Baijun Ji
CPRM: A LLM-based Continual Pre-training Framework for Relevance Modeling in Commercial Search
Dec 03, 2024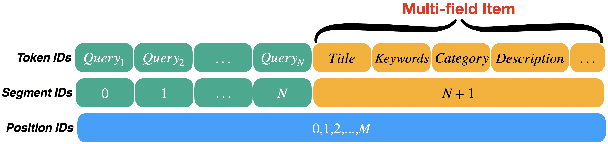
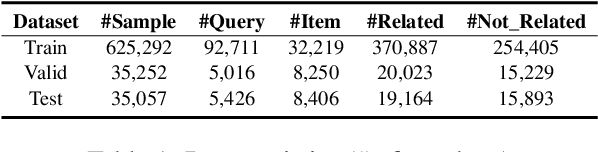
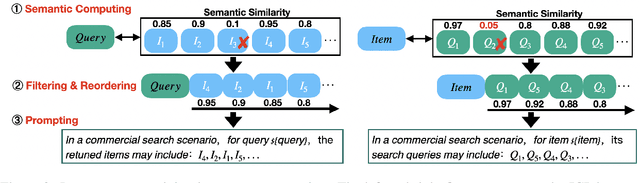
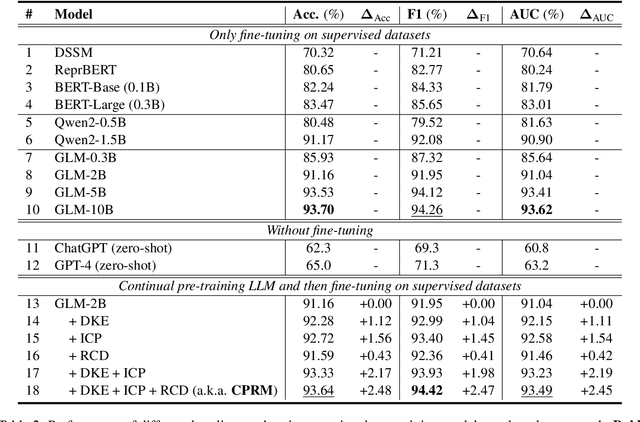
Abstract:Relevance modeling between queries and items stands as a pivotal component in commercial search engines, directly affecting the user experience. Given the remarkable achievements of large language models (LLMs) in various natural language processing (NLP) tasks, LLM-based relevance modeling is gradually being adopted within industrial search systems. Nevertheless, foundational LLMs lack domain-specific knowledge and do not fully exploit the potential of in-context learning. Furthermore, structured item text remains underutilized, and there is a shortage in the supply of corresponding queries and background knowledge. We thereby propose CPRM (Continual Pre-training for Relevance Modeling), a framework designed for the continual pre-training of LLMs to address these issues. Our CPRM framework includes three modules: 1) employing both queries and multi-field item to jointly pre-train for enhancing domain knowledge, 2) applying in-context pre-training, a novel approach where LLMs are pre-trained on a sequence of related queries or items, and 3) conducting reading comprehension on items to produce associated domain knowledge and background information (e.g., generating summaries and corresponding queries) to further strengthen LLMs. Results on offline experiments and online A/B testing demonstrate that our model achieves convincing performance compared to strong baselines.
Increasing Visual Awareness in Multimodal Neural Machine Translation from an Information Theoretic Perspective
Oct 16, 2022
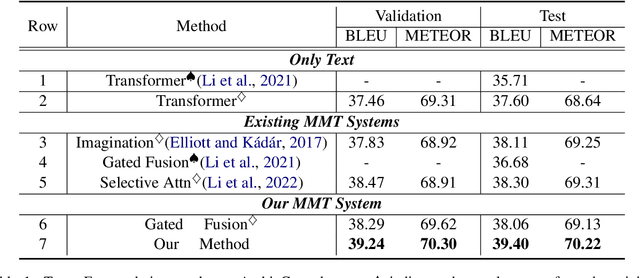

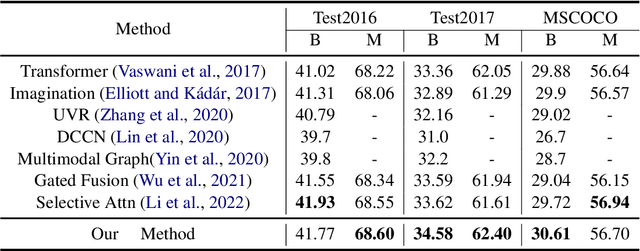
Abstract:Multimodal machine translation (MMT) aims to improve translation quality by equipping the source sentence with its corresponding image. Despite the promising performance, MMT models still suffer the problem of input degradation: models focus more on textual information while visual information is generally overlooked. In this paper, we endeavor to improve MMT performance by increasing visual awareness from an information theoretic perspective. In detail, we decompose the informative visual signals into two parts: source-specific information and target-specific information. We use mutual information to quantify them and propose two methods for objective optimization to better leverage visual signals. Experiments on two datasets demonstrate that our approach can effectively enhance the visual awareness of MMT model and achieve superior results against strong baselines.
Combining Static Word Embeddings and Contextual Representations for Bilingual Lexicon Induction
Jun 10, 2021



Abstract:Bilingual Lexicon Induction (BLI) aims to map words in one language to their translations in another, and is typically through learning linear projections to align monolingual word representation spaces. Two classes of word representations have been explored for BLI: static word embeddings and contextual representations, but there is no studies to combine both. In this paper, we propose a simple yet effective mechanism to combine the static word embeddings and the contextual representations to utilize the advantages of both paradigms. We test the combination mechanism on various language pairs under the supervised and unsupervised BLI benchmark settings. Experiments show that our mechanism consistently improves performances over robust BLI baselines on all language pairs by averagely improving 3.2 points in the supervised setting, and 3.1 points in the unsupervised setting.
Bilingual Dictionary Based Neural Machine Translation without Using Parallel Sentences
Jul 06, 2020



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a new task of machine translation (MT), which is based on no parallel sentences but can refer to a ground-truth bilingual dictionary. Motivated by the ability of a monolingual speaker learning to translate via looking up the bilingual dictionary, we propose the task to see how much potential an MT system can attain using the bilingual dictionary and large scale monolingual corpora, while is independent on parallel sentences. We propose anchored training (AT) to tackle the task. AT uses the bilingual dictionary to establish anchoring points for closing the gap between source language and target language. Experiments on various language pairs show that our approaches are significantly better than various baselines, including dictionary-based word-by-word translation, dictionary-supervised cross-lingual word embedding transformation, and unsupervised MT. On distant language pairs that are hard for unsupervised MT to perform well, AT performs remarkably better, achieving performances comparable to supervised SMT trained on more than 4M parallel sentences.
Cross-lingual Pre-training Based Transfer for Zero-shot Neural Machine Translation
Dec 03, 2019



Abstract:Transfer learning between different language pairs has shown its effectiveness for Neural Machine Translation (NMT) in low-resource scenario. However, existing transfer methods involving a common target language are far from success in the extreme scenario of zero-shot translation, due to the language space mismatch problem between transferor (the parent model) and transferee (the child model) on the source side. To address this challenge, we propose an effective transfer learning approach based on cross-lingual pre-training. Our key idea is to make all source languages share the same feature space and thus enable a smooth transition for zero-shot translation. To this end, we introduce one monolingual pre-training method and two bilingual pre-training methods to obtain a universal encoder for different languages. Once the universal encoder is constructed, the parent model built on such encoder is trained with large-scale annotated data and then directly applied in zero-shot translation scenario. Experiments on two public datasets show that our approach significantly outperforms strong pivot-based baseline and various multilingual NMT approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge