Yang Yan
School of Computing and Artificial Intelligence, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu, China
Agent Skills for Large Language Models: Architecture, Acquisition, Security, and the Path Forward
Feb 17, 2026Abstract:The transition from monolithic language models to modular, skill-equipped agents marks a defining shift in how large language models (LLMs) are deployed in practice. Rather than encoding all procedural knowledge within model weights, agent skills -- composable packages of instructions, code, and resources that agents load on demand -- enable dynamic capability extension without retraining. It is formalized in a paradigm of progressive disclosure, portable skill definitions, and integration with the Model Context Protocol (MCP). This survey provides a comprehensive treatment of the agent skills landscape, as it has rapidly evolved during the last few months. We organize the field along four axes: (i) architectural foundations, examining the SKILL$.$md specification, progressive context loading, and the complementary roles of skills and MCP; (ii) skill acquisition, covering reinforcement learning with skill libraries, autonomous skill discovery (SEAgent), and compositional skill synthesis; (iii) deployment at scale, including the computer-use agent (CUA) stack, GUI grounding advances, and benchmark progress on OSWorld and SWE-bench; and (iv) security, where recent empirical analyses reveal that 26.1% of community-contributed skills contain vulnerabilities, motivating our proposed Skill Trust and Lifecycle Governance Framework -- a four-tier, gate-based permission model that maps skill provenance to graduated deployment capabilities. We identify seven open challenges -- from cross-platform skill portability to capability-based permission models -- and propose a research agenda for realizing trustworthy, self-improving skill ecosystems. Unlike prior surveys that broadly cover LLM agents or tool use, this work focuses specifically on the emerging skill abstraction layer and its implications for the next generation of agentic systems. Project repo: https://github.com/scienceaix/agentskills
Towards Safeguarding LLM Fine-tuning APIs against Cipher Attacks
Aug 23, 2025Abstract:Large language model fine-tuning APIs enable widespread model customization, yet pose significant safety risks. Recent work shows that adversaries can exploit access to these APIs to bypass model safety mechanisms by encoding harmful content in seemingly harmless fine-tuning data, evading both human monitoring and standard content filters. We formalize the fine-tuning API defense problem, and introduce the Cipher Fine-tuning Robustness benchmark (CIFR), a benchmark for evaluating defense strategies' ability to retain model safety in the face of cipher-enabled attackers while achieving the desired level of fine-tuning functionality. We include diverse cipher encodings and families, with some kept exclusively in the test set to evaluate for generalization across unseen ciphers and cipher families. We then evaluate different defenses on the benchmark and train probe monitors on model internal activations from multiple fine-tunes. We show that probe monitors achieve over 99% detection accuracy, generalize to unseen cipher variants and families, and compare favorably to state-of-the-art monitoring approaches. We open-source CIFR and the code to reproduce our experiments to facilitate further research in this critical area. Code and data are available online https://github.com/JackYoustra/safe-finetuning-api
Do PhD-level LLMs Truly Grasp Elementary Addition? Probing Rule Learning vs. Memorization in Large Language Models
Apr 07, 2025Abstract:Despite high benchmark scores, Large Language Models (LLMs) often fail simple problem, raising a critical question: Do LLMs learn mathematical principles or merely memorize patterns? Rather than designing increasingly complex benchmarks like recent works, we investigate this using elementary two-integer addition ($0$ to $2^{64}$), probing two core properties: commutativity ($A+B=B+A$) and compositional generalization (via isomorphic symbolic mappings, e.g., $7 \rightarrow y$). While state-of-the-art LLMs achieve 73.8-99.8\% accuracy on numerical addition, performance collapses to $\leq$7.5\% under symbolic mapping, indicating failure to generalize learned rules. Non-monotonic performance scaling with digit count and frequent commutativity violations (over 1,700 cases of $A+B \neq B+A$) further support this. Explicitly providing addition rules degrades performance by 81.2\% on average, while self-explanation maintains baseline accuracy, suggesting LLM arithmetic processing is misaligned with human-defined principles. Our findings indicate current LLMs rely on memory pattern over genuine rule learning, highlighting architectural limitations and the need for new approaches to achieve true mathematical reasoning.
Enhancing Chest X-ray Classification through Knowledge Injection in Cross-Modality Learning
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:The integration of artificial intelligence in medical imaging has shown tremendous potential, yet the relationship between pre-trained knowledge and performance in cross-modality learning remains unclear. This study investigates how explicitly injecting medical knowledge into the learning process affects the performance of cross-modality classification, focusing on Chest X-ray (CXR) images. We introduce a novel Set Theory-based knowledge injection framework that generates captions for CXR images with controllable knowledge granularity. Using this framework, we fine-tune CLIP model on captions with varying levels of medical information. We evaluate the model's performance through zero-shot classification on the CheXpert dataset, a benchmark for CXR classification. Our results demonstrate that injecting fine-grained medical knowledge substantially improves classification accuracy, achieving 72.5\% compared to 49.9\% when using human-generated captions. This highlights the crucial role of domain-specific knowledge in medical cross-modality learning. Furthermore, we explore the influence of knowledge density and the use of domain-specific Large Language Models (LLMs) for caption generation, finding that denser knowledge and specialized LLMs contribute to enhanced performance. This research advances medical image analysis by demonstrating the effectiveness of knowledge injection for improving automated CXR classification, paving the way for more accurate and reliable diagnostic tools.
An Oversampling-enhanced Multi-class Imbalanced Classification Framework for Patient Health Status Prediction Using Patient-reported Outcomes
Nov 16, 2024



Abstract:Patient-reported outcomes (PROs) directly collected from cancer patients being treated with radiation therapy play a vital role in assisting clinicians in counseling patients regarding likely toxicities. Precise prediction and evaluation of symptoms or health status associated with PROs are fundamental to enhancing decision-making and planning for the required services and support as patients transition into survivorship. However, the raw PRO data collected from hospitals exhibits some intrinsic challenges such as incomplete item reports and imbalance patient toxicities. To the end, in this study, we explore various machine learning techniques to predict patient outcomes related to health status such as pain levels and sleep discomfort using PRO datasets from a cancer photon/proton therapy center. Specifically, we deploy six advanced machine learning classifiers -- Random Forest (RF), XGBoost, Gradient Boosting (GB), Support Vector Machine (SVM), Multi-Layer Perceptron with Bagging (MLP-Bagging), and Logistic Regression (LR) -- to tackle a multi-class imbalance classification problem across three prevalent cancer types: head and neck, prostate, and breast cancers. To address the class imbalance issue, we employ an oversampling strategy, adjusting the training set sample sizes through interpolations of in-class neighboring samples, thereby augmenting minority classes without deviating from the original skewed class distribution. Our experimental findings across multiple PRO datasets indicate that the RF and XGB methods achieve robust generalization performance, evidenced by weighted AUC and detailed confusion matrices, in categorizing outcomes as mild, intermediate, and severe post-radiation therapy. These results underscore the models' effectiveness and potential utility in clinical settings.
LLM4PR: Improving Post-Ranking in Search Engine with Large Language Models
Nov 02, 2024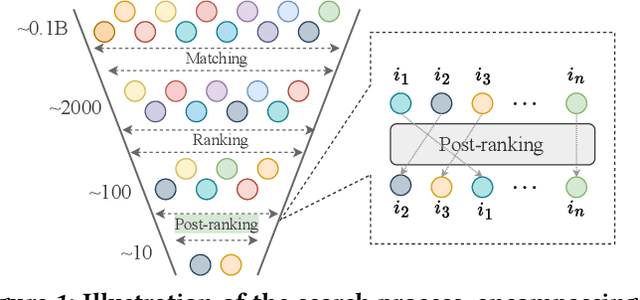



Abstract:Alongside the rapid development of Large Language Models (LLMs), there has been a notable increase in efforts to integrate LLM techniques in information retrieval (IR) and search engines (SE). Recently, an additional post-ranking stage is suggested in SE to enhance user satisfaction in practical applications. Nevertheless, research dedicated to enhancing the post-ranking stage through LLMs remains largely unexplored. In this study, we introduce a novel paradigm named Large Language Models for Post-Ranking in search engine (LLM4PR), which leverages the capabilities of LLMs to accomplish the post-ranking task in SE. Concretely, a Query-Instructed Adapter (QIA) module is designed to derive the user/item representation vectors by incorporating their heterogeneous features. A feature adaptation step is further introduced to align the semantics of user/item representations with the LLM. Finally, the LLM4PR integrates a learning to post-rank step, leveraging both a main task and an auxiliary task to fine-tune the model to adapt the post-ranking task. Experiment studies demonstrate that the proposed framework leads to significant improvements and exhibits state-of-the-art performance compared with other alternatives.
Predicting the Big Five Personality Traits in Chinese Counselling Dialogues Using Large Language Models
Jun 25, 2024Abstract:Accurate assessment of personality traits is crucial for effective psycho-counseling, yet traditional methods like self-report questionnaires are time-consuming and biased. This study exams whether Large Language Models (LLMs) can predict the Big Five personality traits directly from counseling dialogues and introduces an innovative framework to perform the task. Our framework applies role-play and questionnaire-based prompting to condition LLMs on counseling sessions, simulating client responses to the Big Five Inventory. We evaluated our framework on 853 real-world counseling sessions, finding a significant correlation between LLM-predicted and actual Big Five traits, proving the validity of framework. Moreover, ablation studies highlight the importance of role-play simulations and task simplification via questionnaires in enhancing prediction accuracy. Meanwhile, our fine-tuned Llama3-8B model, utilizing Direct Preference Optimization with Supervised Fine-Tuning, achieves a 130.95\% improvement, surpassing the state-of-the-art Qwen1.5-110B by 36.94\% in personality prediction validity. In conclusion, LLMs can predict personality based on counseling dialogues. Our code and model are publicly available at \url{https://github.com/kuri-leo/BigFive-LLM-Predictor}, providing a valuable tool for future research in computational psychometrics.
LanguageBind: Extending Video-Language Pretraining to N-modality by Language-based Semantic Alignment
Oct 14, 2023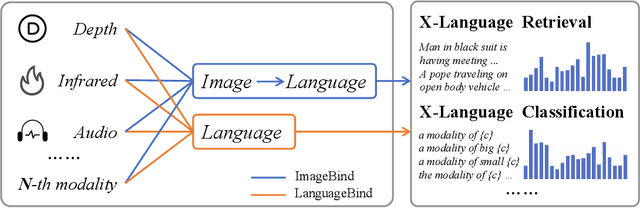
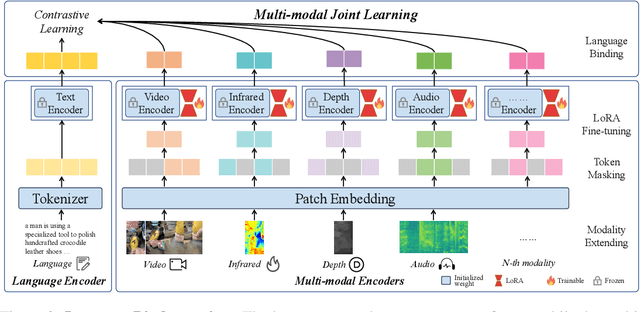
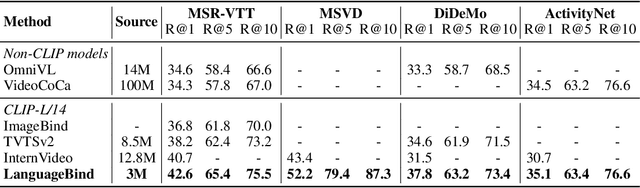
Abstract:The video-language (VL) pretraining has achieved remarkable improvement in multiple downstream tasks. However, the current VL pretraining framework is hard to extend to multiple modalities (N modalities, N>=3) beyond vision and language. We thus propose LanguageBind, taking the language as the bind across different modalities because the language modality is well-explored and contains rich semantics. Specifically, we freeze the language encoder acquired by VL pretraining, then train encoders for other modalities with contrastive learning. As a result, all modalities are mapped to a shared feature space, implementing multi-modal semantic alignment. While LanguageBind ensures that we can extend VL modalities to N modalities, we also need a high-quality dataset with alignment data pairs centered on language. We thus propose VIDAL-10M with Video, Infrared, Depth, Audio and their corresponding Language, naming as VIDAL-10M. In our VIDAL-10M, all videos are from short video platforms with complete semantics rather than truncated segments from long videos, and all the video, depth, infrared, and audio modalities are aligned to their textual descriptions. After pretraining on VIDAL-10M, we outperform ImageBind by 5.8% R@1 on the MSR-VTT dataset with only 15% of the parameters in the zero-shot video-text retrieval task. Beyond this, our LanguageBind has greatly improved in the zero-shot video, audio, depth, and infrared understanding tasks. For instance, LanguageBind surpassing InterVideo by 1.9% on MSR-VTT, 8.8% on MSVD, 6.3% on DiDeMo, and 4.4% on ActivityNet. On the LLVIP and NYU-D datasets, LanguageBind outperforms ImageBind with 23.8% and 11.1% top-1 accuracy. Code address: https://github.com/PKU-YuanGroup/LanguageBind.
ChatLaw: Open-Source Legal Large Language Model with Integrated External Knowledge Bases
Jun 28, 2023Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown the potential to revolutionize natural language processing tasks in various domains, sparking great interest in vertical-specific large models. However, unlike proprietary models such as BloombergGPT and FinGPT, which have leveraged their unique data accumulations to make strides in the finance domain, there hasn't not many similar large language models in the Chinese legal domain to facilitate its digital transformation. In this paper, we propose an open-source legal large language model named ChatLaw. Due to the importance of data quality, we carefully designed a legal domain fine-tuning dataset. Additionally, to overcome the problem of model hallucinations in legal data screening during reference data retrieval, we introduce a method that combines vector database retrieval with keyword retrieval to effectively reduce the inaccuracy of relying solely on vector database retrieval. Furthermore, we propose a self-attention method to enhance the ability of large models to overcome errors present in reference data, further optimizing the issue of model hallucinations at the model level and improving the problem-solving capabilities of large models. We also open-sourced our model and part of the data at https://github.com/PKU-YuanGroup/ChatLaw.
SINCERE: Sequential Interaction Networks representation learning on Co-Evolving RiEmannian manifolds
May 06, 2023Abstract:Sequential interaction networks (SIN) have been commonly adopted in many applications such as recommendation systems, search engines and social networks to describe the mutual influence between users and items/products. Efforts on representing SIN are mainly focused on capturing the dynamics of networks in Euclidean space, and recently plenty of work has extended to hyperbolic geometry for implicit hierarchical learning. Previous approaches which learn the embedding trajectories of users and items achieve promising results. However, there are still a range of fundamental issues remaining open. For example, is it appropriate to place user and item nodes in one identical space regardless of their inherent discrepancy? Instead of residing in a single fixed curvature space, how will the representation spaces evolve when new interaction occurs? To explore these issues for sequential interaction networks, we propose SINCERE, a novel method representing Sequential Interaction Networks on Co-Evolving RiEmannian manifolds. SIN- CERE not only takes the user and item embedding trajectories in respective spaces into account, but also emphasizes on the space evolvement that how curvature changes over time. Specifically, we introduce a fresh cross-geometry aggregation which allows us to propagate information across different Riemannian manifolds without breaking conformal invariance, and a curvature estimator which is delicately designed to predict global curvatures effectively according to current local Ricci curvatures. Extensive experiments on several real-world datasets demonstrate the promising performance of SINCERE over the state-of-the-art sequential interaction prediction methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge