Bin Zhu
DevPiolt: Operation Recommendation for IoT Devices at Xiaomi Home
Nov 18, 2025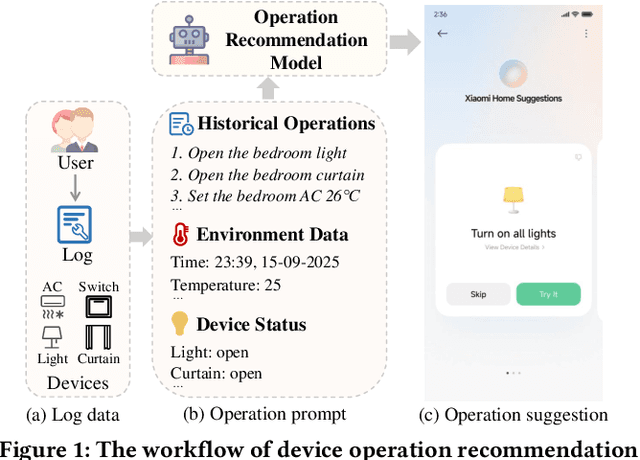
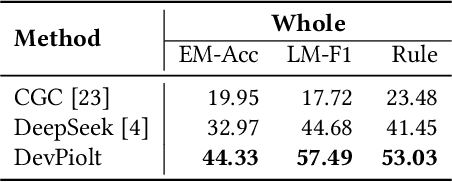
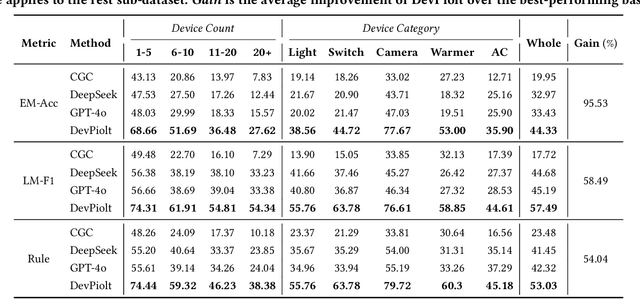
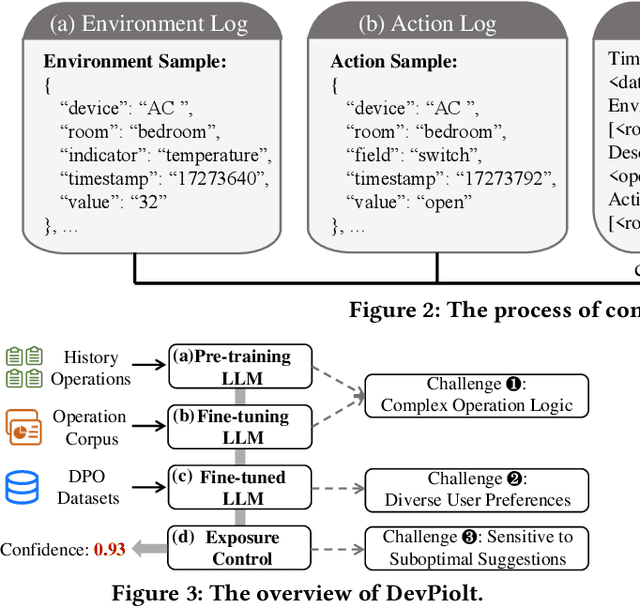
Abstract:Operation recommendation for IoT devices refers to generating personalized device operations for users based on their context, such as historical operations, environment information, and device status. This task is crucial for enhancing user satisfaction and corporate profits. Existing recommendation models struggle with complex operation logic, diverse user preferences, and sensitive to suboptimal suggestions, limiting their applicability to IoT device operations. To address these issues, we propose DevPiolt, a LLM-based recommendation model for IoT device operations. Specifically, we first equip the LLM with fundamental domain knowledge of IoT operations via continual pre-training and multi-task fine-tuning. Then, we employ direct preference optimization to align the fine-tuned LLM with specific user preferences. Finally, we design a confidence-based exposure control mechanism to avoid negative user experiences from low-quality recommendations. Extensive experiments show that DevPiolt significantly outperforms baselines on all datasets, with an average improvement of 69.5% across all metrics. DevPiolt has been practically deployed in Xiaomi Home app for one quarter, providing daily operation recommendations to 255,000 users. Online experiment results indicate a 21.6% increase in unique visitor device coverage and a 29.1% increase in page view acceptance rates.
Dual-LoRA and Quality-Enhanced Pseudo Replay for Multimodal Continual Food Learning
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Food analysis has become increasingly critical for health-related tasks such as personalized nutrition and chronic disease prevention. However, existing large multimodal models (LMMs) in food analysis suffer from catastrophic forgetting when learning new tasks, requiring costly retraining from scratch. To address this, we propose a novel continual learning framework for multimodal food learning, integrating a Dual-LoRA architecture with Quality-Enhanced Pseudo Replay. We introduce two complementary low-rank adapters for each task: a specialized LoRA that learns task-specific knowledge with orthogonal constraints to previous tasks' subspaces, and a cooperative LoRA that consolidates shared knowledge across tasks via pseudo replay. To improve the reliability of replay data, our Quality-Enhanced Pseudo Replay strategy leverages self-consistency and semantic similarity to reduce hallucinations in generated samples. Experiments on the comprehensive Uni-Food dataset show superior performance in mitigating forgetting, representing the first effective continual learning approach for complex food tasks.
Reasoning Models Are More Easily Gaslighted Than You Think
Jun 11, 2025



Abstract:Recent advances in reasoning-centric models promise improved robustness through mechanisms such as chain-of-thought prompting and test-time scaling. However, their ability to withstand misleading user input remains underexplored. In this paper, we conduct a systematic evaluation of three state-of-the-art reasoning models, i.e., OpenAI's o4-mini, Claude-3.7-Sonnet and Gemini-2.5-Flash, across three multimodal benchmarks: MMMU, MathVista, and CharXiv. Our evaluation reveals significant accuracy drops (25-29% on average) following gaslighting negation prompts, indicating that even top-tier reasoning models struggle to preserve correct answers under manipulative user feedback. Built upon the insights of the evaluation and to further probe this vulnerability, we introduce GaslightingBench-R, a new diagnostic benchmark specifically designed to evaluate reasoning models' susceptibility to defend their belief under gaslighting negation prompt. Constructed by filtering and curating 1,025 challenging samples from the existing benchmarks, GaslightingBench-R induces even more dramatic failures, with accuracy drops exceeding 53% on average. Our findings reveal fundamental limitations in the robustness of reasoning models, highlighting the gap between step-by-step reasoning and belief persistence.
Advancing Food Nutrition Estimation via Visual-Ingredient Feature Fusion
May 13, 2025Abstract:Nutrition estimation is an important component of promoting healthy eating and mitigating diet-related health risks. Despite advances in tasks such as food classification and ingredient recognition, progress in nutrition estimation is limited due to the lack of datasets with nutritional annotations. To address this issue, we introduce FastFood, a dataset with 84,446 images across 908 fast food categories, featuring ingredient and nutritional annotations. In addition, we propose a new model-agnostic Visual-Ingredient Feature Fusion (VIF$^2$) method to enhance nutrition estimation by integrating visual and ingredient features. Ingredient robustness is improved through synonym replacement and resampling strategies during training. The ingredient-aware visual feature fusion module combines ingredient features and visual representation to achieve accurate nutritional prediction. During testing, ingredient predictions are refined using large multimodal models by data augmentation and majority voting. Our experiments on both FastFood and Nutrition5k datasets validate the effectiveness of our proposed method built in different backbones (e.g., Resnet, InceptionV3 and ViT), which demonstrates the importance of ingredient information in nutrition estimation. https://huiyanqi.github.io/fastfood-nutrition-estimation/.
Preference Optimization for Combinatorial Optimization Problems
May 13, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement Learning (RL) has emerged as a powerful tool for neural combinatorial optimization, enabling models to learn heuristics that solve complex problems without requiring expert knowledge. Despite significant progress, existing RL approaches face challenges such as diminishing reward signals and inefficient exploration in vast combinatorial action spaces, leading to inefficiency. In this paper, we propose Preference Optimization, a novel method that transforms quantitative reward signals into qualitative preference signals via statistical comparison modeling, emphasizing the superiority among sampled solutions. Methodologically, by reparameterizing the reward function in terms of policy and utilizing preference models, we formulate an entropy-regularized RL objective that aligns the policy directly with preferences while avoiding intractable computations. Furthermore, we integrate local search techniques into the fine-tuning rather than post-processing to generate high-quality preference pairs, helping the policy escape local optima. Empirical results on various benchmarks, such as the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP), the Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem (CVRP) and the Flexible Flow Shop Problem (FFSP), demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing RL algorithms, achieving superior convergence efficiency and solution quality.
Don't Deceive Me: Mitigating Gaslighting through Attention Reallocation in LMMs
Apr 13, 2025



Abstract:Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across a wide range of tasks. However, their vulnerability to user gaslighting-the deliberate use of misleading or contradictory inputs-raises critical concerns about their reliability in real-world applications. In this paper, we address the novel and challenging issue of mitigating the negative impact of negation-based gaslighting on LMMs, where deceptive user statements lead to significant drops in model accuracy. Specifically, we introduce GasEraser, a training-free approach that reallocates attention weights from misleading textual tokens to semantically salient visual regions. By suppressing the influence of "attention sink" tokens and enhancing focus on visually grounded cues, GasEraser significantly improves LMM robustness without requiring retraining or additional supervision. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that GasEraser is effective across several leading open-source LMMs on the GaslightingBench. Notably, for LLaVA-v1.5-7B, GasEraser reduces the misguidance rate by 48.2%, demonstrating its potential for more trustworthy LMMs.
Evaluating LLM-based Agents for Multi-Turn Conversations: A Survey
Mar 28, 2025Abstract:This survey examines evaluation methods for large language model (LLM)-based agents in multi-turn conversational settings. Using a PRISMA-inspired framework, we systematically reviewed nearly 250 scholarly sources, capturing the state of the art from various venues of publication, and establishing a solid foundation for our analysis. Our study offers a structured approach by developing two interrelated taxonomy systems: one that defines \emph{what to evaluate} and another that explains \emph{how to evaluate}. The first taxonomy identifies key components of LLM-based agents for multi-turn conversations and their evaluation dimensions, including task completion, response quality, user experience, memory and context retention, as well as planning and tool integration. These components ensure that the performance of conversational agents is assessed in a holistic and meaningful manner. The second taxonomy system focuses on the evaluation methodologies. It categorizes approaches into annotation-based evaluations, automated metrics, hybrid strategies that combine human assessments with quantitative measures, and self-judging methods utilizing LLMs. This framework not only captures traditional metrics derived from language understanding, such as BLEU and ROUGE scores, but also incorporates advanced techniques that reflect the dynamic, interactive nature of multi-turn dialogues.
SwapAnyone: Consistent and Realistic Video Synthesis for Swapping Any Person into Any Video
Mar 12, 2025
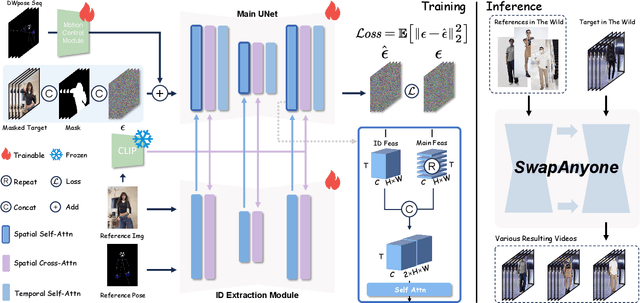
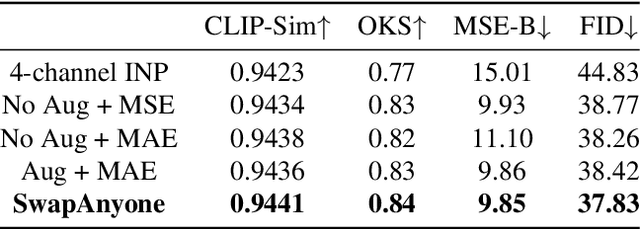

Abstract:Video body-swapping aims to replace the body in an existing video with a new body from arbitrary sources, which has garnered more attention in recent years. Existing methods treat video body-swapping as a composite of multiple tasks instead of an independent task and typically rely on various models to achieve video body-swapping sequentially. However, these methods fail to achieve end-to-end optimization for the video body-swapping which causes issues such as variations in luminance among frames, disorganized occlusion relationships, and the noticeable separation between bodies and background. In this work, we define video body-swapping as an independent task and propose three critical consistencies: identity consistency, motion consistency, and environment consistency. We introduce an end-to-end model named SwapAnyone, treating video body-swapping as a video inpainting task with reference fidelity and motion control. To improve the ability to maintain environmental harmony, particularly luminance harmony in the resulting video, we introduce a novel EnvHarmony strategy for training our model progressively. Additionally, we provide a dataset named HumanAction-32K covering various videos about human actions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves State-Of-The-Art (SOTA) performance among open-source methods while approaching or surpassing closed-source models across multiple dimensions. All code, model weights, and the HumanAction-32K dataset will be open-sourced at https://github.com/PKU-YuanGroup/SwapAnyone.
WISE: A World Knowledge-Informed Semantic Evaluation for Text-to-Image Generation
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:Text-to-Image (T2I) models are capable of generating high-quality artistic creations and visual content. However, existing research and evaluation standards predominantly focus on image realism and shallow text-image alignment, lacking a comprehensive assessment of complex semantic understanding and world knowledge integration in text to image generation. To address this challenge, we propose $\textbf{WISE}$, the first benchmark specifically designed for $\textbf{W}$orld Knowledge-$\textbf{I}$nformed $\textbf{S}$emantic $\textbf{E}$valuation. WISE moves beyond simple word-pixel mapping by challenging models with 1000 meticulously crafted prompts across 25 sub-domains in cultural common sense, spatio-temporal reasoning, and natural science. To overcome the limitations of traditional CLIP metric, we introduce $\textbf{WiScore}$, a novel quantitative metric for assessing knowledge-image alignment. Through comprehensive testing of 20 models (10 dedicated T2I models and 10 unified multimodal models) using 1,000 structured prompts spanning 25 subdomains, our findings reveal significant limitations in their ability to effectively integrate and apply world knowledge during image generation, highlighting critical pathways for enhancing knowledge incorporation and application in next-generation T2I models. Code and data are available at https://github.com/PKU-YuanGroup/WISE.
OSCAR: Object Status and Contextual Awareness for Recipes to Support Non-Visual Cooking
Mar 07, 2025



Abstract:Following recipes while cooking is an important but difficult task for visually impaired individuals. We developed OSCAR (Object Status Context Awareness for Recipes), a novel approach that provides recipe progress tracking and context-aware feedback on the completion of cooking tasks through tracking object statuses. OSCAR leverages both Large-Language Models (LLMs) and Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to manipulate recipe steps, extract object status information, align visual frames with object status, and provide cooking progress tracking log. We evaluated OSCAR's recipe following functionality using 173 YouTube cooking videos and 12 real-world non-visual cooking videos to demonstrate OSCAR's capability to track cooking steps and provide contextual guidance. Our results highlight the effectiveness of using object status to improve performance compared to baseline by over 20% across different VLMs, and we present factors that impact prediction performance. Furthermore, we contribute a dataset of real-world non-visual cooking videos with step annotations as an evaluation benchmark.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge