Yixin Ji
Taming the Titans: A Survey of Efficient LLM Inference Serving
Apr 28, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) for Generative AI have achieved remarkable progress, evolving into sophisticated and versatile tools widely adopted across various domains and applications. However, the substantial memory overhead caused by their vast number of parameters, combined with the high computational demands of the attention mechanism, poses significant challenges in achieving low latency and high throughput for LLM inference services. Recent advancements, driven by groundbreaking research, have significantly accelerated progress in this field. This paper provides a comprehensive survey of these methods, covering fundamental instance-level approaches, in-depth cluster-level strategies, emerging scenario directions, and other miscellaneous but important areas. At the instance level, we review model placement, request scheduling, decoding length prediction, storage management, and the disaggregation paradigm. At the cluster level, we explore GPU cluster deployment, multi-instance load balancing, and cloud service solutions. For emerging scenarios, we organize the discussion around specific tasks, modules, and auxiliary methods. To ensure a holistic overview, we also highlight several niche yet critical areas. Finally, we outline potential research directions to further advance the field of LLM inference serving.
Test-time Computing: from System-1 Thinking to System-2 Thinking
Jan 05, 2025



Abstract:The remarkable performance of the o1 model in complex reasoning demonstrates that test-time computing scaling can further unlock the model's potential, enabling powerful System-2 thinking. However, there is still a lack of comprehensive surveys for test-time computing scaling. We trace the concept of test-time computing back to System-1 models. In System-1 models, test-time computing addresses distribution shifts and improves robustness and generalization through parameter updating, input modification, representation editing, and output calibration. In System-2 models, it enhances the model's reasoning ability to solve complex problems through repeated sampling, self-correction, and tree search. We organize this survey according to the trend of System-1 to System-2 thinking, highlighting the key role of test-time computing in the transition from System-1 models to weak System-2 models, and then to strong System-2 models. We also point out a few possible future directions.
Boosting LLM-based Relevance Modeling with Distribution-Aware Robust Learning
Dec 17, 2024Abstract:With the rapid advancement of pre-trained large language models (LLMs), recent endeavors have leveraged the capabilities of LLMs in relevance modeling, resulting in enhanced performance. This is usually done through the process of fine-tuning LLMs on specifically annotated datasets to determine the relevance between queries and items. However, there are two limitations when LLMs are naively employed for relevance modeling through fine-tuning and inference. First, it is not inherently efficient for performing nuanced tasks beyond simple yes or no answers, such as assessing search relevance. It may therefore tend to be overconfident and struggle to distinguish fine-grained degrees of relevance (e.g., strong relevance, weak relevance, irrelevance) used in search engines. Second, it exhibits significant performance degradation when confronted with data distribution shift in real-world scenarios. In this paper, we propose a novel Distribution-Aware Robust Learning framework (DaRL) for relevance modeling in Alipay Search. Specifically, we design an effective loss function to enhance the discriminability of LLM-based relevance modeling across various fine-grained degrees of query-item relevance. To improve the generalizability of LLM-based relevance modeling, we first propose the Distribution-Aware Sample Augmentation (DASA) module. This module utilizes out-of-distribution (OOD) detection techniques to actively select appropriate samples that are not well covered by the original training set for model fine-tuning. Furthermore, we adopt a multi-stage fine-tuning strategy to simultaneously improve in-distribution (ID) and OOD performance, bridging the performance gap between them. DaRL has been deployed online to serve the Alipay's insurance product search...
* 8 pages
CPRM: A LLM-based Continual Pre-training Framework for Relevance Modeling in Commercial Search
Dec 03, 2024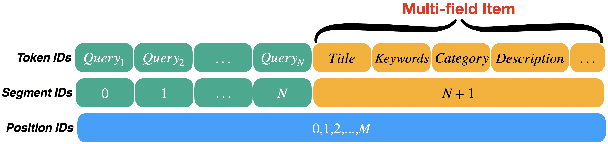
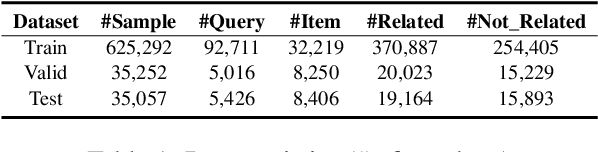
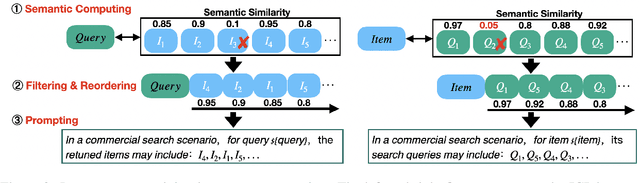
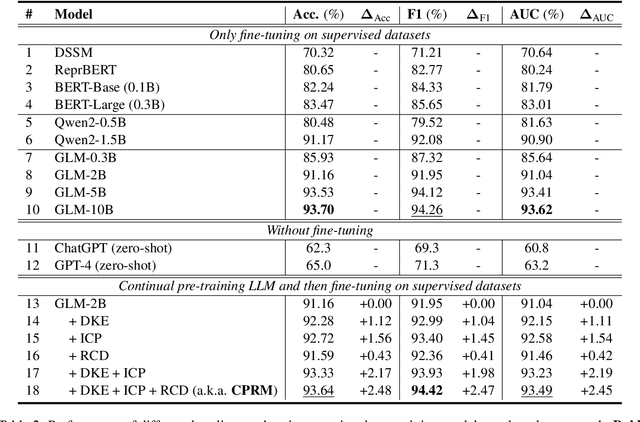
Abstract:Relevance modeling between queries and items stands as a pivotal component in commercial search engines, directly affecting the user experience. Given the remarkable achievements of large language models (LLMs) in various natural language processing (NLP) tasks, LLM-based relevance modeling is gradually being adopted within industrial search systems. Nevertheless, foundational LLMs lack domain-specific knowledge and do not fully exploit the potential of in-context learning. Furthermore, structured item text remains underutilized, and there is a shortage in the supply of corresponding queries and background knowledge. We thereby propose CPRM (Continual Pre-training for Relevance Modeling), a framework designed for the continual pre-training of LLMs to address these issues. Our CPRM framework includes three modules: 1) employing both queries and multi-field item to jointly pre-train for enhancing domain knowledge, 2) applying in-context pre-training, a novel approach where LLMs are pre-trained on a sequence of related queries or items, and 3) conducting reading comprehension on items to produce associated domain knowledge and background information (e.g., generating summaries and corresponding queries) to further strengthen LLMs. Results on offline experiments and online A/B testing demonstrate that our model achieves convincing performance compared to strong baselines.
Beware of Calibration Data for Pruning Large Language Models
Oct 23, 2024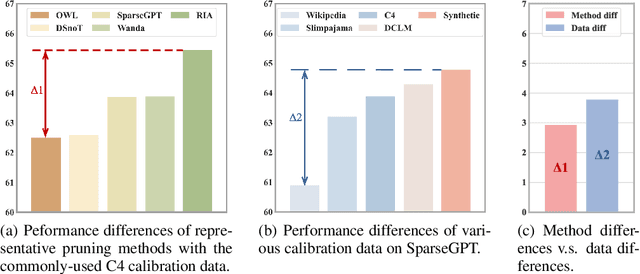

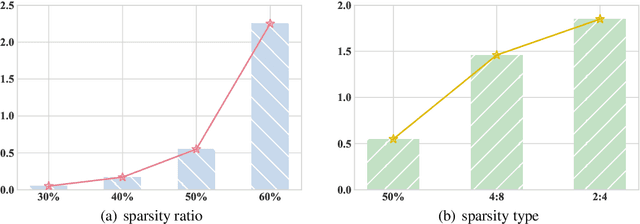

Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) are widely applied across various fields, model compression has become increasingly crucial for reducing costs and improving inference efficiency. Post-training pruning is a promising method that does not require resource-intensive iterative training and only needs a small amount of calibration data to assess the importance of parameters. Previous research has primarily focused on designing advanced pruning methods, while different calibration data's impact on pruning performance still lacks systematical exploration. We fill this blank and surprisingly observe that the effects of calibration data even value more than designing advanced pruning strategies, especially for high sparsity. Our preliminary exploration also discloses that using calibration data similar to the training data can yield better performance. As pre-training data is usually inaccessible for advanced LLMs, we further provide a self-generating calibration data synthesis strategy to construct feasible calibration data. We conduct experiments on the recent strong open-source LLMs (e.g., DCLM, and LLaMA-3), and the results show that the proposed method outperforms commonly used calibration data and can effectively enhance strong pruning methods (e.g., Wanda, OWL).
IPL: Leveraging Multimodal Large Language Models for Intelligent Product Listing
Oct 22, 2024



Abstract:Unlike professional Business-to-Consumer (B2C) e-commerce platforms (e.g., Amazon), Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) platforms (e.g., Facebook marketplace) are mainly targeting individual sellers who usually lack sufficient experience in e-commerce. Individual sellers often struggle to compose proper descriptions for selling products. With the recent advancement of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), we attempt to integrate such state-of-the-art generative AI technologies into the product listing process. To this end, we develop IPL, an Intelligent Product Listing tool tailored to generate descriptions using various product attributes such as category, brand, color, condition, etc. IPL enables users to compose product descriptions by merely uploading photos of the selling product. More importantly, it can imitate the content style of our C2C platform Xianyu. This is achieved by employing domain-specific instruction tuning on MLLMs and adopting the multi-modal Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) process. A comprehensive empirical evaluation demonstrates that the underlying model of IPL significantly outperforms the base model in domain-specific tasks while producing less hallucination. IPL has been successfully deployed in our production system, where 72% of users have their published product listings based on the generated content, and those product listings are shown to have a quality score 5.6% higher than those without AI assistance.
Demonstration Augmentation for Zero-shot In-context Learning
Jun 03, 2024

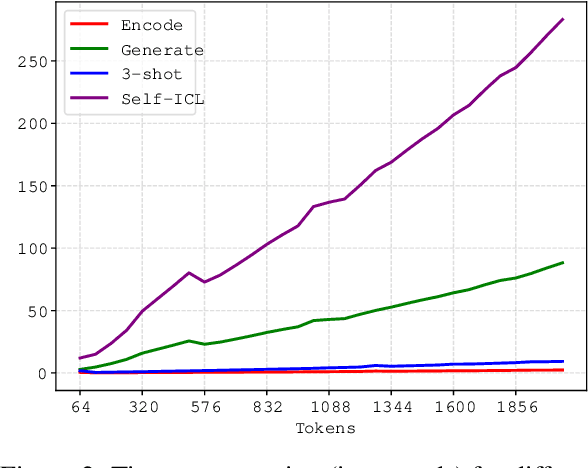

Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated an impressive capability known as In-context Learning (ICL), which enables them to acquire knowledge from textual demonstrations without the need for parameter updates. However, many studies have highlighted that the model's performance is sensitive to the choice of demonstrations, presenting a significant challenge for practical applications where we lack prior knowledge of user queries. Consequently, we need to construct an extensive demonstration pool and incorporate external databases to assist the model, leading to considerable time and financial costs. In light of this, some recent research has shifted focus towards zero-shot ICL, aiming to reduce the model's reliance on external information by leveraging their inherent generative capabilities. Despite the effectiveness of these approaches, the content generated by the model may be unreliable, and the generation process is time-consuming. To address these issues, we propose Demonstration Augmentation for In-context Learning (DAIL), which employs the model's previously predicted historical samples as demonstrations for subsequent ones. DAIL brings no additional inference cost and does not rely on the model's generative capabilities. Our experiments reveal that DAIL can significantly improve the model's performance over direct zero-shot inference and can even outperform few-shot ICL without any external information.
Feature-based Low-Rank Compression of Large Language Models via Bayesian Optimization
May 17, 2024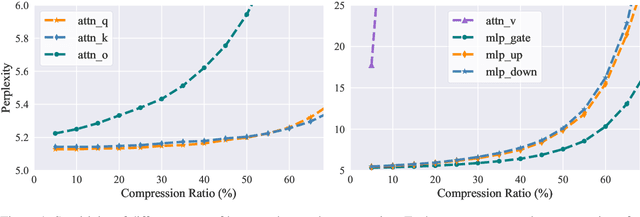

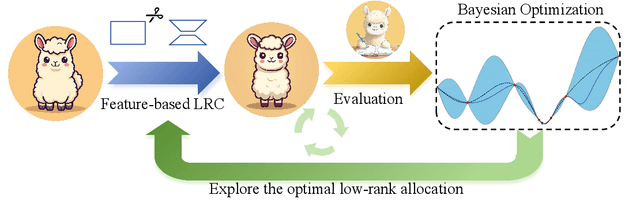

Abstract:In recent years, large language models (LLMs) have driven advances in natural language processing. Still, their growing scale has increased the computational burden, necessitating a balance between efficiency and performance. Low-rank compression, a promising technique, reduces non-essential parameters by decomposing weight matrices into products of two low-rank matrices. Yet, its application in LLMs has not been extensively studied. The key to low-rank compression lies in low-rank factorization and low-rank dimensions allocation. To address the challenges of low-rank compression in LLMs, we conduct empirical research on the low-rank characteristics of large models. We propose a low-rank compression method suitable for LLMs. This approach involves precise estimation of feature distributions through pooled covariance matrices and a Bayesian optimization strategy for allocating low-rank dimensions. Experiments on the LLaMA-2 models demonstrate that our method outperforms existing strong structured pruning and low-rank compression techniques in maintaining model performance at the same compression ratio.
OpenBA-V2: Reaching 77.3% High Compression Ratio with Fast Multi-Stage Pruning
May 09, 2024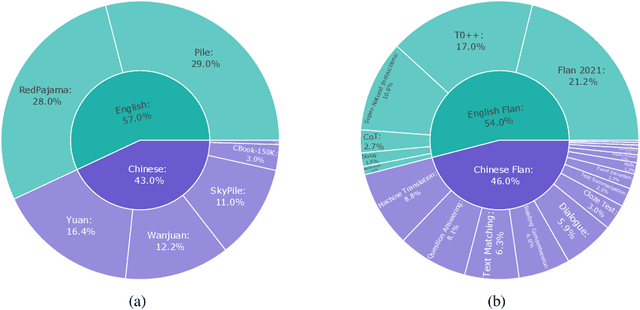
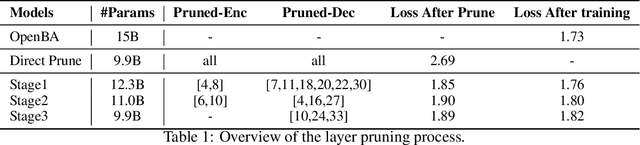
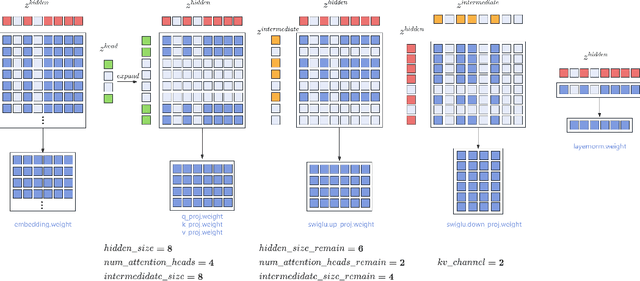
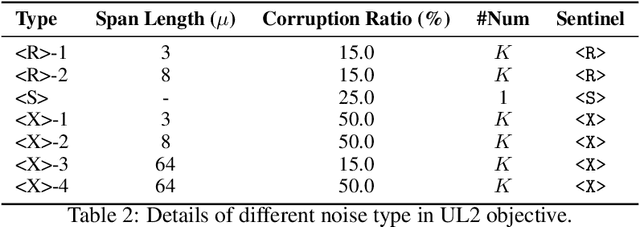
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have played an important role in many fields due to their powerful capabilities.However, their massive number of parameters leads to high deployment requirements and incurs significant inference costs, which impedes their practical applications. Training smaller models is an effective way to address this problem. Therefore, we introduce OpenBA-V2, a 3.4B model derived from multi-stage compression and continual pre-training from the original 15B OpenBA model. OpenBA-V2 utilizes more data, more flexible training objectives, and techniques such as layer pruning, neural pruning, and vocabulary pruning to achieve a compression rate of 77.3\% with minimal performance loss. OpenBA-V2 demonstrates competitive performance compared to other open-source models of similar size, achieving results close to or on par with the 15B OpenBA model in downstream tasks such as common sense reasoning and Named Entity Recognition (NER). OpenBA-V2 illustrates that LLMs can be compressed into smaller ones with minimal performance loss by employing advanced training objectives and data strategies, which may help deploy LLMs in resource-limited scenarios.
Test-Time Adaptation with Perturbation Consistency Learning
Apr 25, 2023



Abstract:Currently, pre-trained language models (PLMs) do not cope well with the distribution shift problem, resulting in models trained on the training set failing in real test scenarios. To address this problem, the test-time adaptation (TTA) shows great potential, which updates model parameters to suit the test data at the testing time. Existing TTA methods rely on well-designed auxiliary tasks or self-training strategies based on pseudo-label. However, these methods do not achieve good trade-offs regarding performance gains and computational costs. To obtain some insights into such a dilemma, we take two representative TTA methods, i.e., Tent and OIL, for exploration and find that stable prediction is the key to achieving a good balance. Accordingly, in this paper, we propose perturbation consistency learning (PCL), a simple test-time adaptation method to promote the model to make stable predictions for samples with distribution shifts. Extensive experiments on adversarial robustness and cross-lingual transferring demonstrate that our method can achieve higher or comparable performance with less inference time over strong PLM backbones and previous state-of-the-art TTA methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge