Moloud Abdar
Debiasing CLIP: Interpreting and Correcting Bias in Attention Heads
May 23, 2025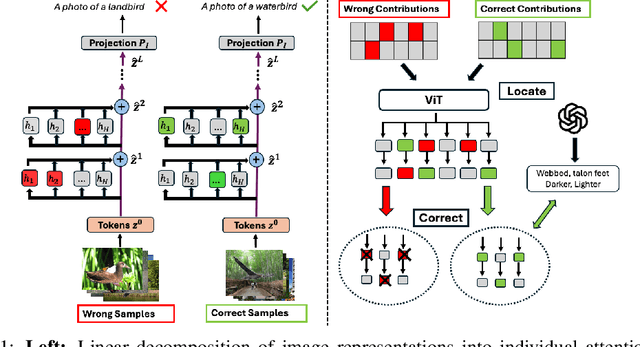
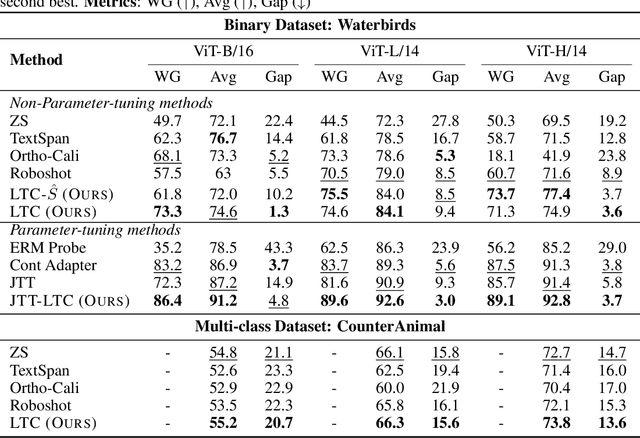
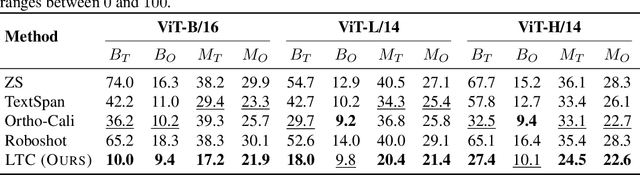
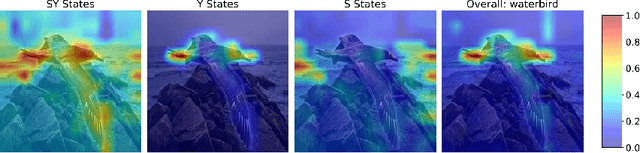
Abstract:Multimodal models like CLIP have gained significant attention due to their remarkable zero-shot performance across various tasks. However, studies have revealed that CLIP can inadvertently learn spurious associations between target variables and confounding factors. To address this, we introduce \textsc{Locate-Then-Correct} (LTC), a contrastive framework that identifies spurious attention heads in Vision Transformers via mechanistic insights and mitigates them through targeted ablation. Furthermore, LTC identifies salient, task-relevant attention heads, enabling the integration of discriminative features through orthogonal projection to improve classification performance. We evaluate LTC on benchmarks with inherent background and gender biases, achieving over a $>50\%$ gain in worst-group accuracy compared to non-training post-hoc baselines. Additionally, we visualize the representation of selected heads and find that the presented interpretation corroborates our contrastive mechanism for identifying both spurious and salient attention heads. Code available at https://github.com/wj210/CLIP_LTC.
ATR-Bench: A Federated Learning Benchmark for Adaptation, Trust, and Reasoning
May 22, 2025Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) has emerged as a promising paradigm for collaborative model training while preserving data privacy across decentralized participants. As FL adoption grows, numerous techniques have been proposed to tackle its practical challenges. However, the lack of standardized evaluation across key dimensions hampers systematic progress and fair comparison of FL methods. In this work, we introduce ATR-Bench, a unified framework for analyzing federated learning through three foundational dimensions: Adaptation, Trust, and Reasoning. We provide an in-depth examination of the conceptual foundations, task formulations, and open research challenges associated with each theme. We have extensively benchmarked representative methods and datasets for adaptation to heterogeneous clients and trustworthiness in adversarial or unreliable environments. Due to the lack of reliable metrics and models for reasoning in FL, we only provide literature-driven insights for this dimension. ATR-Bench lays the groundwork for a systematic and holistic evaluation of federated learning with real-world relevance. We will make our complete codebase publicly accessible and a curated repository that continuously tracks new developments and research in the FL literature.
FedMVP: Federated Multi-modal Visual Prompt Tuning for Vision-Language Models
Apr 29, 2025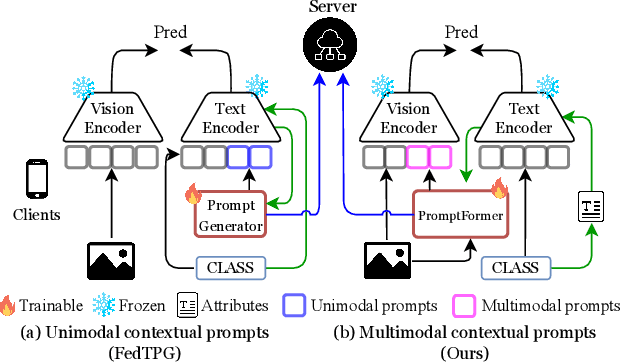
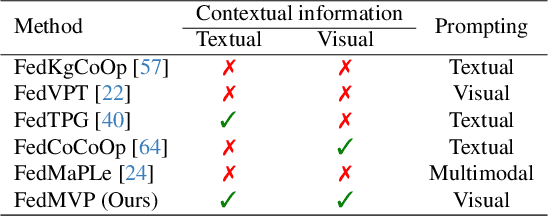
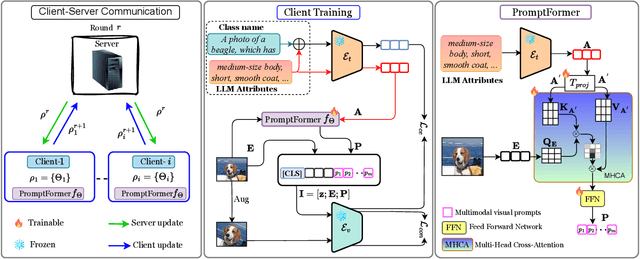
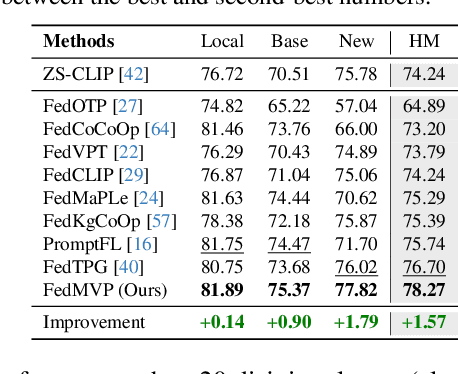
Abstract:Textual prompt tuning adapts Vision-Language Models (e.g., CLIP) in federated learning by tuning lightweight input tokens (or prompts) on local client data, while keeping network weights frozen. Post training, only the prompts are shared by the clients with the central server for aggregation. However, textual prompt tuning often struggles with overfitting to known concepts and may be overly reliant on memorized text features, limiting its adaptability to unseen concepts. To address this limitation, we propose Federated Multimodal Visual Prompt Tuning (FedMVP) that conditions the prompts on comprehensive contextual information -- image-conditioned features and textual attribute features of a class -- that is multimodal in nature. At the core of FedMVP is a PromptFormer module that synergistically aligns textual and visual features through cross-attention, enabling richer contexual integration. The dynamically generated multimodal visual prompts are then input to the frozen vision encoder of CLIP, and trained with a combination of CLIP similarity loss and a consistency loss. Extensive evaluation on 20 datasets spanning three generalization settings demonstrates that FedMVP not only preserves performance on in-distribution classes and domains, but also displays higher generalizability to unseen classes and domains when compared to state-of-the-art methods. Codes will be released upon acceptance.
Enhance Hyperbolic Representation Learning via Second-order Pooling
Oct 29, 2024



Abstract:Hyperbolic representation learning is well known for its ability to capture hierarchical information. However, the distance between samples from different levels of hierarchical classes can be required large. We reveal that the hyperbolic discriminant objective forces the backbone to capture this hierarchical information, which may inevitably increase the Lipschitz constant of the backbone. This can hinder the full utilization of the backbone's generalization ability. To address this issue, we introduce second-order pooling into hyperbolic representation learning, as it naturally increases the distance between samples without compromising the generalization ability of the input features. In this way, the Lipschitz constant of the backbone does not necessarily need to be large. However, current off-the-shelf low-dimensional bilinear pooling methods cannot be directly employed in hyperbolic representation learning because they inevitably reduce the distance expansion capability. To solve this problem, we propose a kernel approximation regularization, which enables the low-dimensional bilinear features to approximate the kernel function well in low-dimensional space. Finally, we conduct extensive experiments on graph-structured datasets to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
BayTTA: Uncertainty-aware medical image classification with optimized test-time augmentation using Bayesian model averaging
Jun 25, 2024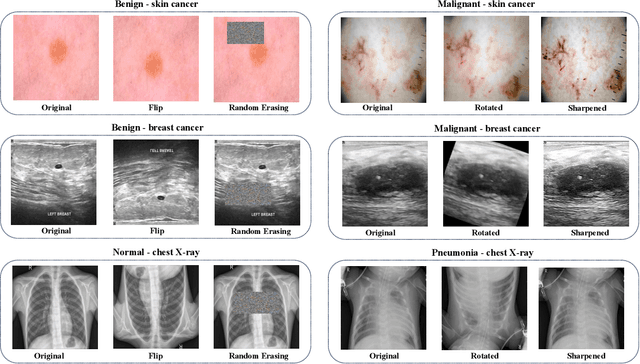
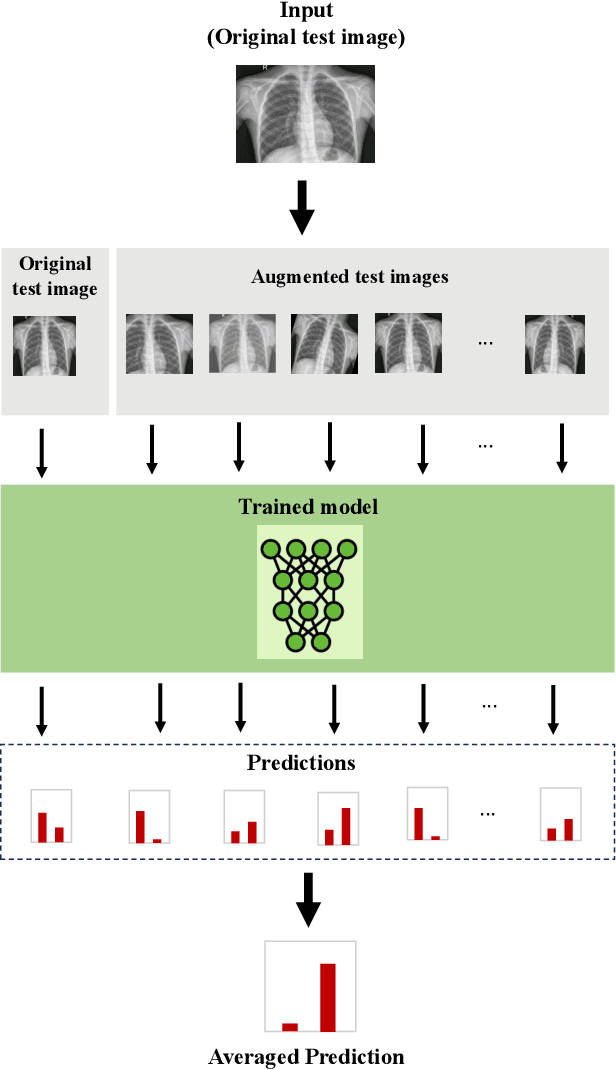
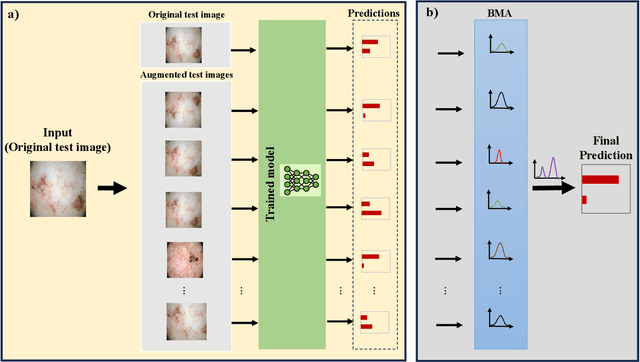
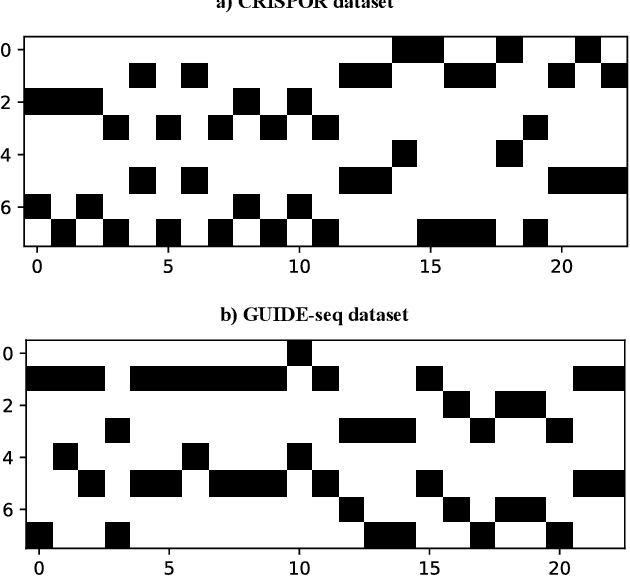
Abstract:Test-time augmentation (TTA) is a well-known technique employed during the testing phase of computer vision tasks. It involves aggregating multiple augmented versions of input data. Combining predictions using a simple average formulation is a common and straightforward approach after performing TTA. This paper introduces a novel framework for optimizing TTA, called BayTTA (Bayesian-based TTA), which is based on Bayesian Model Averaging (BMA). First, we generate a model list associated with different variations of the input data created through TTA. Then, we use BMA to combine model predictions weighted by their respective posterior probabilities. Such an approach allows one to take into account model uncertainty, and thus to enhance the predictive performance of the related machine learning or deep learning model. We evaluate the performance of BayTTA on various public data, including three medical image datasets comprising skin cancer, breast cancer, and chest X-ray images and two well-known gene editing datasets, CRISPOR and GUIDE-seq. Our experimental results indicate that BayTTA can be effectively integrated into state-of-the-art deep learning models used in medical image analysis as well as into some popular pre-trained CNN models such as VGG-16, MobileNetV2, DenseNet201, ResNet152V2, and InceptionRes-NetV2, leading to the enhancement in their accuracy and robustness performance.
Unknown Prompt, the only Lacuna: Unveiling CLIP's Potential for Open Domain Generalization
Mar 31, 2024
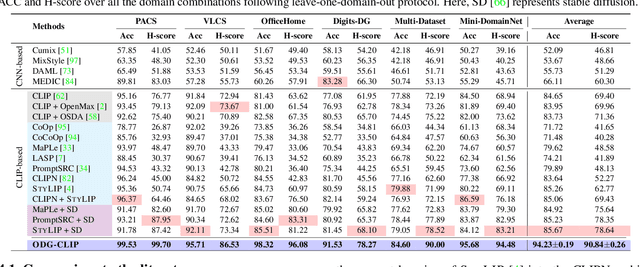
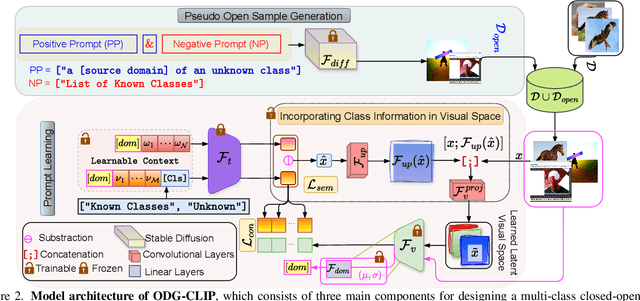
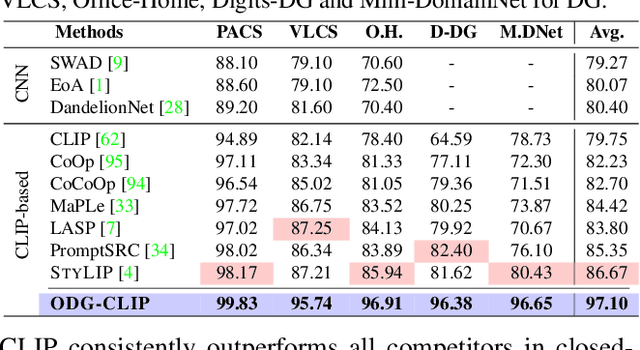
Abstract:We delve into Open Domain Generalization (ODG), marked by domain and category shifts between training's labeled source and testing's unlabeled target domains. Existing solutions to ODG face limitations due to constrained generalizations of traditional CNN backbones and errors in detecting target open samples in the absence of prior knowledge. Addressing these pitfalls, we introduce ODG-CLIP, harnessing the semantic prowess of the vision-language model, CLIP. Our framework brings forth three primary innovations: Firstly, distinct from prevailing paradigms, we conceptualize ODG as a multi-class classification challenge encompassing both known and novel categories. Central to our approach is modeling a unique prompt tailored for detecting unknown class samples, and to train this, we employ a readily accessible stable diffusion model, elegantly generating proxy images for the open class. Secondly, aiming for domain-tailored classification (prompt) weights while ensuring a balance of precision and simplicity, we devise a novel visual stylecentric prompt learning mechanism. Finally, we infuse images with class-discriminative knowledge derived from the prompt space to augment the fidelity of CLIP's visual embeddings. We introduce a novel objective to safeguard the continuity of this infused semantic intel across domains, especially for the shared classes. Through rigorous testing on diverse datasets, covering closed and open-set DG contexts, ODG-CLIP demonstrates clear supremacy, consistently outpacing peers with performance boosts between 8%-16%. Code will be available at https://github.com/mainaksingha01/ODG-CLIP.
A Review of Deep Learning for Video Captioning
Apr 22, 2023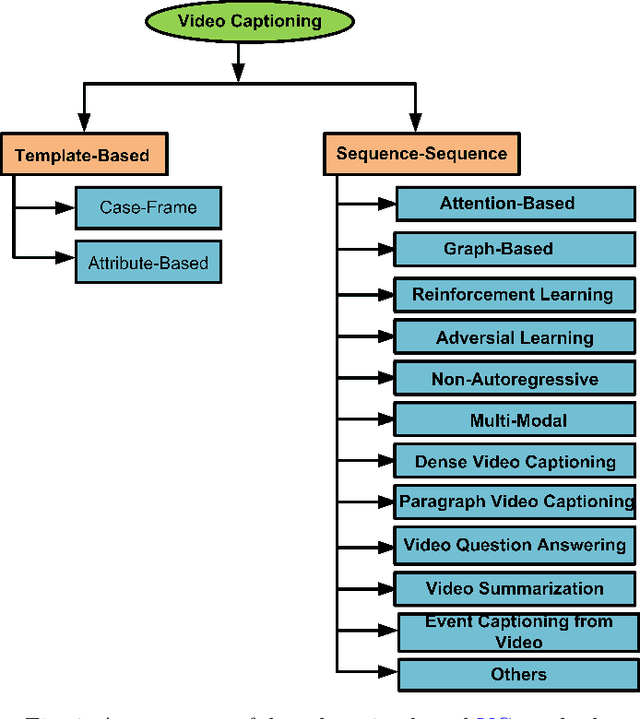
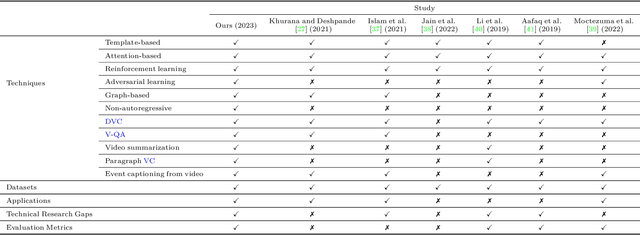
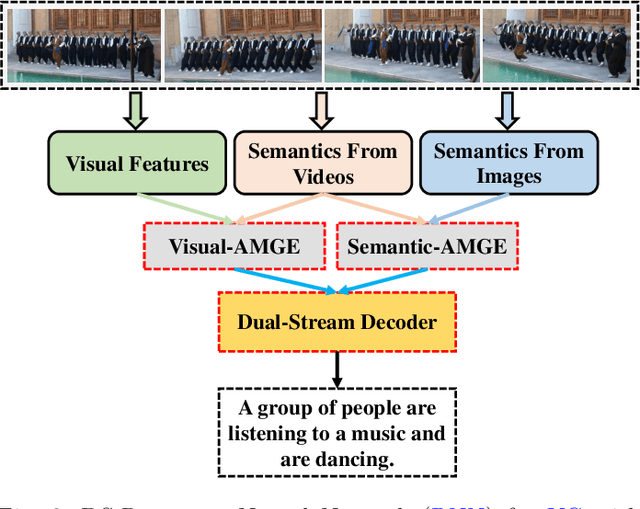
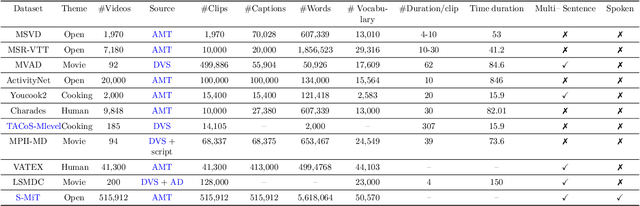
Abstract:Video captioning (VC) is a fast-moving, cross-disciplinary area of research that bridges work in the fields of computer vision, natural language processing (NLP), linguistics, and human-computer interaction. In essence, VC involves understanding a video and describing it with language. Captioning is used in a host of applications from creating more accessible interfaces (e.g., low-vision navigation) to video question answering (V-QA), video retrieval and content generation. This survey covers deep learning-based VC, including but, not limited to, attention-based architectures, graph networks, reinforcement learning, adversarial networks, dense video captioning (DVC), and more. We discuss the datasets and evaluation metrics used in the field, and limitations, applications, challenges, and future directions for VC.
Survey on Leveraging Uncertainty Estimation Towards Trustworthy Deep Neural Networks: The Case of Reject Option and Post-training Processing
Apr 11, 2023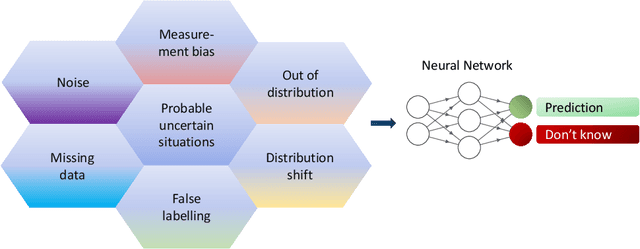
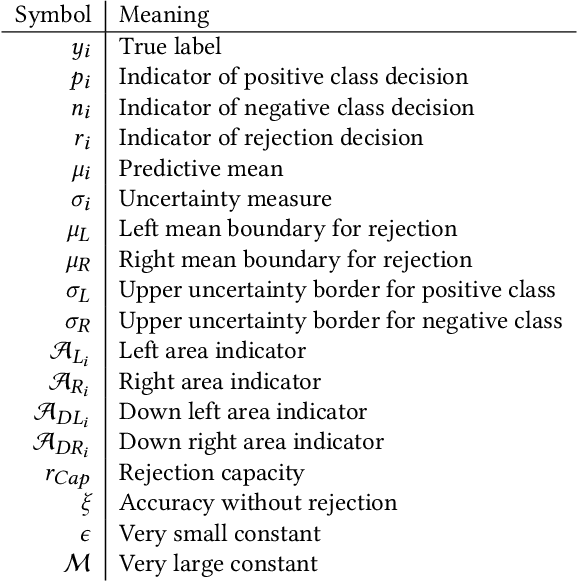
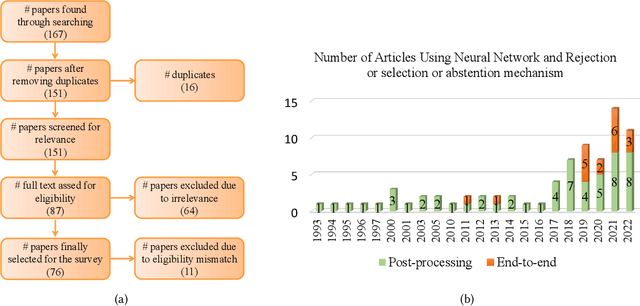
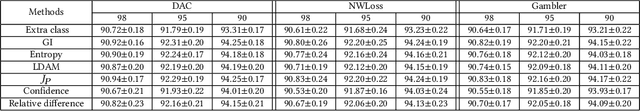
Abstract:Although neural networks (especially deep neural networks) have achieved \textit{better-than-human} performance in many fields, their real-world deployment is still questionable due to the lack of awareness about the limitation in their knowledge. To incorporate such awareness in the machine learning model, prediction with reject option (also known as selective classification or classification with abstention) has been proposed in literature. In this paper, we present a systematic review of the prediction with the reject option in the context of various neural networks. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study focusing on this aspect of neural networks. Moreover, we discuss different novel loss functions related to the reject option and post-training processing (if any) of network output for generating suitable measurements for knowledge awareness of the model. Finally, we address the application of the rejection option in reducing the prediction time for the real-time problems and present a comprehensive summary of the techniques related to the reject option in the context of extensive variety of neural networks. Our code is available on GitHub: \url{https://github.com/MehediHasanTutul/Reject_option}
SFE: A Simple, Fast and Efficient Feature Selection Algorithm for High-Dimensional Data
Mar 17, 2023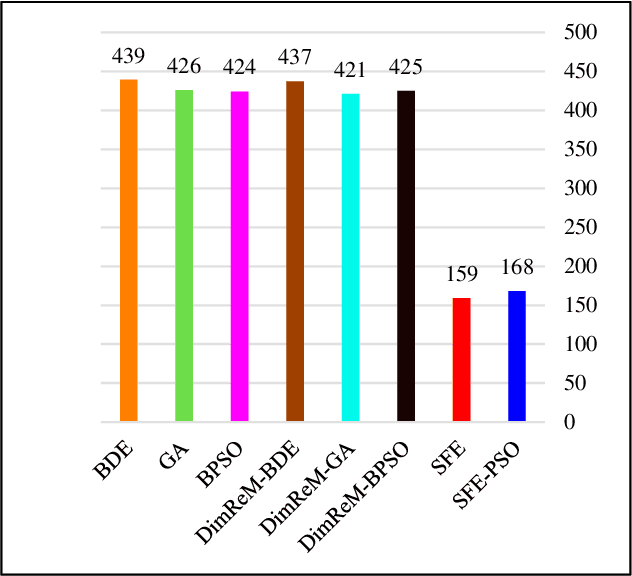
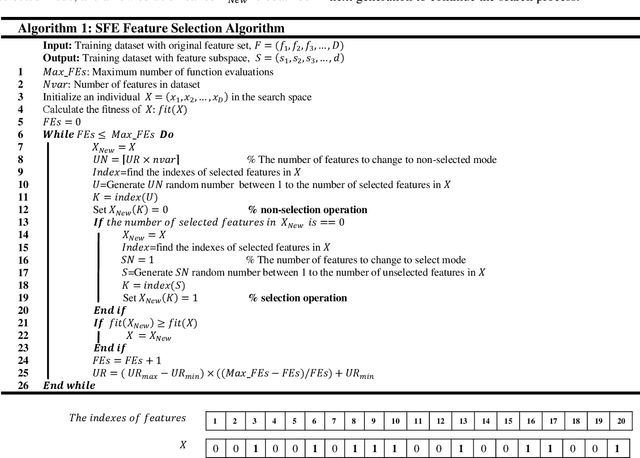
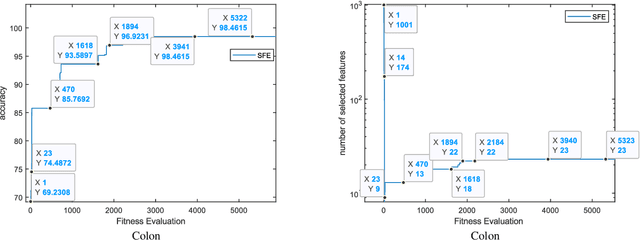
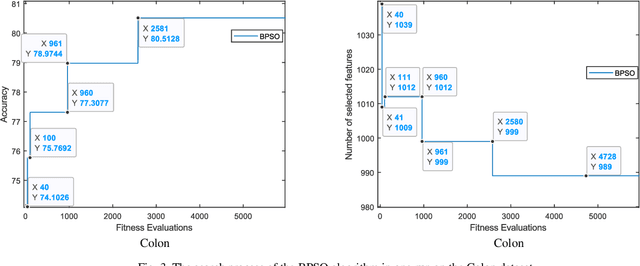
Abstract:In this paper, a new feature selection algorithm, called SFE (Simple, Fast, and Efficient), is proposed for high-dimensional datasets. The SFE algorithm performs its search process using a search agent and two operators: non-selection and selection. It comprises two phases: exploration and exploitation. In the exploration phase, the non-selection operator performs a global search in the entire problem search space for the irrelevant, redundant, trivial, and noisy features, and changes the status of the features from selected mode to non-selected mode. In the exploitation phase, the selection operator searches the problem search space for the features with a high impact on the classification results, and changes the status of the features from non-selected mode to selected mode. The proposed SFE is successful in feature selection from high-dimensional datasets. However, after reducing the dimensionality of a dataset, its performance cannot be increased significantly. In these situations, an evolutionary computational method could be used to find a more efficient subset of features in the new and reduced search space. To overcome this issue, this paper proposes a hybrid algorithm, SFE-PSO (particle swarm optimization) to find an optimal feature subset. The efficiency and effectiveness of the SFE and the SFE-PSO for feature selection are compared on 40 high-dimensional datasets. Their performances were compared with six recently proposed feature selection algorithms. The results obtained indicate that the two proposed algorithms significantly outperform the other algorithms, and can be used as efficient and effective algorithms in selecting features from high-dimensional datasets.
Improving MC-Dropout Uncertainty Estimates with Calibration Error-based Optimization
Oct 07, 2021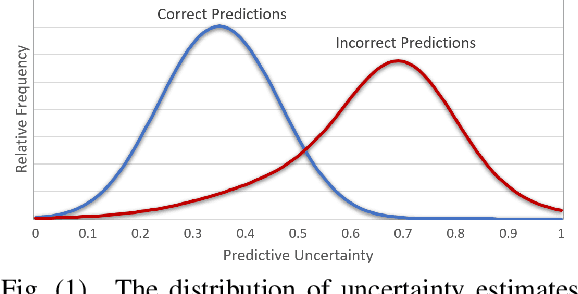
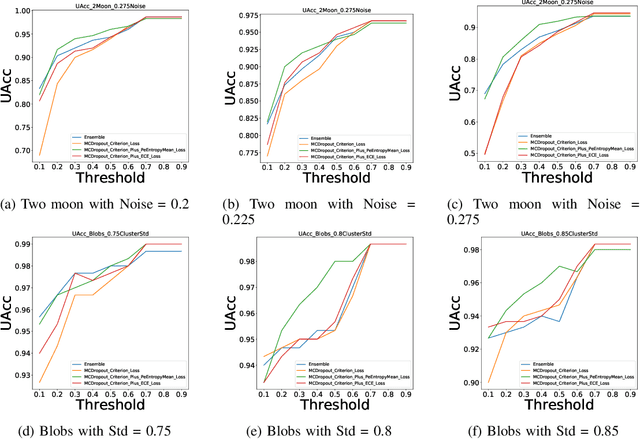
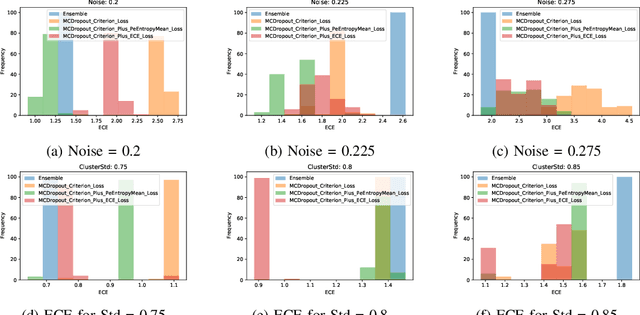
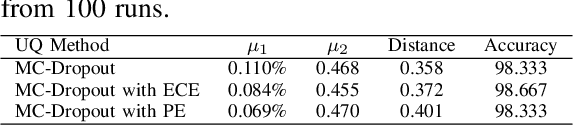
Abstract:Uncertainty quantification of machine learning and deep learning methods plays an important role in enhancing trust to the obtained result. In recent years, a numerous number of uncertainty quantification methods have been introduced. Monte Carlo dropout (MC-Dropout) is one of the most well-known techniques to quantify uncertainty in deep learning methods. In this study, we propose two new loss functions by combining cross entropy with Expected Calibration Error (ECE) and Predictive Entropy (PE). The obtained results clearly show that the new proposed loss functions lead to having a calibrated MC-Dropout method. Our results confirmed the great impact of the new hybrid loss functions for minimising the overlap between the distributions of uncertainty estimates for correct and incorrect predictions without sacrificing the model's overall performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge