Shijie Xu
Wavelet-Aware Anomaly Detection in Multi-Channel User Logs via Deviation Modulation and Resolution-Adaptive Attention
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Insider threat detection is a key challenge in enterprise security, relying on user activity logs that capture rich and complex behavioral patterns. These logs are often multi-channel, non-stationary, and anomalies are rare, making anomaly detection challenging. To address these issues, we propose a novel framework that integrates wavelet-aware modulation, multi-resolution wavelet decomposition, and resolution-adaptive attention for robust anomaly detection. Our approach first applies a deviation-aware modulation scheme to suppress routine behaviors while amplifying anomalous deviations. Next, discrete wavelet transform (DWT) decomposes the log signals into multi-resolution representations, capturing both long-term trends and short-term anomalies. Finally, a learnable attention mechanism dynamically reweights the most discriminative frequency bands for detection. On the CERT r4.2 benchmark, our approach consistently outperforms existing baselines in precision, recall, and F1 score across various time granularities and scenarios.
Xiaomi MiMo-VL-Miloco Technical Report
Dec 22, 2025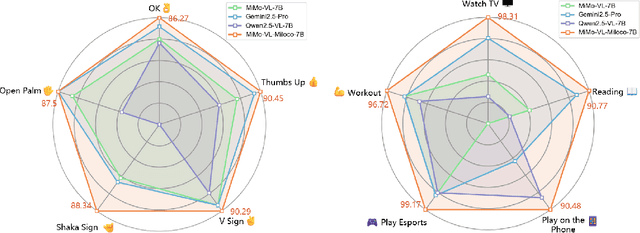
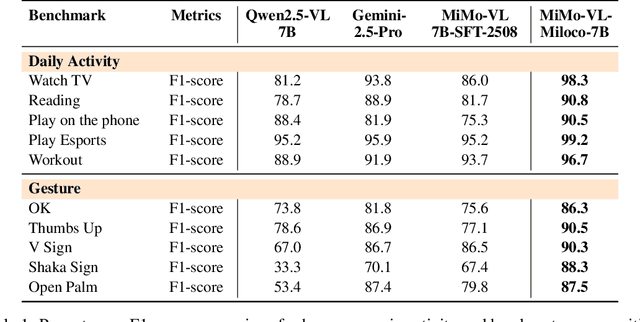
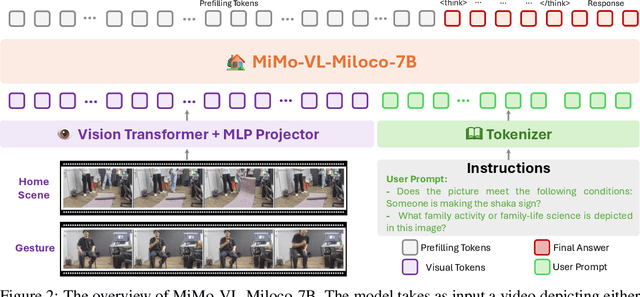
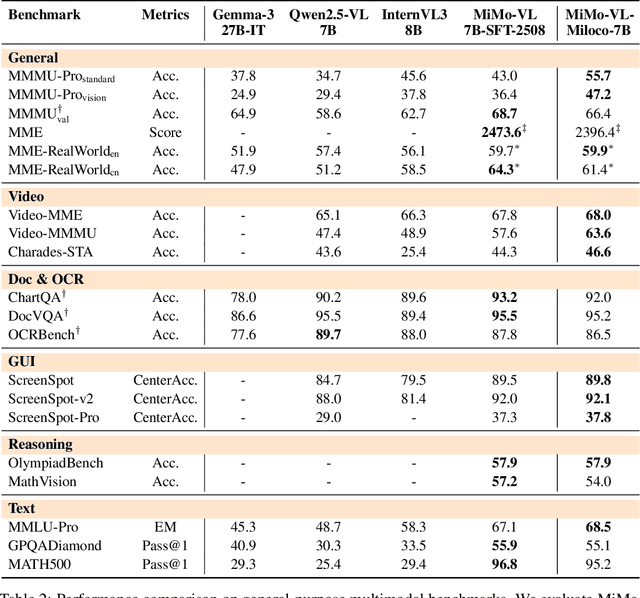
Abstract:We open-source MiMo-VL-Miloco-7B and its quantized variant MiMo-VL-Miloco-7B-GGUF, a pair of home-centric vision-language models that achieve strong performance on both home-scenario understanding and general multimodal reasoning. Built on the MiMo-VL-7B backbone, MiMo-VL-Miloco-7B is specialized for smart-home environments, attaining leading F1 scores on gesture recognition and common home-scenario understanding, while also delivering consistent gains across video benchmarks such as Video-MME, Video-MMMU, and Charades-STA, as well as language understanding benchmarks including MMMU-Pro and MMLU-Pro. In our experiments, MiMo-VL-Miloco-7B outperforms strong closed-source and open-source baselines on home-scenario understanding and several multimodal reasoning benchmarks. To balance specialization and generality, we design a two-stage training pipeline that combines supervised fine-tuning with reinforcement learning based on Group Relative Policy Optimization, leveraging efficient multi-domain data. We further incorporate chain-of-thought supervision and token-budget-aware reasoning, enabling the model to learn knowledge in a data-efficient manner while also performing reasoning efficiently. Our analysis shows that targeted home-scenario training not only enhances activity and gesture understanding, but also improves text-only reasoning with only modest trade-offs on document-centric tasks. Model checkpoints, quantized GGUF weights, and our home-scenario evaluation toolkit are publicly available at https://github.com/XiaoMi/xiaomi-mimo-vl-miloco to support research and deployment in real-world smart-home applications.
The Panaceas for Improving Low-Rank Decomposition in Communication-Efficient Federated Learning
May 29, 2025Abstract:To improve the training efficiency of federated learning (FL), previous research has employed low-rank decomposition techniques to reduce communication overhead. In this paper, we seek to enhance the performance of these low-rank decomposition methods. Specifically, we focus on three key issues related to decomposition in FL: what to decompose, how to decompose, and how to aggregate. Subsequently, we introduce three novel techniques: Model Update Decomposition (MUD), Block-wise Kronecker Decomposition (BKD), and Aggregation-Aware Decomposition (AAD), each targeting a specific issue. These techniques are complementary and can be applied simultaneously to achieve optimal performance. Additionally, we provide a rigorous theoretical analysis to ensure the convergence of the proposed MUD. Extensive experimental results show that our approach achieves faster convergence and superior accuracy compared to relevant baseline methods. The code is available at https://github.com/Leopold1423/fedmud-icml25.
Mixed-Precision Embeddings for Large-Scale Recommendation Models
Sep 30, 2024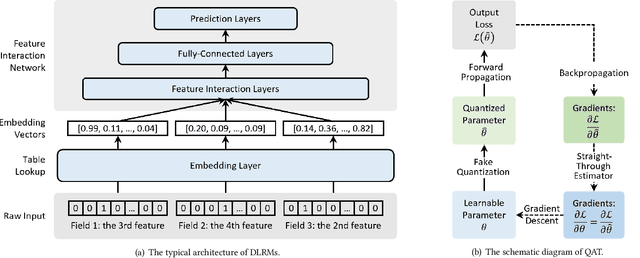
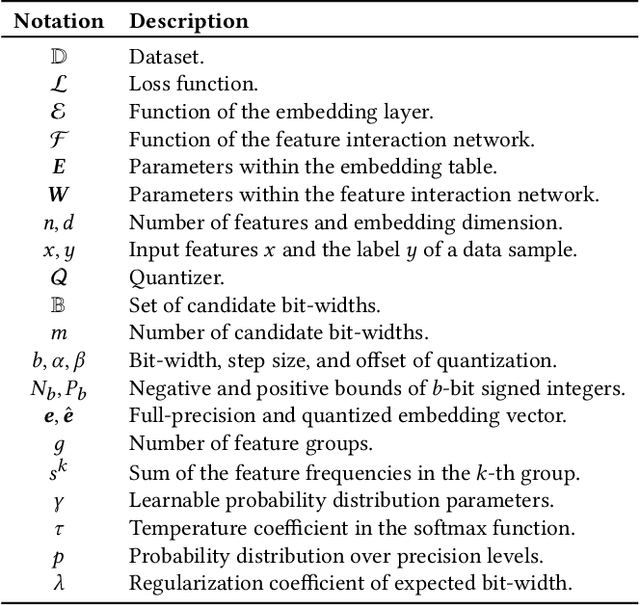
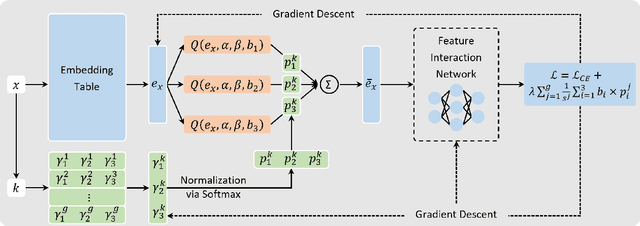
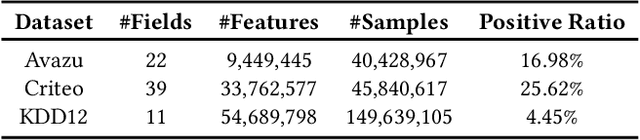
Abstract:Embedding techniques have become essential components of large databases in the deep learning era. By encoding discrete entities, such as words, items, or graph nodes, into continuous vector spaces, embeddings facilitate more efficient storage, retrieval, and processing in large databases. Especially in the domain of recommender systems, millions of categorical features are encoded as unique embedding vectors, which facilitates the modeling of similarities and interactions among features. However, numerous embedding vectors can result in significant storage overhead. In this paper, we aim to compress the embedding table through quantization techniques. Given that features vary in importance levels, we seek to identify an appropriate precision for each feature to balance model accuracy and memory usage. To this end, we propose a novel embedding compression method, termed Mixed-Precision Embeddings (MPE). Specifically, to reduce the size of the search space, we first group features by frequency and then search precision for each feature group. MPE further learns the probability distribution over precision levels for each feature group, which can be used to identify the most suitable precision with a specially designed sampling strategy. Extensive experiments on three public datasets demonstrate that MPE significantly outperforms existing embedding compression methods. Remarkably, MPE achieves about 200x compression on the Criteo dataset without comprising the prediction accuracy.
FedBAT: Communication-Efficient Federated Learning via Learnable Binarization
Aug 06, 2024



Abstract:Federated learning is a promising distributed machine learning paradigm that can effectively exploit large-scale data without exposing users' privacy. However, it may incur significant communication overhead, thereby potentially impairing the training efficiency. To address this challenge, numerous studies suggest binarizing the model updates. Nonetheless, traditional methods usually binarize model updates in a post-training manner, resulting in significant approximation errors and consequent degradation in model accuracy. To this end, we propose Federated Binarization-Aware Training (FedBAT), a novel framework that directly learns binary model updates during the local training process, thus inherently reducing the approximation errors. FedBAT incorporates an innovative binarization operator, along with meticulously designed derivatives to facilitate efficient learning. In addition, we establish theoretical guarantees regarding the convergence of FedBAT. Extensive experiments are conducted on four popular datasets. The results show that FedBAT significantly accelerates the convergence and exceeds the accuracy of baselines by up to 9\%, even surpassing that of FedAvg in some cases.
Masked Random Noise for Communication Efficient Federaetd Learning
Aug 06, 2024Abstract:Federated learning is a promising distributed training paradigm that effectively safeguards data privacy. However, it may involve significant communication costs, which hinders training efficiency. In this paper, we aim to enhance communication efficiency from a new perspective. Specifically, we request the distributed clients to find optimal model updates relative to global model parameters within predefined random noise. For this purpose, we propose Federated Masked Random Noise (FedMRN), a novel framework that enables clients to learn a 1-bit mask for each model parameter and apply masked random noise (i.e., the Hadamard product of random noise and masks) to represent model updates. To make FedMRN feasible, we propose an advanced mask training strategy, called progressive stochastic masking (PSM). After local training, each client only need to transmit local masks and a random seed to the server. Additionally, we provide theoretical guarantees for the convergence of FedMRN under both strongly convex and non-convex assumptions. Extensive experiments are conducted on four popular datasets. The results show that FedMRN exhibits superior convergence speed and test accuracy compared to relevant baselines, while attaining a similar level of accuracy as FedAvg.
Weighted Laplacian and Its Theoretical Applications
Nov 23, 2019


Abstract:In this paper, we develop a novel weighted Laplacian method, which is partially inspired by the theory of graph Laplacian, to study recent popular graph problems, such as multilevel graph partitioning and balanced minimum cut problem, in a more convenient manner. Since the weighted Laplacian strategy inherits the virtues of spectral methods, graph algorithms designed using weighted Laplacian will necessarily possess more robust theoretical guarantees for algorithmic performances, comparing with those existing algorithms that are heuristically proposed. In order to illustrate its powerful utility both in theory and in practice, we also present two effective applications of our weighted Laplacian method to multilevel graph partitioning and balanced minimum cut problem, respectively. By means of variational methods and theory of partial differential equations (PDEs), we have established the equivalence relations among the weighted cut problem, balanced minimum cut problem and the initial clustering problem that arises in the middle stage of graph partitioning algorithms under a multilevel structure. These equivalence relations can indeed provide solid theoretical support for algorithms based on our proposed weighted Laplacian strategy. Moreover, from the perspective of the application to the balanced minimum cut problem, weighted Laplacian can make it possible for research of numerical solutions of PDEs to be a powerful tool for the algorithmic study of graph problems. Experimental results also indicate that the algorithm embedded with our strategy indeed outperforms other existing graph algorithms, especially in terms of accuracy, thus verifying the efficacy of the proposed weighted Laplacian.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge