Shuguang Han
DAIAN: Deep Adaptive Intent-Aware Network for CTR Prediction in Trigger-Induced Recommendation
Feb 15, 2026Abstract:Recommendation systems are essential for personalizing e-commerce shopping experiences. Among these, Trigger-Induced Recommendation (TIR) has emerged as a key scenario, which utilizes a trigger item (explicitly represents a user's instantaneous interest), enabling precise, real-time recommendations. Although several trigger-based techniques have been proposed, most of them struggle to address the intent myopia issue, that is, a recommendation system overemphasizes the role of trigger items and narrowly focuses on suggesting commodities that are highly relevant to trigger items. Meanwhile, existing methods rely on collaborative behavior patterns between trigger and recommended items to identify the user's preferences, yet the sparsity of ID-based interaction restricts their effectiveness. To this end, we propose the Deep Adaptive Intent-Aware Network (DAIAN) that dynamically adapts to users' intent preferences. In general, we first extract the users' personalized intent representations by analyzing the correlation between a user's click and the trigger item, and accordingly retrieve the user's related historical behaviors to mine the user's diverse intent. Besides, sparse collaborative behaviors constrain the performance in capturing items associated with user intent. Hence, we reinforce similarity by leveraging a hybrid enhancer with ID and semantic information, followed by adaptive selection based on varying intents. Experimental results on public datasets and our industrial e-commerce datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of DAIAN.
Equity vs. Equality: Optimizing Ranking Fairness for Tailored Provider Needs
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Ranking plays a central role in connecting users and providers in Information Retrieval (IR) systems, making provider-side fairness an important challenge. While recent research has begun to address fairness in ranking, most existing approaches adopt an equality-based perspective, aiming to ensure that providers with similar content receive similar exposure. However, it overlooks the diverse needs of real-world providers, whose utility from ranking may depend not only on exposure but also on outcomes like sales or engagement. Consequently, exposure-based fairness may not accurately capture the true utility perceived by different providers with varying priorities. To this end, we introduce an equity-oriented fairness framework that explicitly models each provider's preferences over key outcomes such as exposure and sales, thus evaluating whether a ranking algorithm can fulfill these individualized goals while maintaining overall fairness across providers. Based on this framework, we develop EquityRank, a gradient-based algorithm that jointly optimizes user-side effectiveness and provider-side equity. Extensive offline and online simulations demonstrate that EquityRank offers improved trade-offs between effectiveness and fairness and adapts to heterogeneous provider needs.
AIF: Asynchronous Inference Framework for Cost-Effective Pre-Ranking
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:In industrial recommendation systems, pre-ranking models based on deep neural networks (DNNs) commonly adopt a sequential execution framework: feature fetching and model forward computation are triggered only after receiving candidates from the upstream retrieval stage. This design introduces inherent bottlenecks, including redundant computations of identical users/items and increased latency due to strictly sequential operations, which jointly constrain the model's capacity and system efficiency. To address these limitations, we propose the Asynchronous Inference Framework (AIF), a cost-effective computational architecture that decouples interaction-independent components, those operating within a single user or item, from real-time prediction. AIF reorganizes the model inference process by performing user-side computations in parallel with the retrieval stage and conducting item-side computations in a nearline manner. This means that interaction-independent components are calculated just once and completed before the real-time prediction phase of the pre-ranking stage. As a result, AIF enhances computational efficiency and reduces latency, freeing up resources to significantly improve the feature set and model architecture of interaction-independent components. Moreover, we delve into model design within the AIF framework, employing approximated methods for interaction-dependent components in online real-time predictions. By co-designing both the framework and the model, our solution achieves notable performance gains without significantly increasing computational and latency costs. This has enabled the successful deployment of AIF in the Taobao display advertising system.
IU4Rec: Interest Unit-Based Product Organization and Recommendation for E-Commerce Platform
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:Most recommendation systems typically follow a product-based paradigm utilizing user-product interactions to identify the most engaging items for users. However, this product-based paradigm has notable drawbacks for Xianyu~\footnote{Xianyu is China's largest online C2C e-commerce platform where a large portion of the product are post by individual sellers}. Most of the product on Xianyu posted from individual sellers often have limited stock available for distribution, and once the product is sold, it's no longer available for distribution. This result in most items distributed product on Xianyu having relatively few interactions, affecting the effectiveness of traditional recommendation depending on accumulating user-item interactions. To address these issues, we introduce \textbf{IU4Rec}, an \textbf{I}nterest \textbf{U}nit-based two-stage \textbf{Rec}ommendation system framework. We first group products into clusters based on attributes such as category, image, and semantics. These IUs are then integrated into the Recommendation system, delivering both product and technological innovations. IU4Rec begins by grouping products into clusters based on attributes such as category, image, and semantics, forming Interest Units (IUs). Then we redesign the recommendation process into two stages. In the first stage, the focus is on recommend these Interest Units, capturing broad-level interests. In the second stage, it guides users to find the best option among similar products within the selected Interest Unit. User-IU interactions are incorporated into our ranking models, offering the advantage of more persistent IU behaviors compared to item-specific interactions. Experimental results on the production dataset and online A/B testing demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our proposed IU-centric recommendation approach.
TACLR: A Scalable and Efficient Retrieval-based Method for Industrial Product Attribute Value Identification
Jan 07, 2025Abstract:Product Attribute Value Identification (PAVI) involves identifying attribute values from product profiles, a key task for improving product search, recommendations, and business analytics on e-commerce platforms. However, existing PAVI methods face critical challenges, such as inferring implicit values, handling out-of-distribution (OOD) values, and producing normalized outputs. To address these limitations, we introduce Taxonomy-Aware Contrastive Learning Retrieval (TACLR), the first retrieval-based method for PAVI. TACLR formulates PAVI as an information retrieval task by encoding product profiles and candidate values into embeddings and retrieving values based on their similarity to the item embedding. It leverages contrastive training with taxonomy-aware hard negative sampling and employs adaptive inference with dynamic thresholds. TACLR offers three key advantages: (1) it effectively handles implicit and OOD values while producing normalized outputs; (2) it scales to thousands of categories, tens of thousands of attributes, and millions of values; and (3) it supports efficient inference for high-load industrial scenarios. Extensive experiments on proprietary and public datasets validate the effectiveness and efficiency of TACLR. Moreover, it has been successfully deployed in a real-world e-commerce platform, processing millions of product listings daily while supporting dynamic, large-scale attribute taxonomies.
IPL: Leveraging Multimodal Large Language Models for Intelligent Product Listing
Oct 22, 2024



Abstract:Unlike professional Business-to-Consumer (B2C) e-commerce platforms (e.g., Amazon), Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) platforms (e.g., Facebook marketplace) are mainly targeting individual sellers who usually lack sufficient experience in e-commerce. Individual sellers often struggle to compose proper descriptions for selling products. With the recent advancement of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), we attempt to integrate such state-of-the-art generative AI technologies into the product listing process. To this end, we develop IPL, an Intelligent Product Listing tool tailored to generate descriptions using various product attributes such as category, brand, color, condition, etc. IPL enables users to compose product descriptions by merely uploading photos of the selling product. More importantly, it can imitate the content style of our C2C platform Xianyu. This is achieved by employing domain-specific instruction tuning on MLLMs and adopting the multi-modal Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) process. A comprehensive empirical evaluation demonstrates that the underlying model of IPL significantly outperforms the base model in domain-specific tasks while producing less hallucination. IPL has been successfully deployed in our production system, where 72% of users have their published product listings based on the generated content, and those product listings are shown to have a quality score 5.6% higher than those without AI assistance.
MetaSplit: Meta-Split Network for Limited-Stock Product Recommendation
Mar 16, 2024Abstract:Compared to business-to-consumer (B2C) e-commerce systems, consumer-to-consumer (C2C) e-commerce platforms usually encounter the limited-stock problem, that is, a product can only be sold one time in a C2C system. This poses several unique challenges for click-through rate (CTR) prediction. Due to limited user interactions for each product (i.e. item), the corresponding item embedding in the CTR model may not easily converge. This makes the conventional sequence modeling based approaches cannot effectively utilize user history information since historical user behaviors contain a mixture of items with different volume of stocks. Particularly, the attention mechanism in a sequence model tends to assign higher score to products with more accumulated user interactions, making limited-stock products being ignored and contribute less to the final output. To this end, we propose the Meta-Split Network (MSNet) to split user history sequence regarding to the volume of stock for each product, and adopt differentiated modeling approaches for different sequences. As for the limited-stock products, a meta-learning approach is applied to address the problem of inconvergence, which is achieved by designing meta scaling and shifting networks with ID and side information. In addition, traditional approach can hardly update item embedding once the product is consumed. Thereby, we propose an auxiliary loss that makes the parameters updatable even when the product is no longer in distribution. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first solution addressing the recommendation of limited-stock product. Experimental results on the production dataset and online A/B testing demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method.
Effective Two-Stage Knowledge Transfer for Multi-Entity Cross-Domain Recommendation
Feb 29, 2024



Abstract:In recent years, the recommendation content on e-commerce platforms has become increasingly rich -- a single user feed may contain multiple entities, such as selling products, short videos, and content posts. To deal with the multi-entity recommendation problem, an intuitive solution is to adopt the shared-network-based architecture for joint training. The idea is to transfer the extracted knowledge from one type of entity (source entity) to another (target entity). However, different from the conventional same-entity cross-domain recommendation, multi-entity knowledge transfer encounters several important issues: (1) data distributions of the source entity and target entity are naturally different, making the shared-network-based joint training susceptible to the negative transfer issue, (2) more importantly, the corresponding feature schema of each entity is not exactly aligned (e.g., price is an essential feature for selling product while missing for content posts), making the existing methods no longer appropriate. Recent researchers have also experimented with the pre-training and fine-tuning paradigm. Again, they only consider the scenarios with the same entity type and feature systems, which is inappropriate in our case. To this end, we design a pre-training & fine-tuning based Multi-entity Knowledge Transfer framework called MKT. MKT utilizes a multi-entity pre-training module to extract transferable knowledge across different entities. In particular, a feature alignment module is first applied to scale and align different feature schemas. Afterward, a couple of knowledge extractors are employed to extract the common and entity-specific knowledge. In the end, the extracted common knowledge is adopted for target entity model training. Through extensive offline and online experiments, we demonstrated the superiority of MKT over multiple State-Of-The-Art methods.
Calibration-compatible Listwise Distillation of Privileged Features for CTR Prediction
Dec 14, 2023



Abstract:In machine learning systems, privileged features refer to the features that are available during offline training but inaccessible for online serving. Previous studies have recognized the importance of privileged features and explored ways to tackle online-offline discrepancies. A typical practice is privileged features distillation (PFD): train a teacher model using all features (including privileged ones) and then distill the knowledge from the teacher model using a student model (excluding the privileged features), which is then employed for online serving. In practice, the pointwise cross-entropy loss is often adopted for PFD. However, this loss is insufficient to distill the ranking ability for CTR prediction. First, it does not consider the non-i.i.d. characteristic of the data distribution, i.e., other items on the same page significantly impact the click probability of the candidate item. Second, it fails to consider the relative item order ranked by the teacher model's predictions, which is essential to distill the ranking ability. To address these issues, we first extend the pointwise-based PFD to the listwise-based PFD. We then define the calibration-compatible property of distillation loss and show that commonly used listwise losses do not satisfy this property when employed as distillation loss, thus compromising the model's calibration ability, which is another important measure for CTR prediction. To tackle this dilemma, we propose Calibration-compatible LIstwise Distillation (CLID), which employs carefully-designed listwise distillation loss to achieve better ranking ability than the pointwise-based PFD while preserving the model's calibration ability. We theoretically prove it is calibration-compatible. Extensive experiments on public datasets and a production dataset collected from the display advertising system of Alibaba further demonstrate the effectiveness of CLID.
Entire Space Cascade Delayed Feedback Modeling for Effective Conversion Rate Prediction
Aug 09, 2023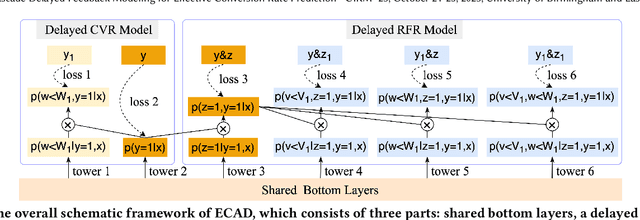
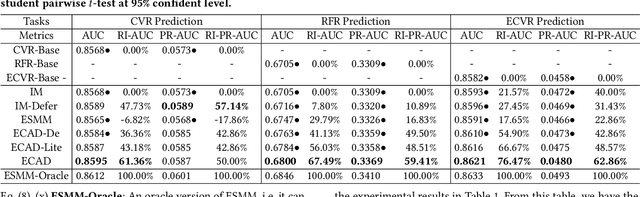
Abstract:Conversion rate (CVR) prediction is an essential task for large-scale e-commerce platforms. However, refund behaviors frequently occur after conversion in online shopping systems, which drives us to pay attention to effective conversion for building healthier shopping services. This paper defines the probability of item purchasing without any subsequent refund as an effective conversion rate (ECVR). A simple paradigm for ECVR prediction is to decompose it into two sub-tasks: CVR prediction and post-conversion refund rate (RFR) prediction. However, RFR prediction suffers from data sparsity (DS) and sample selection bias (SSB) issues, as the refund behaviors are only available after user purchase. Furthermore, there is delayed feedback in both conversion and refund events and they are sequentially dependent, named cascade delayed feedback (CDF), which significantly harms data freshness for model training. Previous studies mainly focus on tackling DS and SSB or delayed feedback for a single event. To jointly tackle these issues in ECVR prediction, we propose an Entire space CAscade Delayed feedback modeling (ECAD) method. Specifically, ECAD deals with DS and SSB by constructing two tasks including CVR prediction and conversion \& refund rate (CVRFR) prediction using the entire space modeling framework. In addition, it carefully schedules auxiliary tasks to leverage both conversion and refund time within data to alleviate CDF. Experimental results on the offline industrial dataset and online A/B testing demonstrate the effectiveness of ECAD. In addition, ECAD has been deployed in one of the recommender systems in Alibaba, contributing to a significant improvement of ECVR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge