Nicola Strisciuglio
Not Only Text: Exploring Compositionality of Visual Representations in Vision-Language Models
Mar 21, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) learn a shared feature space for text and images, enabling the comparison of inputs of different modalities. While prior works demonstrated that VLMs organize natural language representations into regular structures encoding composite meanings, it remains unclear if compositional patterns also emerge in the visual embedding space. In this work, we investigate compositionality in the image domain, where the analysis of compositional properties is challenged by noise and sparsity of visual data. We address these problems and propose a framework, called Geodesically Decomposable Embeddings (GDE), that approximates image representations with geometry-aware compositional structures in the latent space. We demonstrate that visual embeddings of pre-trained VLMs exhibit a compositional arrangement, and evaluate the effectiveness of this property in the tasks of compositional classification and group robustness. GDE achieves stronger performance in compositional classification compared to its counterpart method that assumes linear geometry of the latent space. Notably, it is particularly effective for group robustness, where we achieve higher results than task-specific solutions. Our results indicate that VLMs can automatically develop a human-like form of compositional reasoning in the visual domain, making their underlying processes more interpretable. Code is available at https://github.com/BerasiDavide/vlm_image_compositionality.
Do ImageNet-trained models learn shortcuts? The impact of frequency shortcuts on generalization
Mar 05, 2025



Abstract:Frequency shortcuts refer to specific frequency patterns that models heavily rely on for correct classification. Previous studies have shown that models trained on small image datasets often exploit such shortcuts, potentially impairing their generalization performance. However, existing methods for identifying frequency shortcuts require expensive computations and become impractical for analyzing models trained on large datasets. In this work, we propose the first approach to more efficiently analyze frequency shortcuts at a larger scale. We show that both CNN and transformer models learn frequency shortcuts on ImageNet. We also expose that frequency shortcut solutions can yield good performance on out-of-distribution (OOD) test sets which largely retain texture information. However, these shortcuts, mostly aligned with texture patterns, hinder model generalization on rendition-based OOD test sets. These observations suggest that current OOD evaluations often overlook the impact of frequency shortcuts on model generalization. Future benchmarks could thus benefit from explicitly assessing and accounting for these shortcuts to build models that generalize across a broader range of OOD scenarios.
Dynamic Sparse Training versus Dense Training: The Unexpected Winner in Image Corruption Robustness
Oct 03, 2024
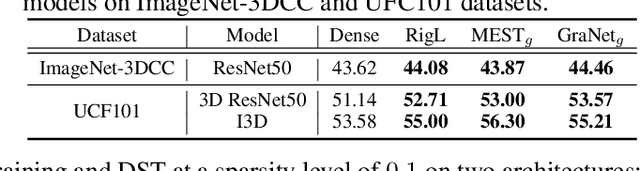
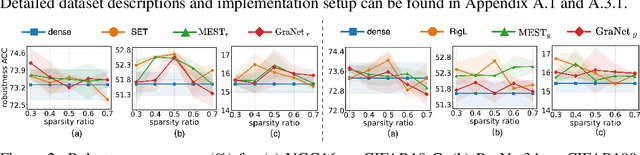
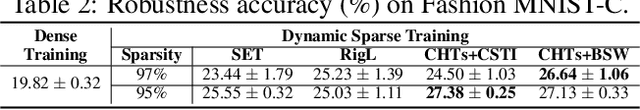
Abstract:It is generally perceived that Dynamic Sparse Training opens the door to a new era of scalability and efficiency for artificial neural networks at, perhaps, some costs in accuracy performance for the classification task. At the same time, Dense Training is widely accepted as being the "de facto" approach to train artificial neural networks if one would like to maximize their robustness against image corruption. In this paper, we question this general practice. Consequently, we claim that, contrary to what is commonly thought, the Dynamic Sparse Training methods can consistently outperform Dense Training in terms of robustness accuracy, particularly if the efficiency aspect is not considered as a main objective (i.e., sparsity levels between 10% and up to 50%), without adding (or even reducing) resource cost. We validate our claim on two types of data, images and videos, using several traditional and modern deep learning architectures for computer vision and three widely studied Dynamic Sparse Training algorithms. Our findings reveal a new yet-unknown benefit of Dynamic Sparse Training and open new possibilities in improving deep learning robustness beyond the current state of the art.
Indoor scene recognition from images under visual corruptions
Aug 23, 2024Abstract:The classification of indoor scenes is a critical component in various applications, such as intelligent robotics for assistive living. While deep learning has significantly advanced this field, models often suffer from reduced performance due to image corruption. This paper presents an innovative approach to indoor scene recognition that leverages multimodal data fusion, integrating caption-based semantic features with visual data to enhance both accuracy and robustness against corruption. We examine two multimodal networks that synergize visual features from CNN models with semantic captions via a Graph Convolutional Network (GCN). Our study shows that this fusion markedly improves model performance, with notable gains in Top-1 accuracy when evaluated against a corrupted subset of the Places365 dataset. Moreover, while standalone visual models displayed high accuracy on uncorrupted images, their performance deteriorated significantly with increased corruption severity. Conversely, the multimodal models demonstrated improved accuracy in clean conditions and substantial robustness to a range of image corruptions. These results highlight the efficacy of incorporating high-level contextual information through captions, suggesting a promising direction for enhancing the resilience of classification systems.
PushPull-Net: Inhibition-driven ResNet robust to image corruptions
Aug 07, 2024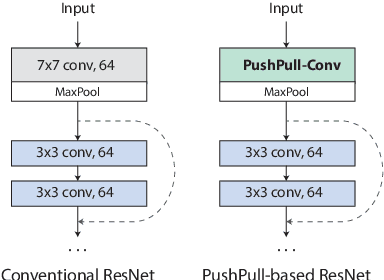
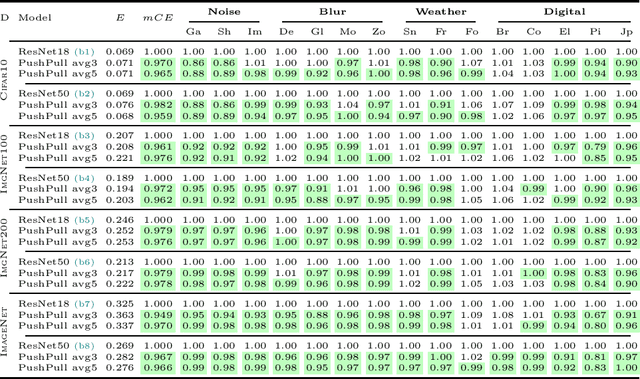
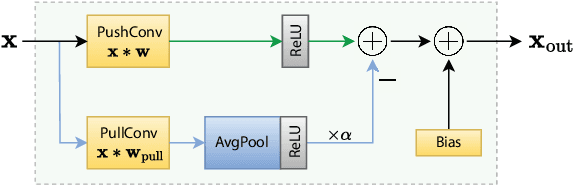
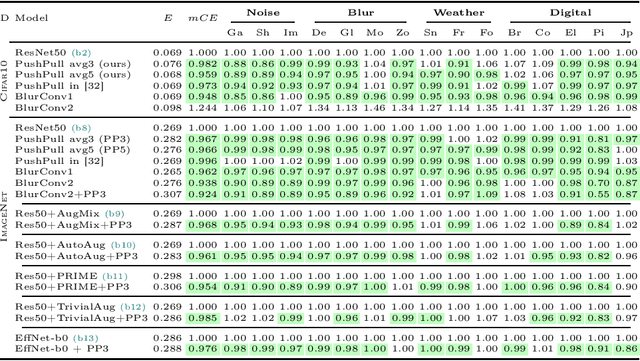
Abstract:We introduce a novel computational unit, termed PushPull-Conv, in the first layer of a ResNet architecture, inspired by the anti-phase inhibition phenomenon observed in the primary visual cortex. This unit redefines the traditional convolutional layer by implementing a pair of complementary filters: a trainable push kernel and its counterpart, the pull kernel. The push kernel (analogous to traditional convolution) learns to respond to specific stimuli, while the pull kernel reacts to the same stimuli but of opposite contrast. This configuration enhances stimulus selectivity and effectively inhibits response in regions lacking preferred stimuli. This effect is attributed to the push and pull kernels, which produce responses of comparable magnitude in such regions, thereby neutralizing each other. The incorporation of the PushPull-Conv into ResNets significantly increases their robustness to image corruption. Our experiments with benchmark corruption datasets show that the PushPull-Conv can be combined with other data augmentation techniques to further improve model robustness. We set a new robustness benchmark on ResNet50 achieving an $mCE$ of 49.95$\%$ on ImageNet-C when combining PRIME augmentation with PushPull inhibition.
Fourier-basis Functions to Bridge Augmentation Gap: Rethinking Frequency Augmentation in Image Classification
Mar 05, 2024Abstract:Computer vision models normally witness degraded performance when deployed in real-world scenarios, due to unexpected changes in inputs that were not accounted for during training. Data augmentation is commonly used to address this issue, as it aims to increase data variety and reduce the distribution gap between training and test data. However, common visual augmentations might not guarantee extensive robustness of computer vision models. In this paper, we propose Auxiliary Fourier-basis Augmentation (AFA), a complementary technique targeting augmentation in the frequency domain and filling the augmentation gap left by visual augmentations. We demonstrate the utility of augmentation via Fourier-basis additive noise in a straightforward and efficient adversarial setting. Our results show that AFA benefits the robustness of models against common corruptions, OOD generalization, and consistency of performance of models against increasing perturbations, with negligible deficit to the standard performance of models. It can be seamlessly integrated with other augmentation techniques to further boost performance. Code and models can be found at: https://github.com/nis-research/afa-augment
CAST: Clustering Self-Attention using Surrogate Tokens for Efficient Transformers
Feb 06, 2024



Abstract:The Transformer architecture has shown to be a powerful tool for a wide range of tasks. It is based on the self-attention mechanism, which is an inherently computationally expensive operation with quadratic computational complexity: memory usage and compute time increase quadratically with the length of the input sequences, thus limiting the application of Transformers. In this work, we propose a novel Clustering self-Attention mechanism using Surrogate Tokens (CAST), to optimize the attention computation and achieve efficient transformers. CAST utilizes learnable surrogate tokens to construct a cluster affinity matrix, used to cluster the input sequence and generate novel cluster summaries. The self-attention from within each cluster is then combined with the cluster summaries of other clusters, enabling information flow across the entire input sequence. CAST improves efficiency by reducing the complexity from $O(N^2)$ to $O(\alpha N)$ where N is the sequence length, and {\alpha} is constant according to the number of clusters and samples per cluster. We show that CAST performs better than or comparable to the baseline Transformers on long-range sequence modeling tasks, while also achieving higher results on time and memory efficiency than other efficient transformers.
Regressing Transformers for Data-efficient Visual Place Recognition
Jan 29, 2024
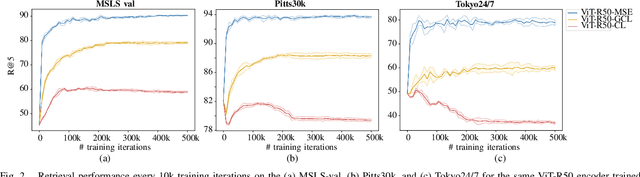
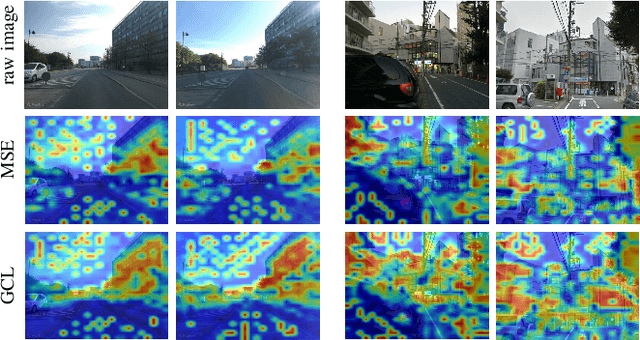
Abstract:Visual place recognition is a critical task in computer vision, especially for localization and navigation systems. Existing methods often rely on contrastive learning: image descriptors are trained to have small distance for similar images and larger distance for dissimilar ones in a latent space. However, this approach struggles to ensure accurate distance-based image similarity representation, particularly when training with binary pairwise labels, and complex re-ranking strategies are required. This work introduces a fresh perspective by framing place recognition as a regression problem, using camera field-of-view overlap as similarity ground truth for learning. By optimizing image descriptors to align directly with graded similarity labels, this approach enhances ranking capabilities without expensive re-ranking, offering data-efficient training and strong generalization across several benchmark datasets.
Quantifying white matter hyperintensity and brain volumes in heterogeneous clinical and low-field portable MRI
Dec 08, 2023
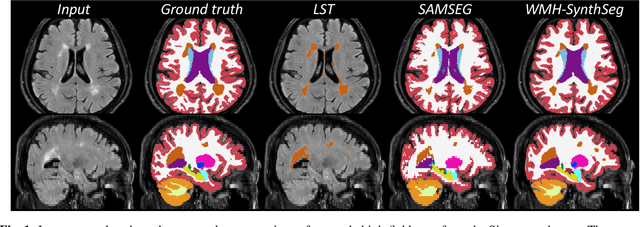
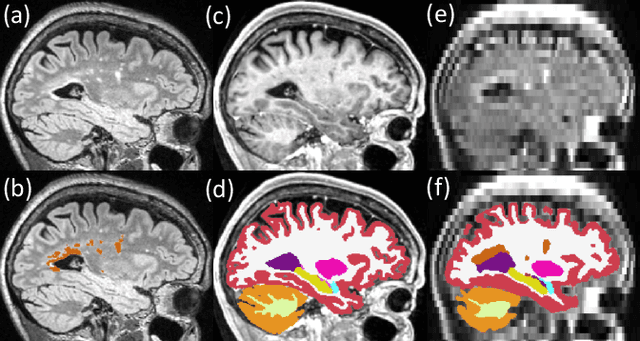

Abstract:Brain atrophy and white matter hyperintensity (WMH) are critical neuroimaging features for ascertaining brain injury in cerebrovascular disease and multiple sclerosis. Automated segmentation and quantification is desirable but existing methods require high-resolution MRI with good signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). This precludes application to clinical and low-field portable MRI (pMRI) scans, thus hampering large-scale tracking of atrophy and WMH progression, especially in underserved areas where pMRI has huge potential. Here we present a method that segments white matter hyperintensity and 36 brain regions from scans of any resolution and contrast (including pMRI) without retraining. We show results on six public datasets and on a private dataset with paired high- and low-field scans (3T and 64mT), where we attain strong correlation between the WMH ($\rho$=.85) and hippocampal volumes (r=.89) estimated at both fields. Our method is publicly available as part of FreeSurfer, at: http://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/WMH-SynthSeg.
DFM-X: Augmentation by Leveraging Prior Knowledge of Shortcut Learning
Aug 12, 2023



Abstract:Neural networks are prone to learn easy solutions from superficial statistics in the data, namely shortcut learning, which impairs generalization and robustness of models. We propose a data augmentation strategy, named DFM-X, that leverages knowledge about frequency shortcuts, encoded in Dominant Frequencies Maps computed for image classification models. We randomly select X% training images of certain classes for augmentation, and process them by retaining the frequencies included in the DFMs of other classes. This strategy compels the models to leverage a broader range of frequencies for classification, rather than relying on specific frequency sets. Thus, the models learn more deep and task-related semantics compared to their counterpart trained with standard setups. Unlike other commonly used augmentation techniques which focus on increasing the visual variations of training data, our method targets exploiting the original data efficiently, by distilling prior knowledge about destructive learning behavior of models from data. Our experimental results demonstrate that DFM-X improves robustness against common corruptions and adversarial attacks. It can be seamlessly integrated with other augmentation techniques to further enhance the robustness of models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge