Zhong Qian
FMNV: A Dataset of Media-Published News Videos for Fake News Detection
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:News media, particularly video-based platforms, have become deeply embedded in daily life, concurrently amplifying risks of misinformation dissemination. Consequently, multimodal fake news detection has garnered significant research attention. However, existing datasets predominantly comprise user-generated videos characterized by crude editing and limited public engagement, whereas professionally crafted fake news videos disseminated by media outlets often politically or virally motivated pose substantially greater societal harm. To address this gap, we construct FMNV, a novel dataset exclusively composed of news videos published by media organizations. Through empirical analysis of existing datasets and our curated collection, we categorize fake news videos into four distinct types. Building upon this taxonomy, we employ Large Language Models (LLMs) to automatically generate deceptive content by manipulating authentic media-published news videos. Furthermore, we propose FMNVD, a baseline model featuring a dual-stream architecture integrating CLIP and Faster R-CNN for video feature extraction, enhanced by co-attention mechanisms for feature refinement and multimodal aggregation. Comparative experiments demonstrate both the generalization capability of FMNV across multiple baselines and the superior detection efficacy of FMNVD. This work establishes critical benchmarks for detecting high-impact fake news in media ecosystems while advancing methodologies for cross-modal inconsistency analysis.
Multimodal Fake News Video Explanation Generation
Jan 15, 2025Abstract:Multi-modal explanation involves the assessment of the veracity of a variety of different content, and relies on multiple information modalities to comprehensively consider the relevance and consistency between modalities. Most existing fake news video detection methods focus on improving accuracy while ignoring the importance of providing explanations. In this paper, we propose a novel problem - Fake News Video Explanation (FNVE) - Given a multimodal news containing both video and caption text, we aim to generate natural language explanations to reveal the truth of predictions. To this end, we develop FakeNVE, a new dataset of explanations for truthfully multimodal posts, where each explanation is a natural language (English) sentence describing the attribution of a news thread. We benchmark FakeNVE by using a multimodal transformer-based architecture. Subsequently, a BART-based autoregressive decoder is used as the generator. Empirical results show compelling results for various baselines (applicable to FNVE) across multiple evaluation metrics. We also perform human evaluation on explanation generation, achieving high scores for both adequacy and fluency.
Official-NV: A News Video Dataset for Multimodal Fake News Detection
Jul 28, 2024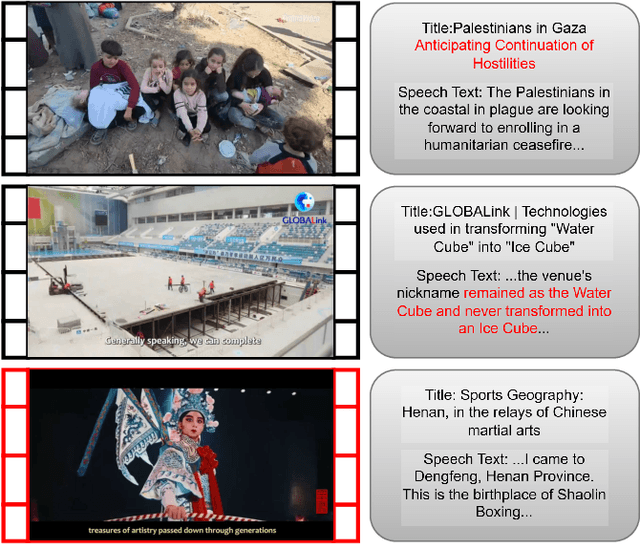


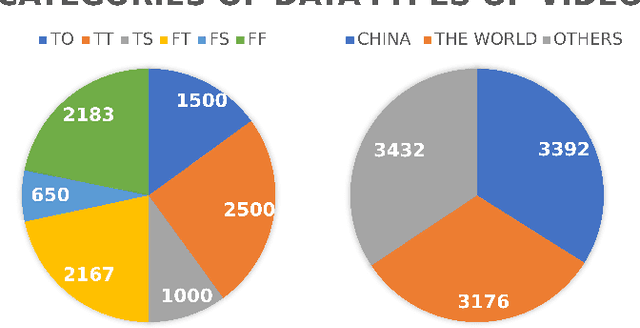
Abstract:News media, especially video news media, have penetrated into every aspect of daily life, which also brings the risk of fake news. Therefore, multimodal fake news detection has recently received more attention. However, the number of fake news detection data sets for video modal is small, and these data sets are composed of unofficial videos uploaded by users, so there is too much useless data. To solve this problem, we present in this paper a dataset named Official-NV, which consists of officially published news videos on Xinhua. We crawled videos on Xinhua, and then extended the data set using LLM generation and manual modification. In addition, we benchmarked the data set presented in this paper using a baseline model to demonstrate the advantage of Official-NV in multimodal fake news detection.
Interpretable Rumor Detection in Microblogs by Attending to User Interactions
Jan 29, 2020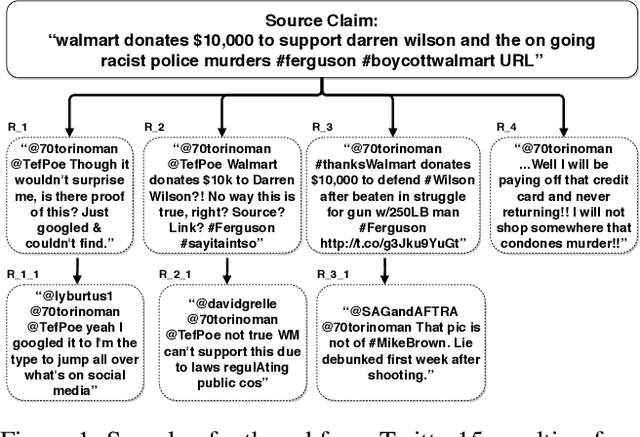
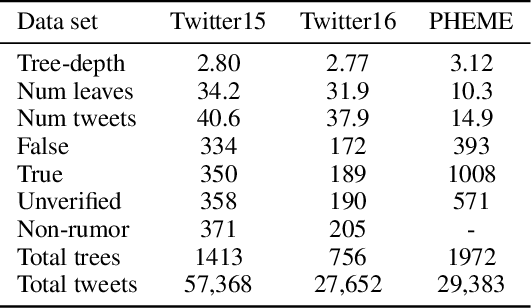
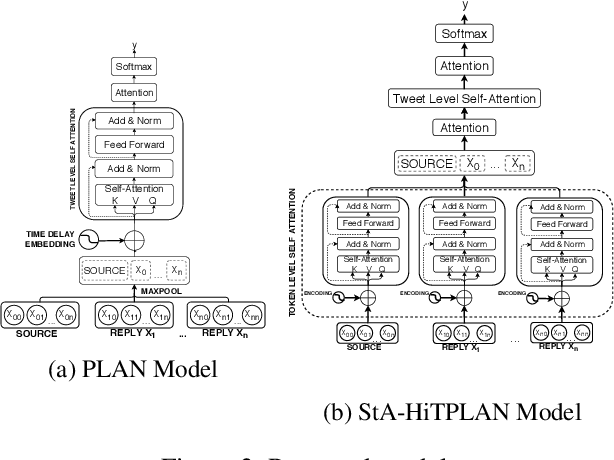
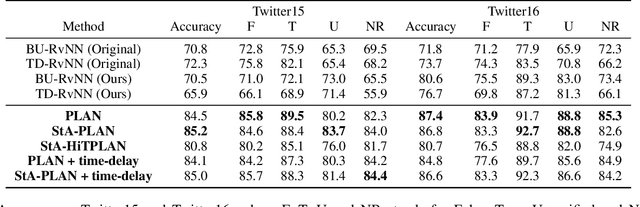
Abstract:We address rumor detection by learning to differentiate between the community's response to real and fake claims in microblogs. Existing state-of-the-art models are based on tree models that model conversational trees. However, in social media, a user posting a reply might be replying to the entire thread rather than to a specific user. We propose a post-level attention model (PLAN) to model long distance interactions between tweets with the multi-head attention mechanism in a transformer network. We investigated variants of this model: (1) a structure aware self-attention model (StA-PLAN) that incorporates tree structure information in the transformer network, and (2) a hierarchical token and post-level attention model (StA-HiTPLAN) that learns a sentence representation with token-level self-attention. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to evaluate our models on two rumor detection data sets: the PHEME data set as well as the Twitter15 and Twitter16 data sets. We show that our best models outperform current state-of-the-art models for both data sets. Moreover, the attention mechanism allows us to explain rumor detection predictions at both token-level and post-level.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge