Xiangyu Duan
Disambiguated Lexically Constrained Neural Machine Translation
May 27, 2023Abstract:Lexically constrained neural machine translation (LCNMT), which controls the translation generation with pre-specified constraints, is important in many practical applications. Current approaches to LCNMT typically assume that the pre-specified lexical constraints are contextually appropriate. This assumption limits their application to real-world scenarios where a source lexicon may have multiple target constraints, and disambiguation is needed to select the most suitable one. In this paper, we propose disambiguated LCNMT (D-LCNMT) to solve the problem. D-LCNMT is a robust and effective two-stage framework that disambiguates the constraints based on contexts at first, then integrates the disambiguated constraints into LCNMT. Experimental results show that our approach outperforms strong baselines including existing data augmentation based approaches on benchmark datasets, and comprehensive experiments in scenarios where a source lexicon corresponds to multiple target constraints demonstrate the constraint disambiguation superiority of our approach.
TSMind: Alibaba and Soochow University's Submission to the WMT22 Translation Suggestion Task
Nov 16, 2022Abstract:This paper describes the joint submission of Alibaba and Soochow University, TSMind, to the WMT 2022 Shared Task on Translation Suggestion (TS). We participate in the English-German and English-Chinese tasks. Basically, we utilize the model paradigm fine-tuning on the downstream tasks based on large-scale pre-trained models, which has recently achieved great success. We choose FAIR's WMT19 English-German news translation system and MBART50 for English-Chinese as our pre-trained models. Considering the task's condition of limited use of training data, we follow the data augmentation strategies proposed by WeTS to boost our TS model performance. The difference is that we further involve the dual conditional cross-entropy model and GPT-2 language model to filter augmented data. The leader board finally shows that our submissions are ranked first in three of four language directions in the Naive TS task of the WMT22 Translation Suggestion task.
Third-Party Aligner for Neural Word Alignments
Nov 08, 2022



Abstract:Word alignment is to find translationally equivalent words between source and target sentences. Previous work has demonstrated that self-training can achieve competitive word alignment results. In this paper, we propose to use word alignments generated by a third-party word aligner to supervise the neural word alignment training. Specifically, source word and target word of each word pair aligned by the third-party aligner are trained to be close neighbors to each other in the contextualized embedding space when fine-tuning a pre-trained cross-lingual language model. Experiments on the benchmarks of various language pairs show that our approach can surprisingly do self-correction over the third-party supervision by finding more accurate word alignments and deleting wrong word alignments, leading to better performance than various third-party word aligners, including the currently best one. When we integrate all supervisions from various third-party aligners, we achieve state-of-the-art word alignment performances, with averagely more than two points lower alignment error rates than the best third-party aligner. We released our code at https://github.com/sdongchuanqi/Third-Party-Supervised-Aligner.
Combining Static Word Embeddings and Contextual Representations for Bilingual Lexicon Induction
Jun 10, 2021



Abstract:Bilingual Lexicon Induction (BLI) aims to map words in one language to their translations in another, and is typically through learning linear projections to align monolingual word representation spaces. Two classes of word representations have been explored for BLI: static word embeddings and contextual representations, but there is no studies to combine both. In this paper, we propose a simple yet effective mechanism to combine the static word embeddings and the contextual representations to utilize the advantages of both paradigms. We test the combination mechanism on various language pairs under the supervised and unsupervised BLI benchmark settings. Experiments show that our mechanism consistently improves performances over robust BLI baselines on all language pairs by averagely improving 3.2 points in the supervised setting, and 3.1 points in the unsupervised setting.
Bilingual Terminology Extraction from Non-Parallel E-Commerce Corpora
Apr 15, 2021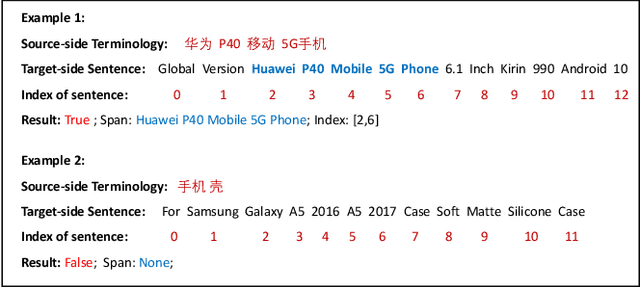
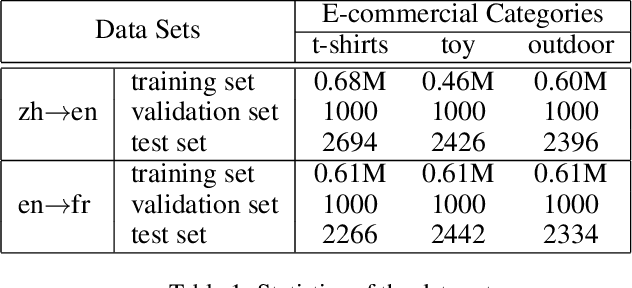
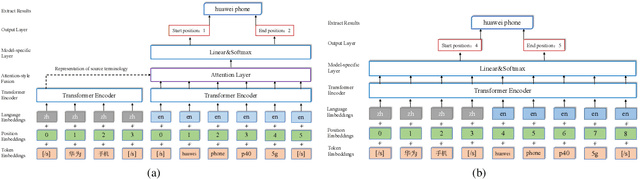
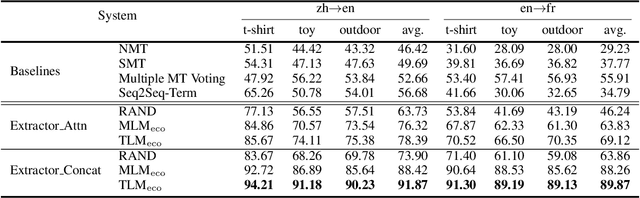
Abstract:Bilingual terminologies are important resources for natural language processing (NLP) applications. The acquisition of bilingual terminology pairs is either human translation or automatic extraction from parallel data. We notice that comparable corpora could also be a good resource for extracting bilingual terminology pairs, especially for e-commerce domain. The parallel corpora are particularly scarce in e-commerce settings, but the non-parallel corpora in different languages from the same domain are easily available. In this paper, we propose a novel framework of extracting bilingual terminologies from non-parallel comparable corpus in e-commerce. Benefiting from cross-lingual pre-training in e-commerce, our framework can extract the corresponding target terminology by fully utilizing the deep semantic relationship between source-side terminology and target-side sentence. Experimental results on various language pairs show that our approaches achieve significantly better performance than various strong baselines.
Token Drop mechanism for Neural Machine Translation
Oct 21, 2020
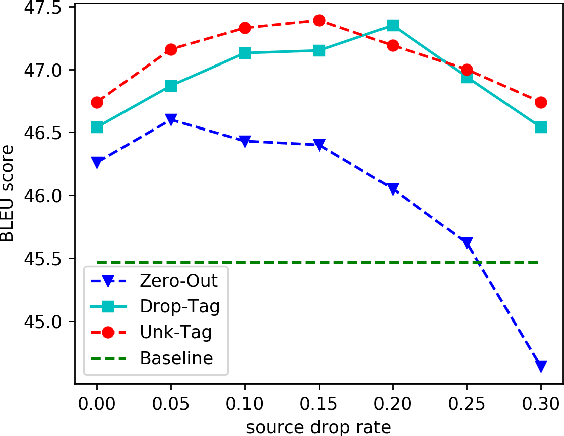


Abstract:Neural machine translation with millions of parameters is vulnerable to unfamiliar inputs. We propose Token Drop to improve generalization and avoid overfitting for the NMT model. Similar to word dropout, whereas we replace dropped token with a special token instead of setting zero to words. We further introduce two self-supervised objectives: Replaced Token Detection and Dropped Token Prediction. Our method aims to force model generating target translation with less information, in this way the model can learn textual representation better. Experiments on Chinese-English and English-Romanian benchmark demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach and our model achieves significant improvements over a strong Transformer baseline.
Bilingual Dictionary Based Neural Machine Translation without Using Parallel Sentences
Jul 06, 2020



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a new task of machine translation (MT), which is based on no parallel sentences but can refer to a ground-truth bilingual dictionary. Motivated by the ability of a monolingual speaker learning to translate via looking up the bilingual dictionary, we propose the task to see how much potential an MT system can attain using the bilingual dictionary and large scale monolingual corpora, while is independent on parallel sentences. We propose anchored training (AT) to tackle the task. AT uses the bilingual dictionary to establish anchoring points for closing the gap between source language and target language. Experiments on various language pairs show that our approaches are significantly better than various baselines, including dictionary-based word-by-word translation, dictionary-supervised cross-lingual word embedding transformation, and unsupervised MT. On distant language pairs that are hard for unsupervised MT to perform well, AT performs remarkably better, achieving performances comparable to supervised SMT trained on more than 4M parallel sentences.
Cross-lingual Pre-training Based Transfer for Zero-shot Neural Machine Translation
Dec 03, 2019



Abstract:Transfer learning between different language pairs has shown its effectiveness for Neural Machine Translation (NMT) in low-resource scenario. However, existing transfer methods involving a common target language are far from success in the extreme scenario of zero-shot translation, due to the language space mismatch problem between transferor (the parent model) and transferee (the child model) on the source side. To address this challenge, we propose an effective transfer learning approach based on cross-lingual pre-training. Our key idea is to make all source languages share the same feature space and thus enable a smooth transition for zero-shot translation. To this end, we introduce one monolingual pre-training method and two bilingual pre-training methods to obtain a universal encoder for different languages. Once the universal encoder is constructed, the parent model built on such encoder is trained with large-scale annotated data and then directly applied in zero-shot translation scenario. Experiments on two public datasets show that our approach significantly outperforms strong pivot-based baseline and various multilingual NMT approaches.
Contrastive Attention Mechanism for Abstractive Sentence Summarization
Oct 30, 2019



Abstract:We propose a contrastive attention mechanism to extend the sequence-to-sequence framework for abstractive sentence summarization task, which aims to generate a brief summary of a given source sentence. The proposed contrastive attention mechanism accommodates two categories of attention: one is the conventional attention that attends to relevant parts of the source sentence, the other is the opponent attention that attends to irrelevant or less relevant parts of the source sentence. Both attentions are trained in an opposite way so that the contribution from the conventional attention is encouraged and the contribution from the opponent attention is discouraged through a novel softmax and softmin functionality. Experiments on benchmark datasets show that, the proposed contrastive attention mechanism is more focused on the relevant parts for the summary than the conventional attention mechanism, and greatly advances the state-of-the-art performance on the abstractive sentence summarization task. We release the code at https://github.com/travel-go/Abstractive-Text-Summarization
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge