Renjun Xu
A Comprehensive Survey of Deep Research: Systems, Methodologies, and Applications
Jun 14, 2025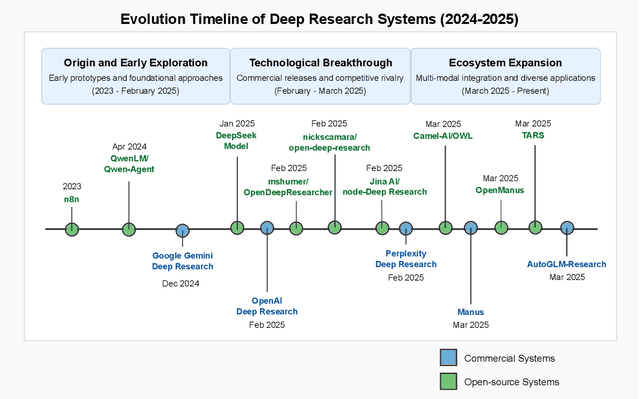

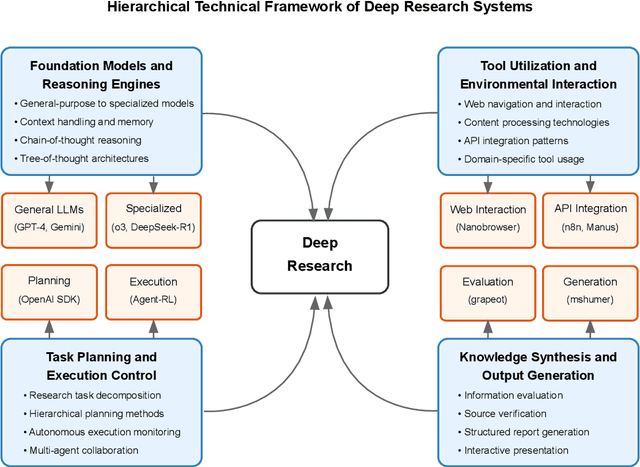

Abstract:This survey examines the rapidly evolving field of Deep Research systems -- AI-powered applications that automate complex research workflows through the integration of large language models, advanced information retrieval, and autonomous reasoning capabilities. We analyze more than 80 commercial and non-commercial implementations that have emerged since 2023, including OpenAI/Deep Research, Gemini/Deep Research, Perplexity/Deep Research, and numerous open-source alternatives. Through comprehensive examination, we propose a novel hierarchical taxonomy that categorizes systems according to four fundamental technical dimensions: foundation models and reasoning engines, tool utilization and environmental interaction, task planning and execution control, and knowledge synthesis and output generation. We explore the architectural patterns, implementation approaches, and domain-specific adaptations that characterize these systems across academic, scientific, business, and educational applications. Our analysis reveals both the significant capabilities of current implementations and the technical and ethical challenges they present regarding information accuracy, privacy, intellectual property, and accessibility. The survey concludes by identifying promising research directions in advanced reasoning architectures, multimodal integration, domain specialization, human-AI collaboration, and ecosystem standardization that will likely shape the future evolution of this transformative technology. By providing a comprehensive framework for understanding Deep Research systems, this survey contributes to both the theoretical understanding of AI-augmented knowledge work and the practical development of more capable, responsible, and accessible research technologies. The paper resources can be viewed at https://github.com/scienceaix/deepresearch.
Do PhD-level LLMs Truly Grasp Elementary Addition? Probing Rule Learning vs. Memorization in Large Language Models
Apr 07, 2025Abstract:Despite high benchmark scores, Large Language Models (LLMs) often fail simple problem, raising a critical question: Do LLMs learn mathematical principles or merely memorize patterns? Rather than designing increasingly complex benchmarks like recent works, we investigate this using elementary two-integer addition ($0$ to $2^{64}$), probing two core properties: commutativity ($A+B=B+A$) and compositional generalization (via isomorphic symbolic mappings, e.g., $7 \rightarrow y$). While state-of-the-art LLMs achieve 73.8-99.8\% accuracy on numerical addition, performance collapses to $\leq$7.5\% under symbolic mapping, indicating failure to generalize learned rules. Non-monotonic performance scaling with digit count and frequent commutativity violations (over 1,700 cases of $A+B \neq B+A$) further support this. Explicitly providing addition rules degrades performance by 81.2\% on average, while self-explanation maintains baseline accuracy, suggesting LLM arithmetic processing is misaligned with human-defined principles. Our findings indicate current LLMs rely on memory pattern over genuine rule learning, highlighting architectural limitations and the need for new approaches to achieve true mathematical reasoning.
Scaling Laws of Scientific Discovery with AI and Robot Scientists
Mar 28, 2025



Abstract:The rapid evolution of scientific inquiry highlights an urgent need for groundbreaking methodologies that transcend the limitations of traditional research. Conventional approaches, bogged down by manual processes and siloed expertise, struggle to keep pace with the demands of modern discovery. We envision an autonomous generalist scientist (AGS) system-a fusion of agentic AI and embodied robotics-that redefines the research lifecycle. This system promises to autonomously navigate physical and digital realms, weaving together insights from disparate disciplines with unprecedented efficiency. By embedding advanced AI and robot technologies into every phase-from hypothesis formulation to peer-ready manuscripts-AGS could slash the time and resources needed for scientific research in diverse field. We foresee a future where scientific discovery follows new scaling laws, driven by the proliferation and sophistication of such systems. As these autonomous agents and robots adapt to extreme environments and leverage a growing reservoir of knowledge, they could spark a paradigm shift, pushing the boundaries of what's possible and ushering in an era of relentless innovation.
Breaking the Box: Enhancing Remote Sensing Image Segmentation with Freehand Sketches
Mar 15, 2025Abstract:This work advances zero-shot interactive segmentation for remote sensing imagery through three key contributions. First, we propose a novel sketch-based prompting method, enabling users to intuitively outline objects, surpassing traditional point or box prompts. Second, we introduce LTL-Sensing, the first dataset pairing human sketches with remote sensing imagery, setting a benchmark for future research. Third, we present LTL-Net, a model featuring a multi-input prompting transport module tailored for freehand sketches. Extensive experiments show our approach significantly improves segmentation accuracy and robustness over state-of-the-art methods like SAM, fostering more intuitive human-AI collaboration in remote sensing analysis and enhancing its applications.
Syllables to Scenes: Literary-Guided Free-Viewpoint 3D Scene Synthesis from Japanese Haiku
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:In the era of the metaverse, where immersive technologies redefine human experiences, translating abstract literary concepts into navigable 3D environments presents a fundamental challenge in preserving semantic and emotional fidelity. This research introduces HaikuVerse, a novel framework for transforming poetic abstraction into spatial representation, with Japanese Haiku serving as an ideal test case due to its sophisticated encapsulation of profound emotions and imagery within minimal text. While existing text-to-3D methods struggle with nuanced interpretations, we present a literary-guided approach that synergizes traditional poetry analysis with advanced generative technologies. Our framework centers on two key innovations: (1) Hierarchical Literary-Criticism Theory Grounded Parsing (H-LCTGP), which captures both explicit imagery and implicit emotional resonance through structured semantic decomposition, and (2) Progressive Dimensional Synthesis (PDS), a multi-stage pipeline that systematically transforms poetic elements into coherent 3D scenes through sequential diffusion processes, geometric optimization, and real-time enhancement. Extensive experiments demonstrate that HaikuVerse significantly outperforms conventional text-to-3D approaches in both literary fidelity and visual quality, establishing a new paradigm for preserving cultural heritage in immersive digital spaces. Project website at: https://syllables-to-scenes.github.io/
UBER: Uncertainty-Based Evolution with Large Language Models for Automatic Heuristic Design
Dec 30, 2024



Abstract:NP-hard problem-solving traditionally relies on heuristics, but manually crafting effective heuristics for complex problems remains challenging. While recent work like FunSearch has demonstrated that large language models (LLMs) can be leveraged for heuristic design in evolutionary algorithm (EA) frameworks, their potential is not fully realized due to its deficiency in exploitation and exploration. We present UBER (Uncertainty-Based Evolution for Refinement), a method that enhances LLM+EA methods for automatic heuristic design by integrating uncertainty on top of the FunSearch framework. UBER introduces two key innovations: an Uncertainty-Inclusive Evolution Process (UIEP) for adaptive exploration-exploitation balance, and a principled Uncertainty-Inclusive Island Reset (UIIS) strategy for maintaining population diversity. Through extensive experiments on challenging NP-complete problems, UBER demonstrates significant improvements over FunSearch. Our work provides a new direction for the synergy of LLMs and EA, advancing the field of automatic heuristic design.
MetaRuleGPT: Recursive Numerical Reasoning of Language Models Trained with Simple Rules
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:Recent studies have highlighted the limitations of large language models in mathematical reasoning, particularly their inability to capture the underlying logic. Inspired by meta-learning, we propose that models should acquire not only task-specific knowledge but also transferable problem-solving skills. We introduce MetaRuleGPT, a novel Transformer-based architecture that performs precise numerical calculations and complex logical operations by learning and combining different rules. In contrast with traditional training sets, which are heavily composed of massive raw instance data, MetaRuleGPT is pre-trained on much less abstract datasets containing basic, compound, and iterative rules for mathematical reasoning. Extensive experimental results demonstrate MetaRuleGPT can mimic human's rule-following capabilities, break down complexity, and iteratively derive accurate results for complex mathematical problems. These findings prove the potential of rule learning to enhance the numerical reasoning abilities of language models.
Nova: An Iterative Planning and Search Approach to Enhance Novelty and Diversity of LLM Generated Ideas
Oct 18, 2024Abstract:Scientific innovation is pivotal for humanity, and harnessing large language models (LLMs) to generate research ideas could transform discovery. However, existing LLMs often produce simplistic and repetitive suggestions due to their limited ability in acquiring external knowledge for innovation. To address this problem, we introduce an enhanced planning and search methodology designed to boost the creative potential of LLM-based systems. Our approach involves an iterative process to purposely plan the retrieval of external knowledge, progressively enriching the idea generation with broader and deeper insights. Validation through automated and human assessments indicates that our framework substantially elevates the quality of generated ideas, particularly in novelty and diversity. The number of unique novel ideas produced by our framework is 3.4 times higher than without it. Moreover, our method outperforms the current state-of-the-art, generating at least 2.5 times more top-rated ideas based on 170 seed papers in a Swiss Tournament evaluation.
Unveiling the Impact of Multi-Modal Interactions on User Engagement: A Comprehensive Evaluation in AI-driven Conversations
Jun 21, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have significantly advanced user-bot interactions, enabling more complex and coherent dialogues. However, the prevalent text-only modality might not fully exploit the potential for effective user engagement. This paper explores the impact of multi-modal interactions, which incorporate images and audio alongside text, on user engagement in chatbot conversations. We conduct a comprehensive analysis using a diverse set of chatbots and real-user interaction data, employing metrics such as retention rate and conversation length to evaluate user engagement. Our findings reveal a significant enhancement in user engagement with multi-modal interactions compared to text-only dialogues. Notably, the incorporation of a third modality significantly amplifies engagement beyond the benefits observed with just two modalities. These results suggest that multi-modal interactions optimize cognitive processing and facilitate richer information comprehension. This study underscores the importance of multi-modality in chatbot design, offering valuable insights for creating more engaging and immersive AI communication experiences and informing the broader AI community about the benefits of multi-modal interactions in enhancing user engagement.
Scientific Large Language Models: A Survey on Biological & Chemical Domains
Jan 26, 2024
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged as a transformative power in enhancing natural language comprehension, representing a significant stride toward artificial general intelligence. The application of LLMs extends beyond conventional linguistic boundaries, encompassing specialized linguistic systems developed within various scientific disciplines. This growing interest has led to the advent of scientific LLMs, a novel subclass specifically engineered for facilitating scientific discovery. As a burgeoning area in the community of AI for Science, scientific LLMs warrant comprehensive exploration. However, a systematic and up-to-date survey introducing them is currently lacking. In this paper, we endeavor to methodically delineate the concept of "scientific language", whilst providing a thorough review of the latest advancements in scientific LLMs. Given the expansive realm of scientific disciplines, our analysis adopts a focused lens, concentrating on the biological and chemical domains. This includes an in-depth examination of LLMs for textual knowledge, small molecules, macromolecular proteins, genomic sequences, and their combinations, analyzing them in terms of model architectures, capabilities, datasets, and evaluation. Finally, we critically examine the prevailing challenges and point out promising research directions along with the advances of LLMs. By offering a comprehensive overview of technical developments in this field, this survey aspires to be an invaluable resource for researchers navigating the intricate landscape of scientific LLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge