Mehedi Hasan
Enhancing EmoBot: An In-Depth Analysis of User Satisfaction and Faults in an Emotion-Aware Chatbot
Nov 05, 2024



Abstract:The research community has traditionally shown a keen interest in emotion modeling, with a notable emphasis on the detection aspect. In contrast, the exploration of emotion generation has received less attention.This study delves into an existing state-of-the-art emotional chatbot, EmoBot, designed for generating emotions in general-purpose conversations. This research involves a comprehensive examination, including a survey to evaluate EmoBot's proficiency in key dimensions like usability, accuracy, and overall user satisfaction, with a specific focus on fault tolerance. By closely examining the chatbot's operations, we identified some noteworthy shortcomings in the existing model. We propose some solutions designed to address and overcome the identified issues.
Bengali Intent Classification with Generative Adversarial BERT
Dec 17, 2023



Abstract:Intent classification is a fundamental task in natural language understanding, aiming to categorize user queries or sentences into predefined classes to understand user intent. The most challenging aspect of this particular task lies in effectively incorporating all possible classes of intent into a dataset while ensuring adequate linguistic variation. Plenty of research has been conducted in the related domains in rich-resource languages like English. In this study, we introduce BNIntent30, a comprehensive Bengali intent classification dataset containing 30 intent classes. The dataset is excerpted and translated from the CLINIC150 dataset containing a diverse range of user intents categorized over 150 classes. Furthermore, we propose a novel approach for Bengali intent classification using Generative Adversarial BERT to evaluate the proposed dataset, which we call GAN-BnBERT. Our approach leverages the power of BERT-based contextual embeddings to capture salient linguistic features and contextual information from the text data, while the generative adversarial network (GAN) component complements the model's ability to learn diverse representations of existing intent classes through generative modeling. Our experimental results demonstrate that the GAN-BnBERT model achieves superior performance on the newly introduced BNIntent30 dataset, surpassing the existing Bi-LSTM and the stand-alone BERT-based classification model.
BanglaBait: Semi-Supervised Adversarial Approach for Clickbait Detection on Bangla Clickbait Dataset
Nov 10, 2023
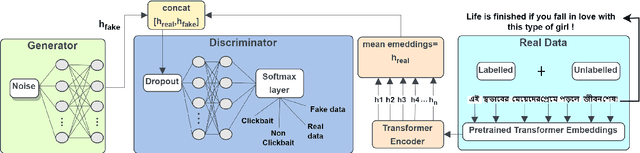
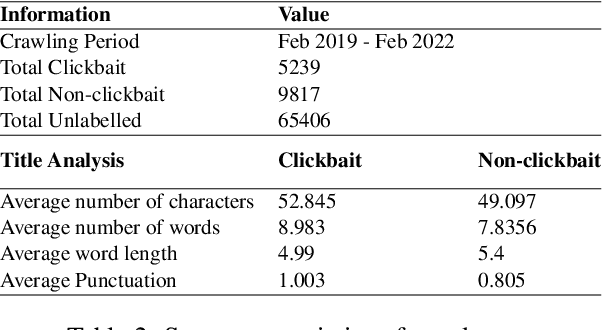
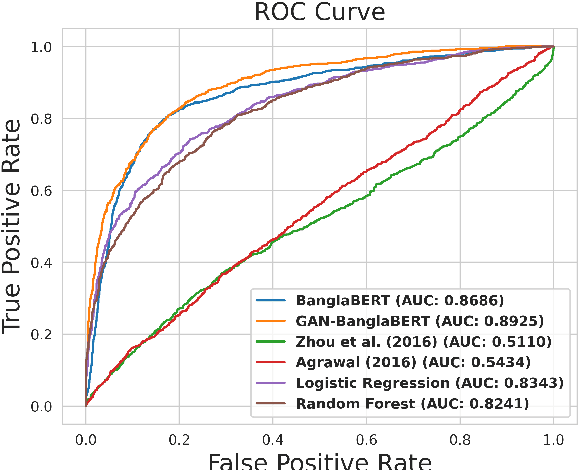
Abstract:Intentionally luring readers to click on a particular content by exploiting their curiosity defines a title as clickbait. Although several studies focused on detecting clickbait titles in English articles, low resource language like Bangla has not been given adequate attention. To tackle clickbait titles in Bangla, we have constructed the first Bangla clickbait detection dataset containing 15,056 labeled news articles and 65,406 unlabelled news articles extracted from clickbait dense news sites. Each article has been labeled by three expert linguists and includes an article's title, body, and other metadata. By incorporating labeled and unlabelled data, we finetune a pretrained Bangla transformer model in an adversarial fashion using Semi Supervised Generative Adversarial Networks (SS GANs). The proposed model acts as a good baseline for this dataset, outperforming traditional neural network models (LSTM, GRU, CNN) and linguistic feature based models. We expect that this dataset and the detailed analysis and comparison of these clickbait detection models will provide a fundamental basis for future research into detecting clickbait titles in Bengali articles. We have released the corresponding code and dataset.
Survey on Leveraging Uncertainty Estimation Towards Trustworthy Deep Neural Networks: The Case of Reject Option and Post-training Processing
Apr 11, 2023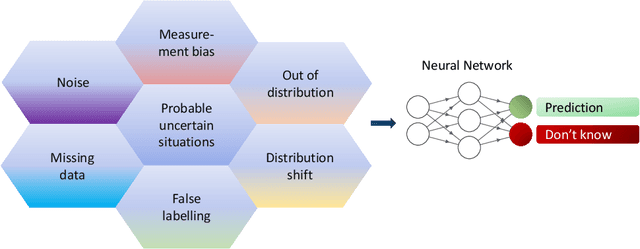
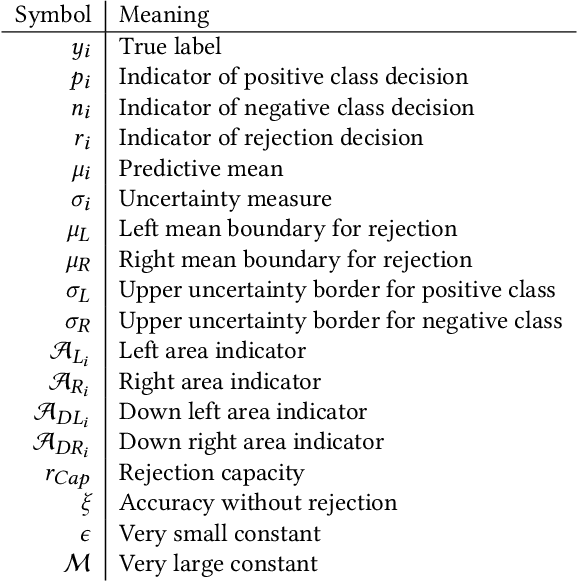
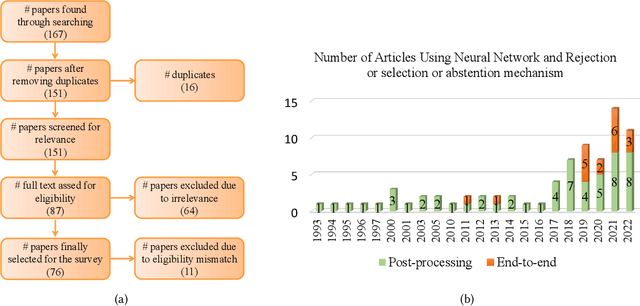
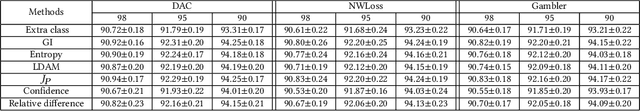
Abstract:Although neural networks (especially deep neural networks) have achieved \textit{better-than-human} performance in many fields, their real-world deployment is still questionable due to the lack of awareness about the limitation in their knowledge. To incorporate such awareness in the machine learning model, prediction with reject option (also known as selective classification or classification with abstention) has been proposed in literature. In this paper, we present a systematic review of the prediction with the reject option in the context of various neural networks. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study focusing on this aspect of neural networks. Moreover, we discuss different novel loss functions related to the reject option and post-training processing (if any) of network output for generating suitable measurements for knowledge awareness of the model. Finally, we address the application of the rejection option in reducing the prediction time for the real-time problems and present a comprehensive summary of the techniques related to the reject option in the context of extensive variety of neural networks. Our code is available on GitHub: \url{https://github.com/MehediHasanTutul/Reject_option}
Continuous tuning & thermally induced frequency drift stabilisation of time delay oscillators such as the optoelectronic oscillator
Jan 12, 2023Abstract:Delay line oscillators based on photonic components, such as the optoelectronic oscillator (OEO), offer the potential for realization of phase noise levels orders of magnitude lower than achievable by conventional microwave sources. Fibre optic-based delay lines can realize the large delay required for low phase noise systems whilst simultaneously achieving insertion loss levels that can be compensated by available microwave and photonic amplification technologies. However, the long fibre is vulnerable to environmental perturbations such as mechanical vibrations and variations in ambient temperature, which result in short term fluctuations and thermally induced drift of the oscillation frequency. The phase shifter used conventionally to adjust the frequency of an OEO to enable phase lock has a finite range that is insufficient to compensate the delay change resulting from operational temperature ranges. A solution to continuous tuning without mode-hopping and to compensation of thermally induced frequency drift without loss of lock of a time delay oscillator is proposed. The basic concept is to introduce a tuning mechanism that works with Cartesian co-ordinates on the complex plane and to avoid explicit use of polar co-ordinates. Consequently, the transmission of the tuning component may traverse the unit circle in either direction multiple times without range limitation to the phase. Thereby tuning by mode-hopping is avoided and expedients to stabilisation, such as the use of tunable lasers within a control loop or precision temperature stabilisation measures are not required. The concept is verified by Simulink simulations. The method has been experimentally tested successfully using a prototype OEO phase locked to a system reference. Solid lock was maintained even when the OEO was placed in an oven and cycled over a temperature range from ambient to 80 {\deg}C.
Controlled Dropout for Uncertainty Estimation
May 06, 2022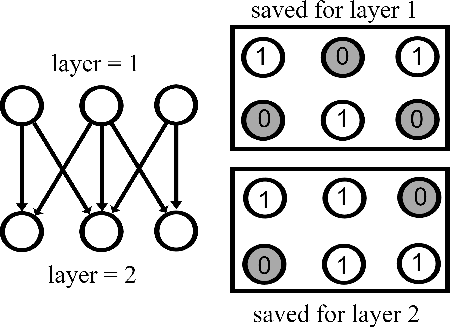
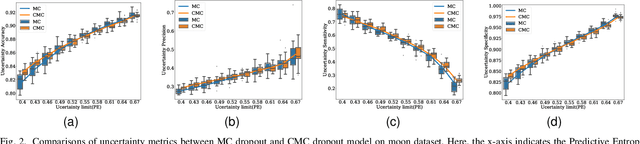
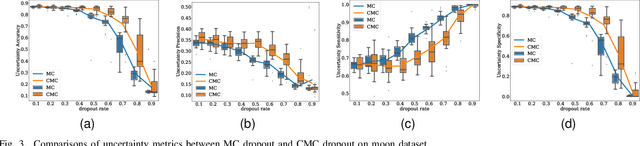
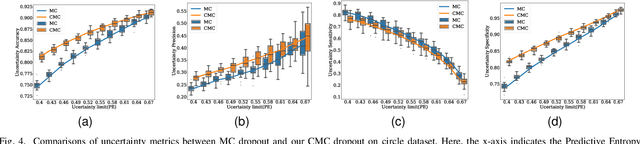
Abstract:Uncertainty quantification in a neural network is one of the most discussed topics for safety-critical applications. Though Neural Networks (NNs) have achieved state-of-the-art performance for many applications, they still provide unreliable point predictions, which lack information about uncertainty estimates. Among various methods to enable neural networks to estimate uncertainty, Monte Carlo (MC) dropout has gained much popularity in a short period due to its simplicity. In this study, we present a new version of the traditional dropout layer where we are able to fix the number of dropout configurations. As such, each layer can take and apply the new dropout layer in the MC method to quantify the uncertainty associated with NN predictions. We conduct experiments on both toy and realistic datasets and compare the results with the MC method using the traditional dropout layer. Performance analysis utilizing uncertainty evaluation metrics corroborates that our dropout layer offers better performance in most cases.
Circuit design and integration feasibility of a high-resolution broadband on-chip spectral monitor
Aug 12, 2021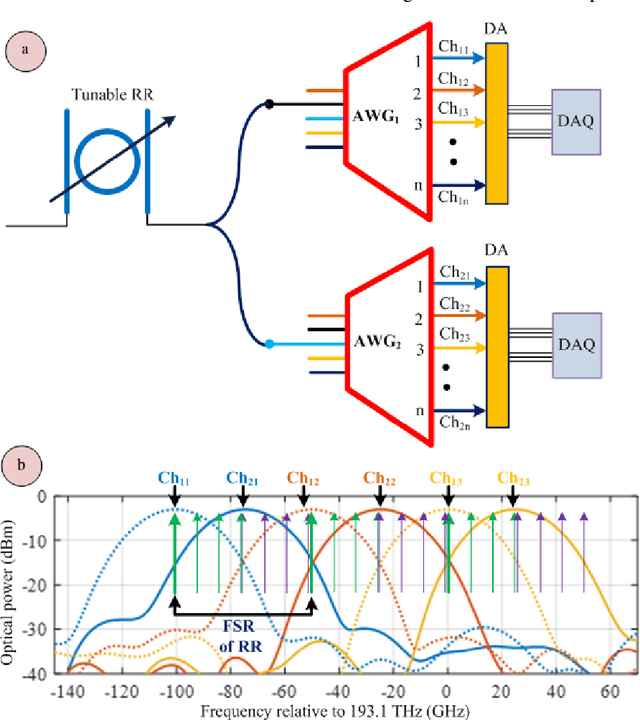
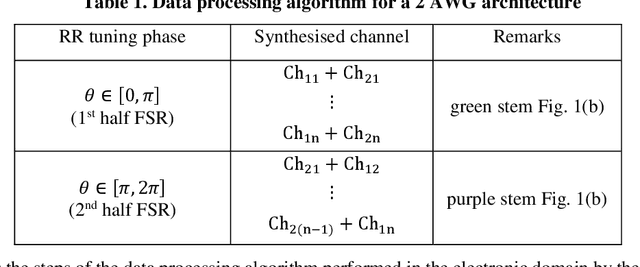
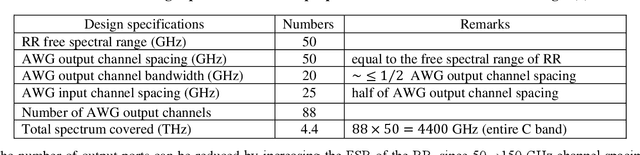
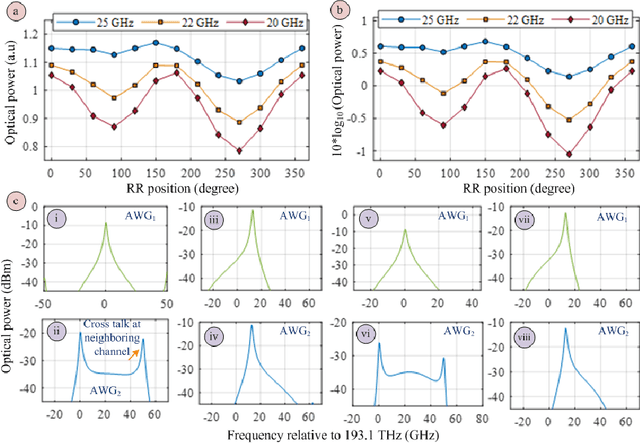
Abstract:Up-to-date network telemetry is the key enabler for resource optimization by a variety of means including capacity scaling, fault recovery, network reconfiguration. Reliable optical performance monitoring in general and specifically the monitoring of the spectral profile of WDM signals in fixed- and flex-grid architecture across the entire C-band remains challenging. This article describes a spectrometer circuit architecture along with an original data processing algorithm that combined can measure the spectrum quantitatively across the entire C-band aiming at 1 GHz resolution bandwidth. The circuit is composed of a scanning ring resonator followed by a parallel arrangement of AWGs with interlaced channel spectra. The comb of ring resonances provides the high resolution and the algorithm creates a virtual tuneable AWG that isolates individual resonances of the comb within the flat pass-band of its synthesized channels. The parallel arrangement of AWGs may be replaced by a time multiplexed multi-input port AWG. The feasibility of a ring resonator functioning over whole C-band is experimentally validated. Full tuning of the comb of resonances over a free spectral range is achieved with a high-resolution bandwidth of 1.30 GHz. Due to its maturity and low loss, CMOS compatible silicon nitride is chosen for integration. Additionally, the whole system demonstration is presented using industry standard simulation tool. The architecture is robust to fabrication process variations owing to its data processing approach.
Convolutional Nets for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening in Bangladeshi Patients
Jul 31, 2021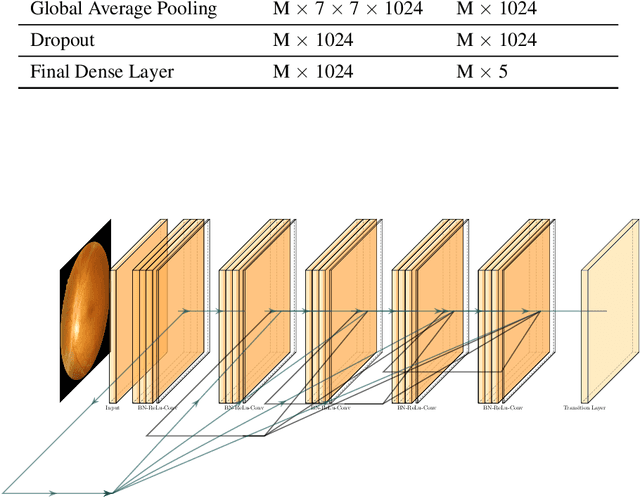
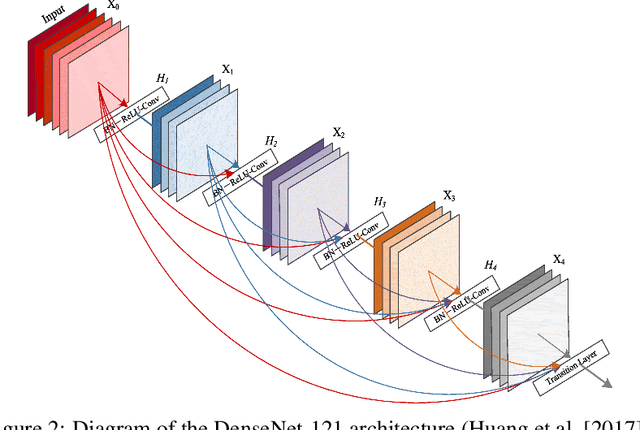
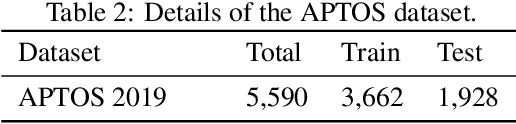
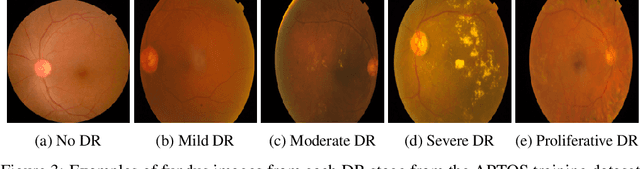
Abstract:Diabetes is one of the most prevalent chronic diseases in Bangladesh, and as a result, Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) is widespread in the population. DR, an eye illness caused by diabetes, can lead to blindness if it is not identified and treated in its early stages. Unfortunately, diagnosis of DR requires medically trained professionals, but Bangladesh has limited specialists in comparison to its population. Moreover, the screening process is often expensive, prohibiting many from receiving timely and proper diagnosis. To address the problem, we introduce a deep learning algorithm which screens for different stages of DR. We use a state-of-the-art CNN architecture to diagnose patients based on retinal fundus imagery. This paper is an experimental evaluation of the algorithm we developed for DR diagnosis and screening specifically for Bangladeshi patients. We perform this validation study using separate pools of retinal image data of real patients from a hospital and field studies in Bangladesh. Our results show that the algorithm is effective at screening Bangladeshi eyes even when trained on a public dataset which is out of domain, and can accurately determine the stage of DR as well, achieving an overall accuracy of 92.27\% and 93.02\% on two validation sets of Bangladeshi eyes. The results confirm the ability of the algorithm to be used in real clinical settings and applications due to its high accuracy and classwise metrics. Our algorithm is implemented in the application Drishti, which is used to screen for DR in patients living in rural areas in Bangladesh, where access to professional screening is limited.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge