Yihao Wang
ResAgent: Entropy-based Prior Point Discovery and Visual Reasoning for Referring Expression Segmentation
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Referring Expression Segmentation (RES) is a core vision-language segmentation task that enables pixel-level understanding of targets via free-form linguistic expressions, supporting critical applications such as human-robot interaction and augmented reality. Despite the progress of Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM)-based approaches, existing RES methods still suffer from two key limitations: first, the coarse bounding boxes from MLLMs lead to redundant or non-discriminative point prompts; second, the prevalent reliance on textual coordinate reasoning is unreliable, as it fails to distinguish targets from visually similar distractors. To address these issues, we propose \textbf{\model}, a novel RES framework integrating \textbf{E}ntropy-\textbf{B}ased Point \textbf{D}iscovery (\textbf{EBD}) and \textbf{V}ision-\textbf{B}ased \textbf{R}easoning (\textbf{VBR}). Specifically, EBD identifies high-information candidate points by modeling spatial uncertainty within coarse bounding boxes, treating point selection as an information maximization process. VBR verifies point correctness through joint visual-semantic alignment, abandoning text-only coordinate inference for more robust validation. Built on these components, \model implements a coarse-to-fine workflow: bounding box initialization, entropy-guided point discovery, vision-based validation, and mask decoding. Extensive evaluations on four benchmark datasets (RefCOCO, RefCOCO+, RefCOCOg, and ReasonSeg) demonstrate that \model achieves new state-of-the-art performance across all four benchmarks, highlighting its effectiveness in generating accurate and semantically grounded segmentation masks with minimal prompts.
VLA-Adapter: An Effective Paradigm for Tiny-Scale Vision-Language-Action Model
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models typically bridge the gap between perceptual and action spaces by pre-training a large-scale Vision-Language Model (VLM) on robotic data. While this approach greatly enhances performance, it also incurs significant training costs. In this paper, we investigate how to effectively bridge vision-language (VL) representations to action (A). We introduce VLA-Adapter, a novel paradigm designed to reduce the reliance of VLA models on large-scale VLMs and extensive pre-training. To this end, we first systematically analyze the effectiveness of various VL conditions and present key findings on which conditions are essential for bridging perception and action spaces. Based on these insights, we propose a lightweight Policy module with Bridge Attention, which autonomously injects the optimal condition into the action space. In this way, our method achieves high performance using only a 0.5B-parameter backbone, without any robotic data pre-training. Extensive experiments on both simulated and real-world robotic benchmarks demonstrate that VLA-Adapter not only achieves state-of-the-art level performance, but also offers the fast inference speed reported to date. Furthermore, thanks to the proposed advanced bridging paradigm, VLA-Adapter enables the training of a powerful VLA model in just 8 hours on a single consumer-grade GPU, greatly lowering the barrier to deploying the VLA model. Project page: https://vla-adapter.github.io/.
FMNV: A Dataset of Media-Published News Videos for Fake News Detection
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:News media, particularly video-based platforms, have become deeply embedded in daily life, concurrently amplifying risks of misinformation dissemination. Consequently, multimodal fake news detection has garnered significant research attention. However, existing datasets predominantly comprise user-generated videos characterized by crude editing and limited public engagement, whereas professionally crafted fake news videos disseminated by media outlets often politically or virally motivated pose substantially greater societal harm. To address this gap, we construct FMNV, a novel dataset exclusively composed of news videos published by media organizations. Through empirical analysis of existing datasets and our curated collection, we categorize fake news videos into four distinct types. Building upon this taxonomy, we employ Large Language Models (LLMs) to automatically generate deceptive content by manipulating authentic media-published news videos. Furthermore, we propose FMNVD, a baseline model featuring a dual-stream architecture integrating CLIP and Faster R-CNN for video feature extraction, enhanced by co-attention mechanisms for feature refinement and multimodal aggregation. Comparative experiments demonstrate both the generalization capability of FMNV across multiple baselines and the superior detection efficacy of FMNVD. This work establishes critical benchmarks for detecting high-impact fake news in media ecosystems while advancing methodologies for cross-modal inconsistency analysis.
LIAM: Multimodal Transformer for Language Instructions, Images, Actions and Semantic Maps
Mar 15, 2025



Abstract:The availability of large language models and open-vocabulary object perception methods enables more flexibility for domestic service robots. The large variability of domestic tasks can be addressed without implementing each task individually by providing the robot with a task description along with appropriate environment information. In this work, we propose LIAM - an end-to-end model that predicts action transcripts based on language, image, action, and map inputs. Language and image inputs are encoded with a CLIP backbone, for which we designed two pre-training tasks to fine-tune its weights and pre-align the latent spaces. We evaluate our method on the ALFRED dataset, a simulator-generated benchmark for domestic tasks. Our results demonstrate the importance of pre-aligning embedding spaces from different modalities and the efficacy of incorporating semantic maps.
A Stronger Mixture of Low-Rank Experts for Fine-Tuning Foundation Models
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:In order to streamline the fine-tuning of foundation models, Low-Rank Adapters (LoRAs) have been substantially adopted across various fields, including instruction tuning and domain adaptation. The underlying concept of LoRA involves decomposing a full-rank matrix into the product of two lower-rank matrices, which reduces storage consumption and accelerates the training process. Furthermore, to address the limited expressive capacity of LoRA, the Mixture-of-Expert (MoE) has been introduced for incorporating multiple LoRA adapters. The integration of LoRA experts leads to a visible improvement across several downstream scenes. However, the mixture of LoRAs (MoE-LoRA) still exhibits its low robustness during tuning and inferring. Inspired by the Riemannian Preconditioners which train LoRA as a sub-space projector, we propose a new training strategy for MoE-LoRA, to stabilize and boost its feature learning procedure by multi-space projections. Examinations on SGD and AdamW optimizers demonstrate the effectiveness of our methodology. Source code is available at https://github.com/THUDM/MoELoRA_Riemannian.
Toward Copyright Integrity and Verifiability via Multi-Bit Watermarking for Intelligent Transportation Systems
Feb 08, 2025Abstract:Intelligent transportation systems (ITS) use advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence to significantly improve traffic flow management efficiency, and promote the intelligent development of the transportation industry. However, if the data in ITS is attacked, such as tampering or forgery, it will endanger public safety and cause social losses. Therefore, this paper proposes a watermarking that can verify the integrity of copyright in response to the needs of ITS, termed ITSmark. ITSmark focuses on functions such as extracting watermarks, verifying permission, and tracing tampered locations. The scheme uses the copyright information to build the multi-bit space and divides this space into multiple segments. These segments will be assigned to tokens. Thus, the next token is determined by its segment which contains the copyright. In this way, the obtained data contains the custom watermark. To ensure the authorization, key parameters are encrypted during copyright embedding to obtain cipher data. Only by possessing the correct cipher data and private key, can the user entirely extract the watermark. Experiments show that ITSmark surpasses baseline performances in data quality, extraction accuracy, and unforgeability. It also shows unique capabilities of permission verification and tampered location tracing, which ensures the security of extraction and the reliability of copyright verification. Furthermore, ITSmark can also customize the watermark embedding position and proportion according to user needs, making embedding more flexible.
* 11 figures, 10 tables. Accepted for publication in IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems (accepted versions, not the IEEE-published versions). \copyright 2025 IEEE. All rights reserved, including rights for text and data mining, and training of artificial intelligence and similar technologies. Personal use is permitted, but republication/redistribution requires IEEE permission
U-GIFT: Uncertainty-Guided Firewall for Toxic Speech in Few-Shot Scenario
Jan 01, 2025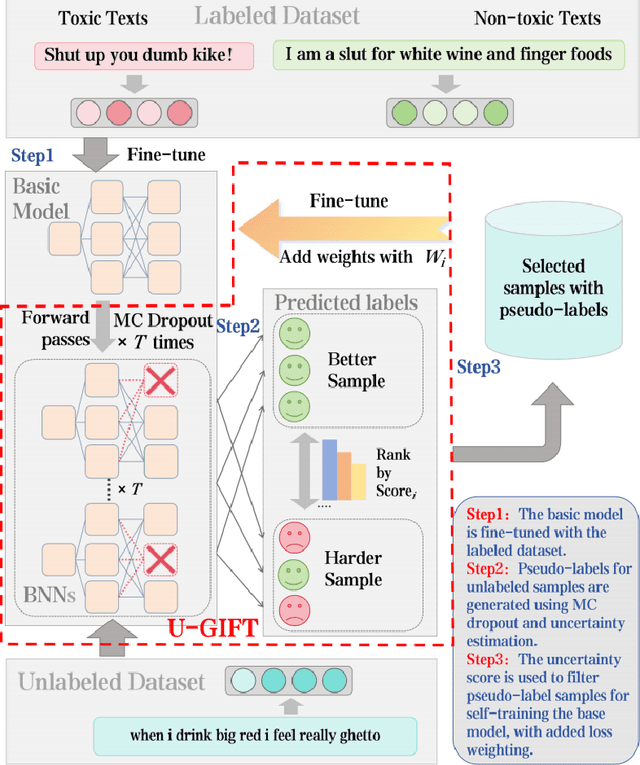
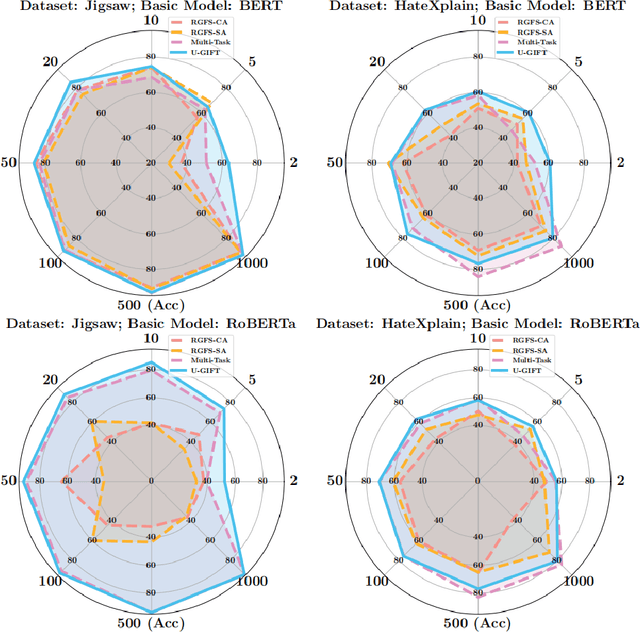
Abstract:With the widespread use of social media, user-generated content has surged on online platforms. When such content includes hateful, abusive, offensive, or cyberbullying behavior, it is classified as toxic speech, posing a significant threat to the online ecosystem's integrity and safety. While manual content moderation is still prevalent, the overwhelming volume of content and the psychological strain on human moderators underscore the need for automated toxic speech detection. Previously proposed detection methods often rely on large annotated datasets; however, acquiring such datasets is both costly and challenging in practice. To address this issue, we propose an uncertainty-guided firewall for toxic speech in few-shot scenarios, U-GIFT, that utilizes self-training to enhance detection performance even when labeled data is limited. Specifically, U-GIFT combines active learning with Bayesian Neural Networks (BNNs) to automatically identify high-quality samples from unlabeled data, prioritizing the selection of pseudo-labels with higher confidence for training based on uncertainty estimates derived from model predictions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that U-GIFT significantly outperforms competitive baselines in few-shot detection scenarios. In the 5-shot setting, it achieves a 14.92\% performance improvement over the basic model. Importantly, U-GIFT is user-friendly and adaptable to various pre-trained language models (PLMs). It also exhibits robust performance in scenarios with sample imbalance and cross-domain settings, while showcasing strong generalization across various language applications. We believe that U-GIFT provides an efficient solution for few-shot toxic speech detection, offering substantial support for automated content moderation in cyberspace, thereby acting as a firewall to promote advancements in cybersecurity.
DeSplat: Decomposed Gaussian Splatting for Distractor-Free Rendering
Nov 29, 2024Abstract:Gaussian splatting enables fast novel view synthesis in static 3D environments. However, reconstructing real-world environments remains challenging as distractors or occluders break the multi-view consistency assumption required for accurate 3D reconstruction. Most existing methods rely on external semantic information from pre-trained models, introducing additional computational overhead as pre-processing steps or during optimization. In this work, we propose a novel method, DeSplat, that directly separates distractors and static scene elements purely based on volume rendering of Gaussian primitives. We initialize Gaussians within each camera view for reconstructing the view-specific distractors to separately model the static 3D scene and distractors in the alpha compositing stages. DeSplat yields an explicit scene separation of static elements and distractors, achieving comparable results to prior distractor-free approaches without sacrificing rendering speed. We demonstrate DeSplat's effectiveness on three benchmark data sets for distractor-free novel view synthesis. See the project website at https://aaltoml.github.io/desplat/.
LLM4PR: Improving Post-Ranking in Search Engine with Large Language Models
Nov 02, 2024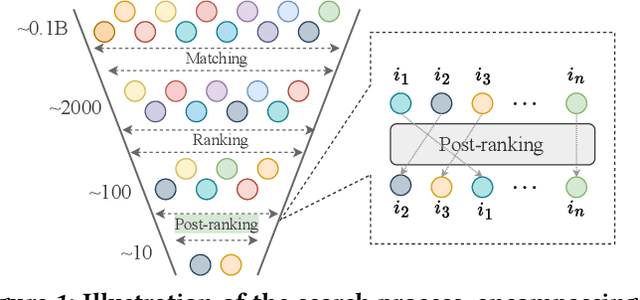



Abstract:Alongside the rapid development of Large Language Models (LLMs), there has been a notable increase in efforts to integrate LLM techniques in information retrieval (IR) and search engines (SE). Recently, an additional post-ranking stage is suggested in SE to enhance user satisfaction in practical applications. Nevertheless, research dedicated to enhancing the post-ranking stage through LLMs remains largely unexplored. In this study, we introduce a novel paradigm named Large Language Models for Post-Ranking in search engine (LLM4PR), which leverages the capabilities of LLMs to accomplish the post-ranking task in SE. Concretely, a Query-Instructed Adapter (QIA) module is designed to derive the user/item representation vectors by incorporating their heterogeneous features. A feature adaptation step is further introduced to align the semantics of user/item representations with the LLM. Finally, the LLM4PR integrates a learning to post-rank step, leveraging both a main task and an auxiliary task to fine-tune the model to adapt the post-ranking task. Experiment studies demonstrate that the proposed framework leads to significant improvements and exhibits state-of-the-art performance compared with other alternatives.
State-of-the-art Advances of Deep-learning Linguistic Steganalysis Research
Sep 03, 2024Abstract:With the evolution of generative linguistic steganography techniques, conventional steganalysis falls short in robustly quantifying the alterations induced by steganography, thereby complicating detection. Consequently, the research paradigm has pivoted towards deep-learning-based linguistic steganalysis. This study offers a comprehensive review of existing contributions and evaluates prevailing developmental trajectories. Specifically, we first provided a formalized exposition of the general formulas for linguistic steganalysis, while comparing the differences between this field and the domain of text classification. Subsequently, we classified the existing work into two levels based on vector space mapping and feature extraction models, thereby comparing the research motivations, model advantages, and other details. A comparative analysis of the experiments is conducted to assess the performances. Finally, the challenges faced by this field are discussed, and several directions for future development and key issues that urgently need to be addressed are proposed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge