Qiaoming Zhu
FieldGen: From Teleoperated Pre-Manipulation Trajectories to Field-Guided Data Generation
Oct 23, 2025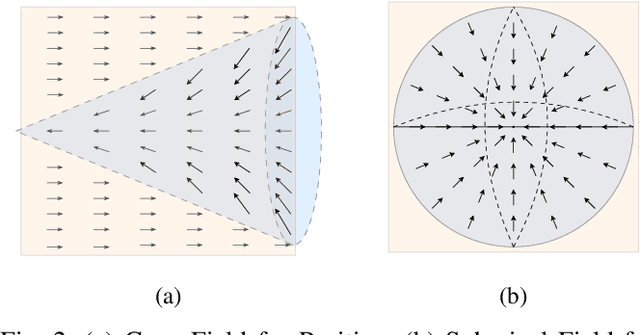
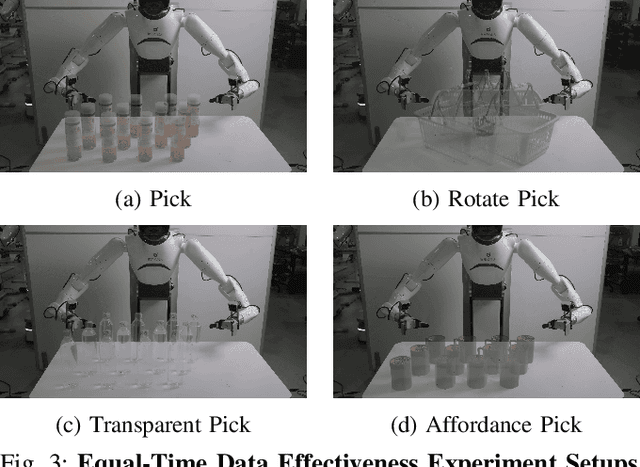
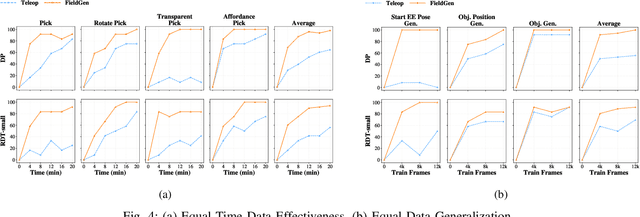
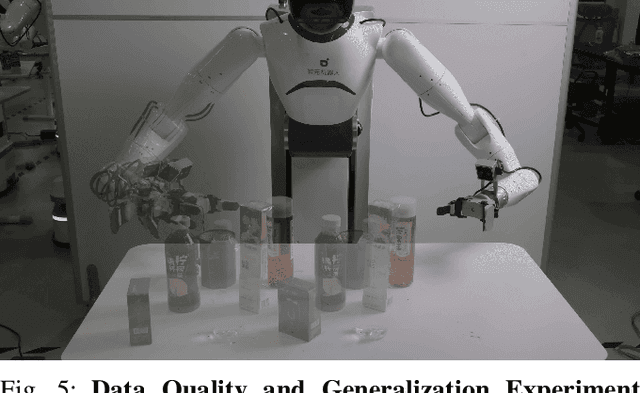
Abstract:Large-scale and diverse datasets are vital for training robust robotic manipulation policies, yet existing data collection methods struggle to balance scale, diversity, and quality. Simulation offers scalability but suffers from sim-to-real gaps, while teleoperation yields high-quality demonstrations with limited diversity and high labor cost. We introduce FieldGen, a field-guided data generation framework that enables scalable, diverse, and high-quality real-world data collection with minimal human supervision. FieldGen decomposes manipulation into two stages: a pre-manipulation phase, allowing trajectory diversity, and a fine manipulation phase requiring expert precision. Human demonstrations capture key contact and pose information, after which an attraction field automatically generates diverse trajectories converging to successful configurations. This decoupled design combines scalable trajectory diversity with precise supervision. Moreover, FieldGen-Reward augments generated data with reward annotations to further enhance policy learning. Experiments demonstrate that policies trained with FieldGen achieve higher success rates and improved stability compared to teleoperation-based baselines, while significantly reducing human effort in long-term real-world data collection. Webpage is available at https://fieldgen.github.io/.
ICR: Iterative Clarification and Rewriting for Conversational Search
Sep 05, 2025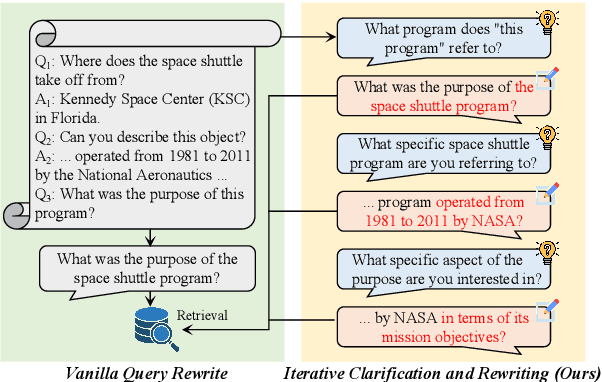
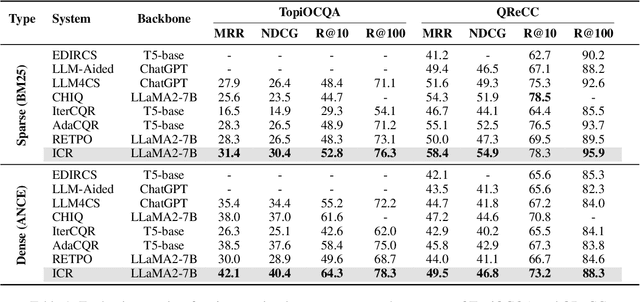
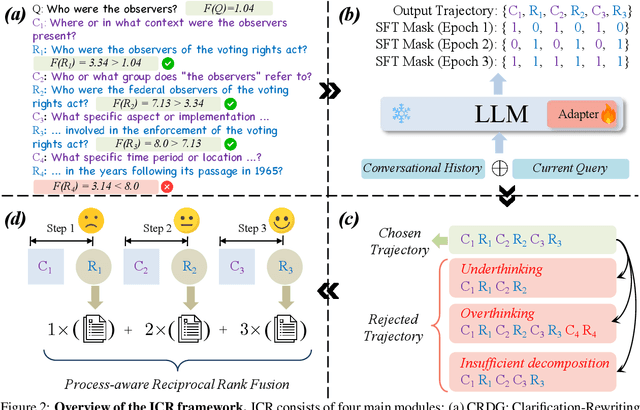
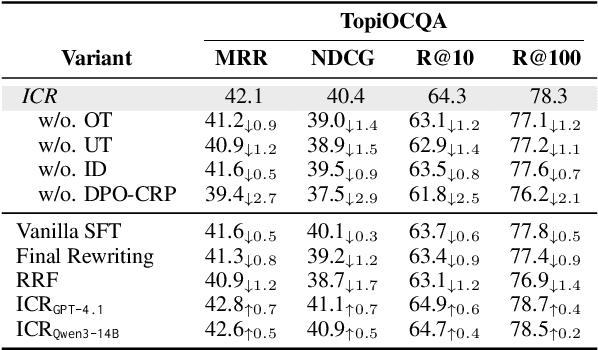
Abstract:Most previous work on Conversational Query Rewriting employs an end-to-end rewriting paradigm. However, this approach is hindered by the issue of multiple fuzzy expressions within the query, which complicates the simultaneous identification and rewriting of multiple positions. To address this issue, we propose a novel framework ICR (Iterative Clarification and Rewriting), an iterative rewriting scheme that pivots on clarification questions. Within this framework, the model alternates between generating clarification questions and rewritten queries. The experimental results show that our ICR can continuously improve retrieval performance in the clarification-rewriting iterative process, thereby achieving state-of-the-art performance on two popular datasets.
Improving Dialogue Discourse Parsing through Discourse-aware Utterance Clarification
Jun 18, 2025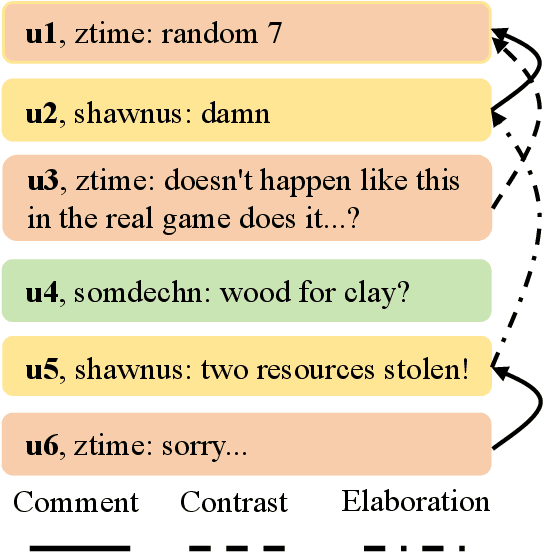
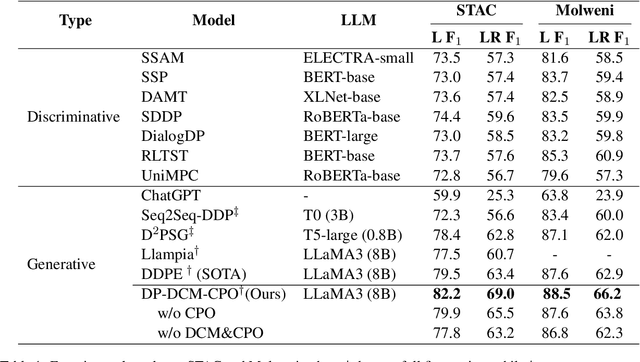
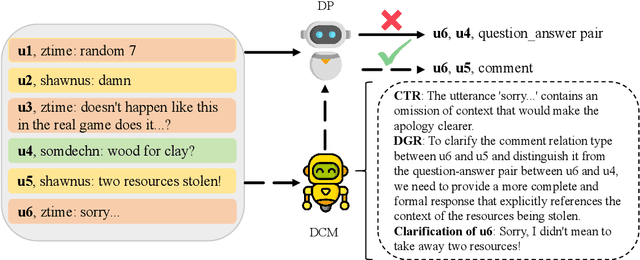
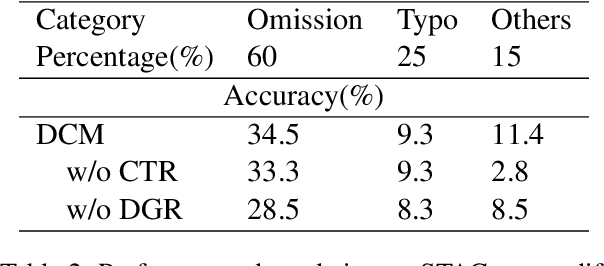
Abstract:Dialogue discourse parsing aims to identify and analyze discourse relations between the utterances within dialogues. However, linguistic features in dialogues, such as omission and idiom, frequently introduce ambiguities that obscure the intended discourse relations, posing significant challenges for parsers. To address this issue, we propose a Discourse-aware Clarification Module (DCM) to enhance the performance of the dialogue discourse parser. DCM employs two distinct reasoning processes: clarification type reasoning and discourse goal reasoning. The former analyzes linguistic features, while the latter distinguishes the intended relation from the ambiguous one. Furthermore, we introduce Contribution-aware Preference Optimization (CPO) to mitigate the risk of erroneous clarifications, thereby reducing cascading errors. CPO enables the parser to assess the contributions of the clarifications from DCM and provide feedback to optimize the DCM, enhancing its adaptability and alignment with the parser's requirements. Extensive experiments on the STAC and Molweni datasets demonstrate that our approach effectively resolves ambiguities and significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art (SOTA) baselines.
Enhancing Goal-oriented Proactive Dialogue Systems via Consistency Reflection and Correction
Jun 16, 2025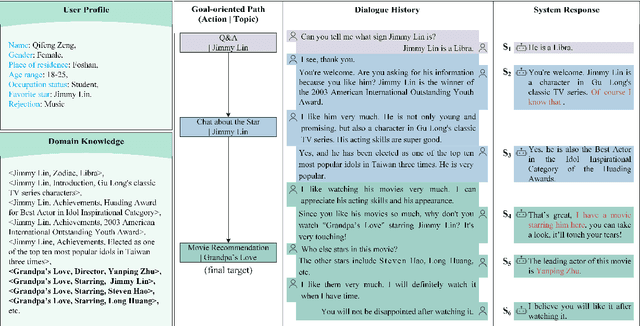
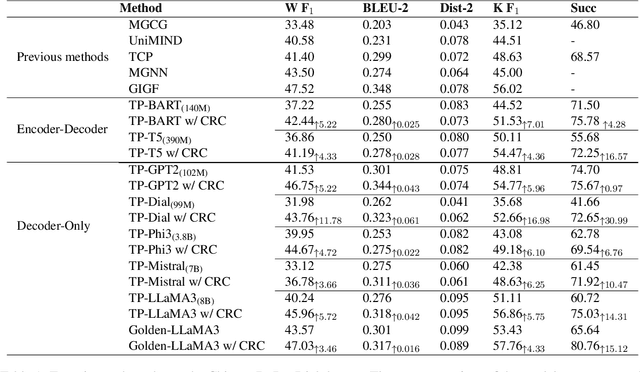
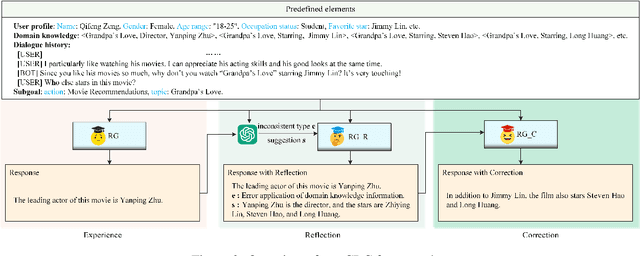
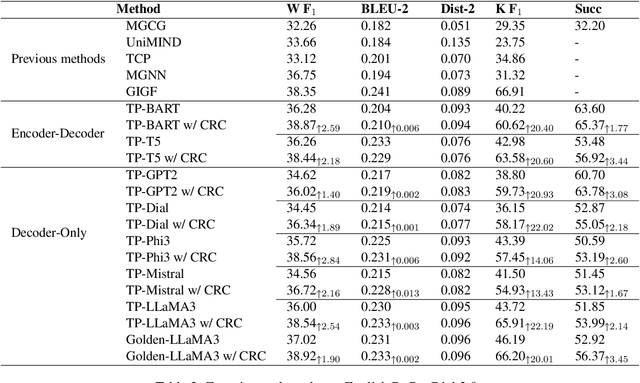
Abstract:This paper proposes a consistency reflection and correction method for goal-oriented dialogue systems.
Incomplete Utterance Rewriting with Editing Operation Guidance and Utterance Augmentation
Mar 20, 2025Abstract:Although existing fashionable generation methods on Incomplete Utterance Rewriting (IUR) can generate coherent utterances, they often result in the inclusion of irrelevant and redundant tokens in rewritten utterances due to their inability to focus on critical tokens in dialogue context. Furthermore, the limited size of the training datasets also contributes to the insufficient training of the IUR model. To address the first issue, we propose a multi-task learning framework EO-IUR (Editing Operation-guided Incomplete Utterance Rewriting) that introduces the editing operation labels generated by sequence labeling module to guide generation model to focus on critical tokens. Furthermore, we introduce a token-level heterogeneous graph to represent dialogues. To address the second issue, we propose a two-dimensional utterance augmentation strategy, namely editing operation-based incomplete utterance augmentation and LLM-based historical utterance augmentation. The experimental results on three datasets demonstrate that our EO-IUR outperforms previous state-of-the-art (SOTA) baselines in both open-domain and task-oriented dialogue. The code will be available at https://github.com/Dewset/EO-IUR.
Two-stage Incomplete Utterance Rewriting on Editing Operation
Mar 20, 2025Abstract:Previous work on Incomplete Utterance Rewriting (IUR) has primarily focused on generating rewritten utterances based solely on dialogue context, ignoring the widespread phenomenon of coreference and ellipsis in dialogues. To address this issue, we propose a novel framework called TEO (\emph{Two-stage approach on Editing Operation}) for IUR, in which the first stage generates editing operations and the second stage rewrites incomplete utterances utilizing the generated editing operations and the dialogue context. Furthermore, an adversarial perturbation strategy is proposed to mitigate cascading errors and exposure bias caused by the inconsistency between training and inference in the second stage. Experimental results on three IUR datasets show that our TEO outperforms the SOTA models significantly.
Revealing and Mitigating Over-Attention in Knowledge Editing
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models have demonstrated superior performance across a wide range of tasks, but they still exhibit undesirable errors due to incorrect knowledge learned from the training data. To avoid this, knowledge editing methods emerged to precisely edit the specific model knowledge via efficiently modifying a very small percentage of parameters. % However, those methods can lead to the problem of Specificity Failure: when the content related to the edited knowledge occurs in the context, it can inadvertently corrupt other pre-existing knowledge. However, those methods can lead to the problem of Specificity Failure, where the existing knowledge and capabilities are severely degraded due to editing. Our preliminary indicates that Specificity Failure primarily stems from the model's attention heads assigning excessive attention scores to entities related to the edited knowledge, thereby unduly focusing on specific snippets within the context, which we denote as the Attention Drift phenomenon. To mitigate such Attention Drift issue, we introduce a simple yet effective method Selective Attention Drift Restriction}(SADR), which introduces an additional regularization term during the knowledge editing process to restrict changes in the attention weight distribution, thereby preventing undue focus on the edited entity. Experiments on five frequently used strong LLMs demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, where SADR can significantly mitigate Specificity Failure in the predominant knowledge editing tasks.
Multimodal Fake News Video Explanation Generation
Jan 15, 2025Abstract:Multi-modal explanation involves the assessment of the veracity of a variety of different content, and relies on multiple information modalities to comprehensively consider the relevance and consistency between modalities. Most existing fake news video detection methods focus on improving accuracy while ignoring the importance of providing explanations. In this paper, we propose a novel problem - Fake News Video Explanation (FNVE) - Given a multimodal news containing both video and caption text, we aim to generate natural language explanations to reveal the truth of predictions. To this end, we develop FakeNVE, a new dataset of explanations for truthfully multimodal posts, where each explanation is a natural language (English) sentence describing the attribution of a news thread. We benchmark FakeNVE by using a multimodal transformer-based architecture. Subsequently, a BART-based autoregressive decoder is used as the generator. Empirical results show compelling results for various baselines (applicable to FNVE) across multiple evaluation metrics. We also perform human evaluation on explanation generation, achieving high scores for both adequacy and fluency.
Unleashing Reasoning Capability of LLMs via Scalable Question Synthesis from Scratch
Oct 24, 2024



Abstract:The availability of high-quality data is one of the most important factors in improving the reasoning capability of LLMs. Existing works have demonstrated the effectiveness of creating more instruction data from seed questions or knowledge bases. Recent research indicates that continually scaling up data synthesis from strong models (e.g., GPT-4) can further elicit reasoning performance. Though promising, the open-sourced community still lacks high-quality data at scale and scalable data synthesis methods with affordable costs. To address this, we introduce ScaleQuest, a scalable and novel data synthesis method that utilizes "small-size" (e.g., 7B) open-source models to generate questions from scratch without the need for seed data with complex augmentation constraints. With the efficient ScaleQuest, we automatically constructed a mathematical reasoning dataset consisting of 1 million problem-solution pairs, which are more effective than existing open-sourced datasets. It can universally increase the performance of mainstream open-source models (i.e., Mistral, Llama3, DeepSeekMath, and Qwen2-Math) by achieving 29.2% to 46.4% gains on MATH. Notably, simply fine-tuning the Qwen2-Math-7B-Base model with our dataset can even surpass Qwen2-Math-7B-Instruct, a strong and well-aligned model on closed-source data, and proprietary models such as GPT-4-Turbo and Claude-3.5 Sonnet.
LOGO -- Long cOntext aliGnment via efficient preference Optimization
Oct 24, 2024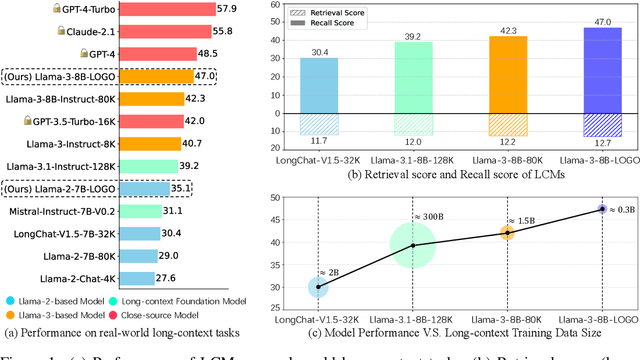
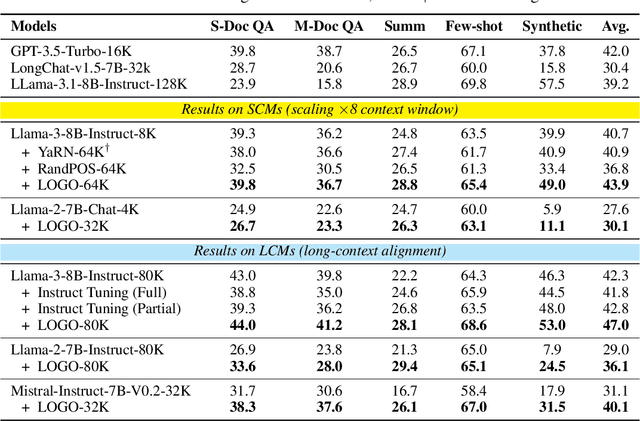
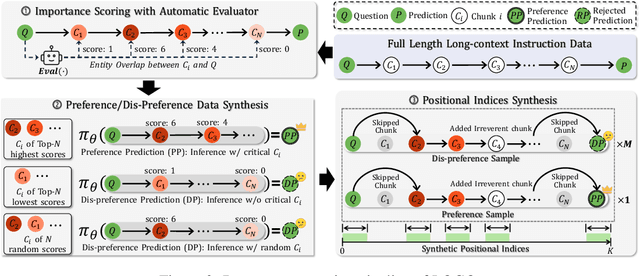
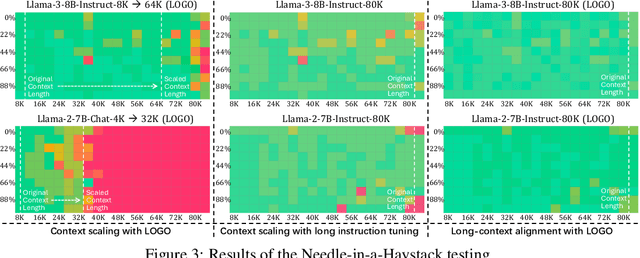
Abstract:Long-context models(LCMs) have shown great potential in processing long input sequences(even more than 100M tokens) conveniently and effectively. With significant progress, recent research has pointed out that LCMs can accurately locate token-level salient information within the context. Yet, the generation performance of these LCMs is far from satisfactory and might result in misaligned responses, such as hallucinations. To enhance the generation capability of LCMs, existing works have investigated the effects of data size and quality for both pre-training and instruction tuning. Though achieving meaningful improvement, previous methods fall short in either effectiveness or efficiency. In this paper, we introduce LOGO(Long cOntext aliGnment via efficient preference Optimization), a training strategy that first introduces preference optimization for long-context alignment. To overcome the GPU memory-bound issue caused by the long sequence, LOGO employs a reference-free preference optimization strategy and adopts a position synthesis method to construct the training data. By training with only 0.3B data on a single 8$\times$A800 GPU machine for 16 hours, LOGO allows the Llama-3-8B-Instruct-80K model to achieve comparable performance with GPT-4 in real-world long-context tasks while preserving the model's original capabilities on other tasks, e.g., language modeling and MMLU. Moreover, LOGO can extend the model's context window size while enhancing its generation performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge