Ruixuan Li
Nonlinearity as Rank: Generative Low-Rank Adapter with Radial Basis Functions
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Low-rank adaptation (LoRA) approximates the update of a pretrained weight matrix using the product of two low-rank matrices. However, standard LoRA follows an explicit-rank paradigm, where increasing model capacity requires adding more rows or columns (i.e., basis vectors) to the low-rank matrices, leading to substantial parameter growth. In this paper, we find that these basis vectors exhibit significant parameter redundancy and can be compactly represented by lightweight nonlinear functions. Therefore, we propose Generative Low-Rank Adapter (GenLoRA), which replaces explicit basis vector storage with nonlinear basis vector generation. Specifically, GenLoRA maintains a latent vector for each low-rank matrix and employs a set of lightweight radial basis functions (RBFs) to synthesize the basis vectors. Each RBF requires far fewer parameters than an explicit basis vector, enabling higher parameter efficiency in GenLoRA. Extensive experiments across multiple datasets and architectures show that GenLoRA attains higher effective LoRA ranks under smaller parameter budgets, resulting in superior fine-tuning performance. The code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/GenLoRA-1519.
SwimBird: Eliciting Switchable Reasoning Mode in Hybrid Autoregressive MLLMs
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have made remarkable progress in multimodal perception and reasoning by bridging vision and language. However, most existing MLLMs perform reasoning primarily with textual CoT, which limits their effectiveness on vision-intensive tasks. Recent approaches inject a fixed number of continuous hidden states as "visual thoughts" into the reasoning process and improve visual performance, but often at the cost of degraded text-based logical reasoning. We argue that the core limitation lies in a rigid, pre-defined reasoning pattern that cannot adaptively choose the most suitable thinking modality for different user queries. We introduce SwimBird, a reasoning-switchable MLLM that dynamically switches among three reasoning modes conditioned on the input: (1) text-only reasoning, (2) vision-only reasoning (continuous hidden states as visual thoughts), and (3) interleaved vision-text reasoning. To enable this capability, we adopt a hybrid autoregressive formulation that unifies next-token prediction for textual thoughts with next-embedding prediction for visual thoughts, and design a systematic reasoning-mode curation strategy to construct SwimBird-SFT-92K, a diverse supervised fine-tuning dataset covering all three reasoning patterns. By enabling flexible, query-adaptive mode selection, SwimBird preserves strong textual logic while substantially improving performance on vision-dense tasks. Experiments across diverse benchmarks covering textual reasoning and challenging visual understanding demonstrate that SwimBird achieves state-of-the-art results and robust gains over prior fixed-pattern multimodal reasoning methods.
Are We Evaluating the Edit Locality of LLM Model Editing Properly?
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Model editing has recently emerged as a popular paradigm for efficiently updating knowledge in LLMs. A central desideratum of updating knowledge is to balance editing efficacy, i.e., the successful injection of target knowledge, and specificity (also known as edit locality), i.e., the preservation of existing non-target knowledge. However, we find that existing specificity evaluation protocols are inadequate for this purpose. We systematically elaborated on the three fundamental issues it faces. Beyond the conceptual issues, we further empirically demonstrate that existing specificity metrics are weakly correlated with the strength of specificity regularizers. We also find that current metrics lack sufficient sensitivity, rendering them ineffective at distinguishing the specificity performance of different methods. Finally, we propose a constructive evaluation protocol. Under this protocol, the conflict between open-ended LLMs and the assumption of determined answers is eliminated, query-independent fluency biases are avoided, and the evaluation strictness can be smoothly adjusted within a near-continuous space. Experiments across various LLMs, datasets, and editing methods show that metrics derived from the proposed protocol are more sensitive to changes in the strength of specificity regularizers and exhibit strong correlation with them, enabling more fine-grained discrimination of different methods' knowledge preservation capabilities.
QKVQA: Question-Focused Filtering for Knowledge-based VQA
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Knowledge-based Visual Question Answering (KB-VQA) aims to answer questions by integrating images with external knowledge. Effective knowledge filtering is crucial for improving accuracy. Typical filtering methods use similarity metrics to locate relevant article sections from one article, leading to information selection errors at the article and intra-article levels. Although recent explorations of Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM)-based filtering methods demonstrate superior semantic understanding and cross-article filtering capabilities, their high computational cost limits practical application. To address these issues, this paper proposes a question-focused filtering method. This approach can perform question-focused, cross-article filtering, efficiently obtaining high-quality filtered knowledge while keeping computational costs comparable to typical methods. Specifically, we design a trainable Question-Focused Filter (QFF) and a Chunk-based Dynamic Multi-Article Selection (CDA) module, which collectively alleviate information selection errors at both the article and intra-article levels. Experiments show that our method outperforms current state-of-the-art models by 4.9% on E-VQA and 3.8% on InfoSeek, validating its effectiveness. The code is publicly available at: https://github.com/leaffeall/QKVQA.
Sketch-in-Latents: Eliciting Unified Reasoning in MLLMs
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:While Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) excel at visual understanding tasks through text reasoning, they often fall short in scenarios requiring visual imagination. Unlike current works that take predefined external toolkits or generate images during thinking, however, humans can form flexible visual-text imagination and interactions during thinking without predefined toolkits, where one important reason is that humans construct the visual-text thinking process in a unified space inside the brain. Inspired by this capability, given that current MLLMs already encode visual and text information in the same feature space, we hold that visual tokens can be seamlessly inserted into the reasoning process carried by text tokens, where ideally, all visual imagination processes can be encoded by the latent features. To achieve this goal, we propose Sketch-in-Latents (SkiLa), a novel paradigm for unified multi-modal reasoning that expands the auto-regressive capabilities of MLLMs to natively generate continuous visual embeddings, termed latent sketch tokens, as visual thoughts. During multi-step reasoning, the model dynamically alternates between textual thinking mode for generating textual think tokens and visual sketching mode for generating latent sketch tokens. A latent visual semantics reconstruction mechanism is proposed to ensure these latent sketch tokens are semantically grounded. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SkiLa achieves superior performance on vision-centric tasks while exhibiting strong generalization to diverse general multi-modal benchmarks. Codes will be released at https://github.com/TungChintao/SkiLa.
FAIR: Focused Attention Is All You Need for Generative Recommendation
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Recently, transformer-based generative recommendation has garnered significant attention for user behavior modeling. However, it often requires discretizing items into multi-code representations (e.g., typically four code tokens or more), which sharply increases the length of the original item sequence. This expansion poses challenges to transformer-based models for modeling user behavior sequences with inherent noises, since they tend to overallocate attention to irrelevant or noisy context. To mitigate this issue, we propose FAIR, the first generative recommendation framework with focused attention, which enhances attention scores to relevant context while suppressing those to irrelevant ones. Specifically, we propose (1) a focused attention mechanism integrated into the standard Transformer, which learns two separate sets of Q and K attention weights and computes their difference as the final attention scores to eliminate attention noise while focusing on relevant contexts; (2) a noise-robustness objective, which encourages the model to maintain stable attention patterns under stochastic perturbations, preventing undesirable shifts toward irrelevant context due to noise; and (3) a mutual information maximization objective, which guides the model to identify contexts that are most informative for next-item prediction. We validate the effectiveness of FAIR on four public benchmarks, demonstrating its superior performance compared to existing methods.
Beyond Higher Rank: Token-wise Input-Output Projections for Efficient Low-Rank Adaptation
Oct 27, 2025



Abstract:Low-rank adaptation (LoRA) is a parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) method widely used in large language models (LLMs). LoRA essentially describes the projection of an input space into a low-dimensional output space, with the dimensionality determined by the LoRA rank. In standard LoRA, all input tokens share the same weights and undergo an identical input-output projection. This limits LoRA's ability to capture token-specific information due to the inherent semantic differences among tokens. To address this limitation, we propose Token-wise Projected Low-Rank Adaptation (TopLoRA), which dynamically adjusts LoRA weights according to the input token, thereby learning token-wise input-output projections in an end-to-end manner. Formally, the weights of TopLoRA can be expressed as $B\Sigma_X A$, where $A$ and $B$ are low-rank matrices (as in standard LoRA), and $\Sigma_X$ is a diagonal matrix generated from each input token $X$. Notably, TopLoRA does not increase the rank of LoRA weights but achieves more granular adaptation by learning token-wise LoRA weights (i.e., token-wise input-output projections). Extensive experiments across multiple models and datasets demonstrate that TopLoRA consistently outperforms LoRA and its variants. The code is available at https://github.com/Leopold1423/toplora-neurips25.
Is Model Editing Built on Sand? Revealing Its Illusory Success and Fragile Foundation
Oct 01, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) inevitably encode outdated or incorrect knowledge. Updating, deleting, and forgetting such knowledge is important for alignment, safety, and other issues. To address this issue, model editing has emerged as a promising paradigm: by precisely editing a small subset of parameters such that a specific fact is updated while preserving other knowledge. Despite its great success reported in previous papers, we find the apparent reliability of editing rests on a fragile foundation and the current literature is largely driven by illusory success. The fundamental goal of steering the model's output toward a target with minimal modification would encourage exploiting hidden shortcuts, rather than utilizing real semantics. This problem directly challenges the feasibility of the current model editing literature at its very foundation, as shortcuts are inherently at odds with robust knowledge integration. Coincidentally, this issue has long been obscured by evaluation frameworks that lack the design of negative examples. To uncover it, we systematically develop a suite of new evaluation methods. Strikingly, we find that state-of-the-art approaches collapse even under the simplest negation queries. Our empirical evidence shows that editing is likely to be based on shortcuts rather than full semantics, calling for an urgent reconsideration of the very basis of model editing before further advancements can be meaningfully pursued.
BoRA: Towards More Expressive Low-Rank Adaptation with Block Diversity
Aug 09, 2025



Abstract:Low-rank adaptation (LoRA) is a parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) method widely used in large language models (LLMs). It approximates the update of a pretrained weight matrix $W\in\mathbb{R}^{m\times n}$ by the product of two low-rank matrices, $BA$, where $A \in\mathbb{R}^{r\times n}$ and $B\in\mathbb{R}^{m\times r} (r\ll\min\{m,n\})$. Increasing the dimension $r$ can raise the rank of LoRA weights (i.e., $BA$), which typically improves fine-tuning performance but also significantly increases the number of trainable parameters. In this paper, we propose Block Diversified Low-Rank Adaptation (BoRA), which improves the rank of LoRA weights with a small number of additional parameters. Specifically, BoRA treats the product $BA$ as a block matrix multiplication, where $A$ and $B$ are partitioned into $b$ blocks along the columns and rows, respectively (i.e., $A=[A_1,\dots,A_b]$ and $B=[B_1,\dots,B_b]^\top$). Consequently, the product $BA$ becomes the concatenation of the block products $B_iA_j$ for $i,j\in[b]$. To enhance the diversity of different block products, BoRA introduces a unique diagonal matrix $\Sigma_{i,j} \in \mathbb{R}^{r\times r}$ for each block multiplication, resulting in $B_i \Sigma_{i,j} A_j$. By leveraging these block-wise diagonal matrices, BoRA increases the rank of LoRA weights by a factor of $b$ while only requiring $b^2r$ additional parameters. Extensive experiments across multiple datasets and models demonstrate the superiority of BoRA, and ablation studies further validate its scalability.
Adapter Naturally Serves as Decoupler for Cross-Domain Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation
Jun 09, 2025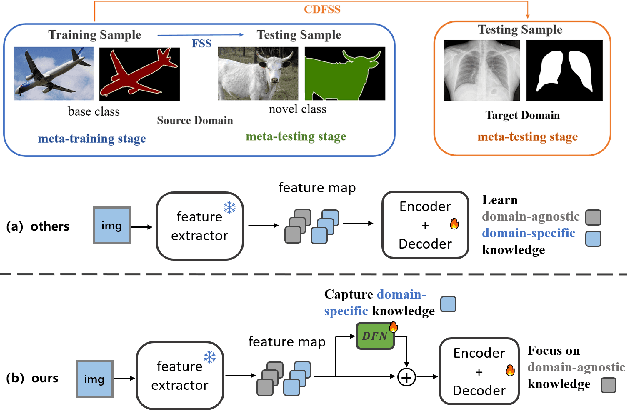
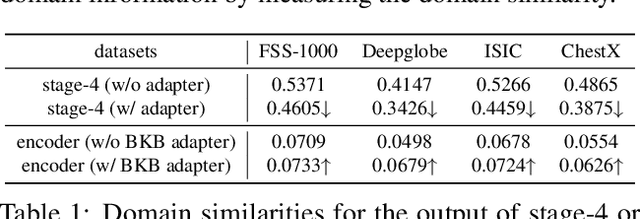
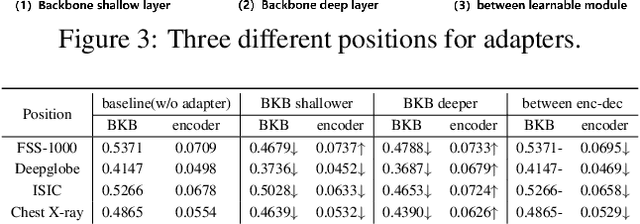
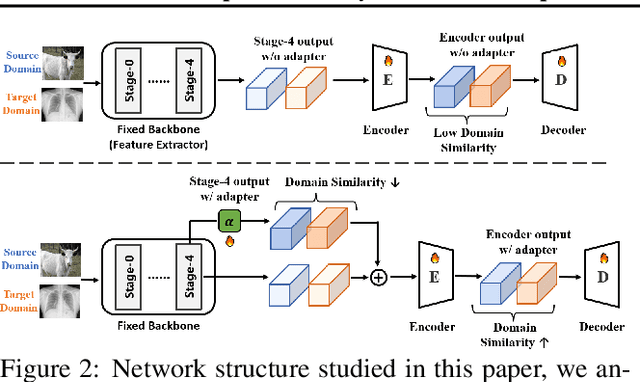
Abstract:Cross-domain few-shot segmentation (CD-FSS) is proposed to pre-train the model on a source-domain dataset with sufficient samples, and then transfer the model to target-domain datasets where only a few samples are available for efficient fine-tuning. There are majorly two challenges in this task: (1) the domain gap and (2) fine-tuning with scarce data. To solve these challenges, we revisit the adapter-based methods, and discover an intriguing insight not explored in previous works: the adapter not only helps the fine-tuning of downstream tasks but also naturally serves as a domain information decoupler. Then, we delve into this finding for an interpretation, and find the model's inherent structure could lead to a natural decoupling of domain information. Building upon this insight, we propose the Domain Feature Navigator (DFN), which is a structure-based decoupler instead of loss-based ones like current works, to capture domain-specific information, thereby directing the model's attention towards domain-agnostic knowledge. Moreover, to prevent the potential excessive overfitting of DFN during the source-domain training, we further design the SAM-SVN method to constrain DFN from learning sample-specific knowledge. On target domains, we freeze the model and fine-tune the DFN to learn target-specific knowledge specific. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method surpasses the state-of-the-art method in CD-FSS significantly by 2.69% and 4.68% MIoU in 1-shot and 5-shot scenarios, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge