Ailong He
MetaSplit: Meta-Split Network for Limited-Stock Product Recommendation
Mar 16, 2024Abstract:Compared to business-to-consumer (B2C) e-commerce systems, consumer-to-consumer (C2C) e-commerce platforms usually encounter the limited-stock problem, that is, a product can only be sold one time in a C2C system. This poses several unique challenges for click-through rate (CTR) prediction. Due to limited user interactions for each product (i.e. item), the corresponding item embedding in the CTR model may not easily converge. This makes the conventional sequence modeling based approaches cannot effectively utilize user history information since historical user behaviors contain a mixture of items with different volume of stocks. Particularly, the attention mechanism in a sequence model tends to assign higher score to products with more accumulated user interactions, making limited-stock products being ignored and contribute less to the final output. To this end, we propose the Meta-Split Network (MSNet) to split user history sequence regarding to the volume of stock for each product, and adopt differentiated modeling approaches for different sequences. As for the limited-stock products, a meta-learning approach is applied to address the problem of inconvergence, which is achieved by designing meta scaling and shifting networks with ID and side information. In addition, traditional approach can hardly update item embedding once the product is consumed. Thereby, we propose an auxiliary loss that makes the parameters updatable even when the product is no longer in distribution. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first solution addressing the recommendation of limited-stock product. Experimental results on the production dataset and online A/B testing demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method.
Unstructured Semantic Model supported Deep Neural Network for Click-Through Rate Prediction
Dec 04, 2018
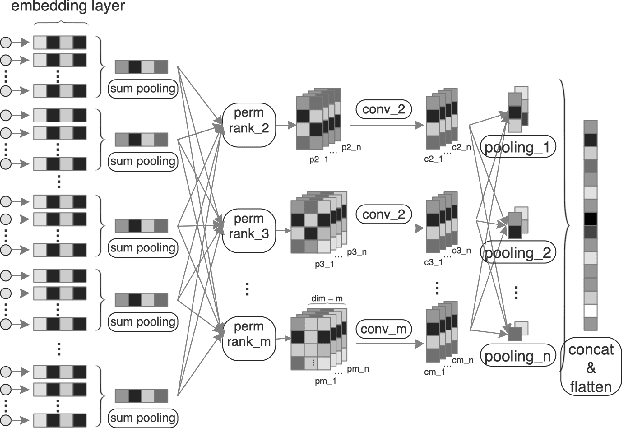
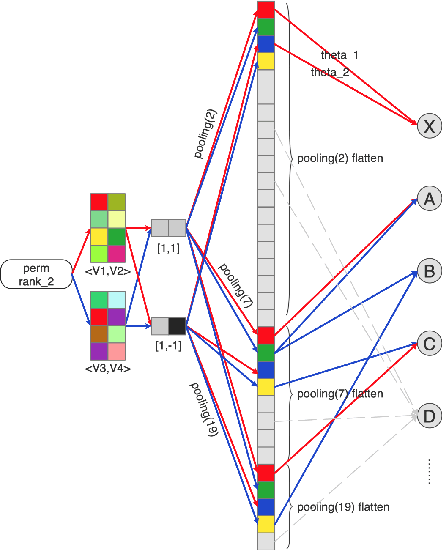

Abstract:With the rapid development of online advertising and recommendation systems, click-through rate prediction is expected to play an increasingly important role.Recently many DNN-based models which follow a similar Embedding&MLP paradigm have been proposed, and have achieved good result in image/voice and nlp fields.In these methods the Wide&Deep model announced by Google plays a key role.Most models first map large scale sparse input features into low-dimensional vectors which are transformed to fixed-length vectors, then concatenated together before being fed into a multilayer perceptron (MLP) to learn non-linear relations among input features. The number of trainable variables normally grow dramatically the number of feature fields and the embedding dimension grow. It is a big challenge to get state-of-the-art result through training deep neural network and embedding together, which falls into local optimal or overfitting easily.In this paper, we propose an Unstructured Semantic Model (USM) to tackles this challenge by designing a orthogonal base convolution and pooling model which adaptively learn the multi-scale base semantic representation between features supervised by the click label.The output of USM are then used in the Wide&Deep for CTR prediction.Experiments on two public datasets as well as real Weibo production dataset with over 1 billion samples have demonstrated the effectiveness of our proposed approach with superior performance comparing to state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge