model collects images for those captions, which are then used to assess the accuracy of the model w.r.t. the given biases. C2B is training-free, does not require any annotations, has no constraints on the list of biases, and can be applied to any pre-trained model on any classification task. Experiments on two publicly available datasets show that C2B discovers biases beyond those of the original datasets and outperforms a recent state-of-the-art bias detection baseline that relies on task-specific annotations, being a promising first step toward addressing task-agnostic unsupervised bias detection.
On Large Multimodal Models as Open-World Image Classifiers
Mar 27, 2025



Abstract:Traditional image classification requires a predefined list of semantic categories. In contrast, Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) can sidestep this requirement by classifying images directly using natural language (e.g., answering the prompt "What is the main object in the image?"). Despite this remarkable capability, most existing studies on LMM classification performance are surprisingly limited in scope, often assuming a closed-world setting with a predefined set of categories. In this work, we address this gap by thoroughly evaluating LMM classification performance in a truly open-world setting. We first formalize the task and introduce an evaluation protocol, defining various metrics to assess the alignment between predicted and ground truth classes. We then evaluate 13 models across 10 benchmarks, encompassing prototypical, non-prototypical, fine-grained, and very fine-grained classes, demonstrating the challenges LMMs face in this task. Further analyses based on the proposed metrics reveal the types of errors LMMs make, highlighting challenges related to granularity and fine-grained capabilities, showing how tailored prompting and reasoning can alleviate them.
Compositional Caching for Training-free Open-vocabulary Attribute Detection
Mar 24, 2025Abstract:Attribute detection is crucial for many computer vision tasks, as it enables systems to describe properties such as color, texture, and material. Current approaches often rely on labor-intensive annotation processes which are inherently limited: objects can be described at an arbitrary level of detail (e.g., color vs. color shades), leading to ambiguities when the annotators are not instructed carefully. Furthermore, they operate within a predefined set of attributes, reducing scalability and adaptability to unforeseen downstream applications. We present Compositional Caching (ComCa), a training-free method for open-vocabulary attribute detection that overcomes these constraints. ComCa requires only the list of target attributes and objects as input, using them to populate an auxiliary cache of images by leveraging web-scale databases and Large Language Models to determine attribute-object compatibility. To account for the compositional nature of attributes, cache images receive soft attribute labels. Those are aggregated at inference time based on the similarity between the input and cache images, refining the predictions of underlying Vision-Language Models (VLMs). Importantly, our approach is model-agnostic, compatible with various VLMs. Experiments on public datasets demonstrate that ComCa significantly outperforms zero-shot and cache-based baselines, competing with recent training-based methods, proving that a carefully designed training-free approach can successfully address open-vocabulary attribute detection.
Training-Free Personalization via Retrieval and Reasoning on Fingerprints
Mar 24, 2025



Abstract:Vision Language Models (VLMs) have lead to major improvements in multimodal reasoning, yet they still struggle to understand user-specific concepts. Existing personalization methods address this limitation but heavily rely on training procedures, that can be either costly or unpleasant to individual users. We depart from existing work, and for the first time explore the training-free setting in the context of personalization. We propose a novel method, Retrieval and Reasoning for Personalization (R2P), leveraging internal knowledge of VLMs. First, we leverage VLMs to extract the concept fingerprint, i.e., key attributes uniquely defining the concept within its semantic class. When a query arrives, the most similar fingerprints are retrieved and scored via chain-of-thought-reasoning. To reduce the risk of hallucinations, the scores are validated through cross-modal verification at the attribute level: in case of a discrepancy between the scores, R2P refines the concept association via pairwise multimodal matching, where the retrieved fingerprints and their images are directly compared with the query. We validate R2P on two publicly available benchmarks and a newly introduced dataset, Personal Concepts with Visual Ambiguity (PerVA), for concept identification highlighting challenges in visual ambiguity. R2P consistently outperforms state-of-the-art approaches on various downstream tasks across all benchmarks. Code will be available upon acceptance.
Not Only Text: Exploring Compositionality of Visual Representations in Vision-Language Models
Mar 21, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) learn a shared feature space for text and images, enabling the comparison of inputs of different modalities. While prior works demonstrated that VLMs organize natural language representations into regular structures encoding composite meanings, it remains unclear if compositional patterns also emerge in the visual embedding space. In this work, we investigate compositionality in the image domain, where the analysis of compositional properties is challenged by noise and sparsity of visual data. We address these problems and propose a framework, called Geodesically Decomposable Embeddings (GDE), that approximates image representations with geometry-aware compositional structures in the latent space. We demonstrate that visual embeddings of pre-trained VLMs exhibit a compositional arrangement, and evaluate the effectiveness of this property in the tasks of compositional classification and group robustness. GDE achieves stronger performance in compositional classification compared to its counterpart method that assumes linear geometry of the latent space. Notably, it is particularly effective for group robustness, where we achieve higher results than task-specific solutions. Our results indicate that VLMs can automatically develop a human-like form of compositional reasoning in the visual domain, making their underlying processes more interpretable. Code is available at https://github.com/BerasiDavide/vlm_image_compositionality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge