Fangquan Lin
Intrinsic and Extrinsic Factor Disentanglement for Recommendation in Various Context Scenarios
Mar 05, 2025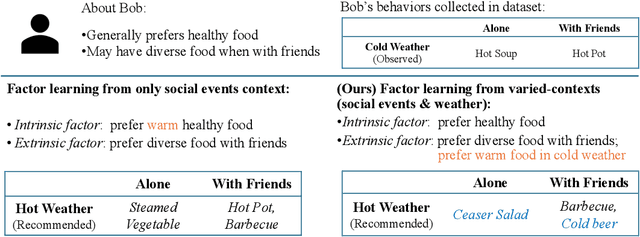
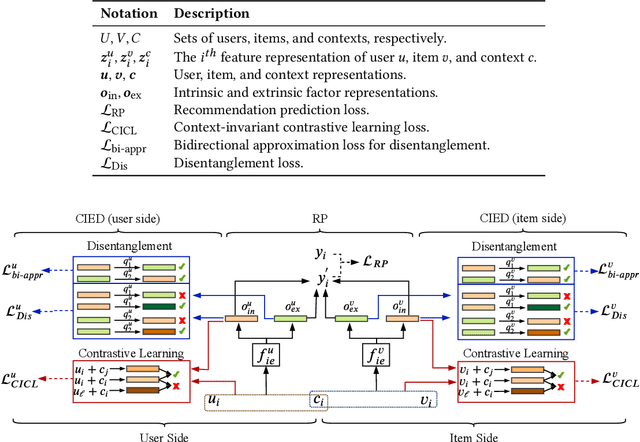
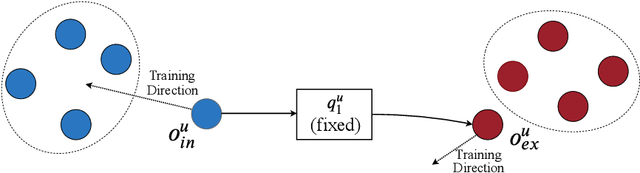
Abstract:In recommender systems, the patterns of user behaviors (e.g., purchase, click) may vary greatly in different contexts (e.g., time and location). This is because user behavior is jointly determined by two types of factors: intrinsic factors, which reflect consistent user preference, and extrinsic factors, which reflect external incentives that may vary in different contexts. Differentiating between intrinsic and extrinsic factors helps learn user behaviors better. However, existing studies have only considered differentiating them from a single, pre-defined context (e.g., time or location), ignoring the fact that a user's extrinsic factors may be influenced by the interplay of various contexts at the same time. In this paper, we propose the Intrinsic-Extrinsic Disentangled Recommendation (IEDR) model, a generic framework that differentiates intrinsic from extrinsic factors considering various contexts simultaneously, enabling more accurate differentiation of factors and hence the improvement of recommendation accuracy. IEDR contains a context-invariant contrastive learning component to capture intrinsic factors, and a disentanglement component to extract extrinsic factors under the interplay of various contexts. The two components work together to achieve effective factor learning. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate IEDR's effectiveness in learning disentangled factors and significantly improving recommendation accuracy by up to 4% in NDCG.
One Size doesn't Fit All: A Personalized Conversational Tutoring Agent for Mathematics Instruction
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have been increasingly employed in various intelligent educational systems, simulating human tutors to facilitate effective human-machine interaction. However, previous studies often overlook the significance of recognizing and adapting to individual learner characteristics. Such adaptation is crucial for enhancing student engagement and learning efficiency, particularly in mathematics instruction, where diverse learning styles require personalized strategies to promote comprehension and enthusiasm. In this paper, we propose a \textbf{P}erson\textbf{A}lized \textbf{C}onversational tutoring ag\textbf{E}nt (PACE) for mathematics instruction. PACE simulates students' learning styles based on the Felder and Silverman learning style model, aligning with each student's persona. In this way, our PACE can effectively assess the personality of students, allowing to develop individualized teaching strategies that resonate with their unique learning styles. To further enhance students' comprehension, PACE employs the Socratic teaching method to provide instant feedback and encourage deep thinking. By constructing personalized teaching data and training models, PACE demonstrates the ability to identify and adapt to the unique needs of each student, significantly improving the overall learning experience and outcomes. Moreover, we establish multi-aspect evaluation criteria and conduct extensive analysis to assess the performance of personalized teaching. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our model in personalizing the educational experience and motivating students compared to existing methods.
SymAgent: A Neural-Symbolic Self-Learning Agent Framework for Complex Reasoning over Knowledge Graphs
Feb 05, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements have highlighted that Large Language Models (LLMs) are prone to hallucinations when solving complex reasoning problems, leading to erroneous results. To tackle this issue, researchers incorporate Knowledge Graphs (KGs) to improve the reasoning ability of LLMs. However, existing methods face two limitations: 1) they typically assume that all answers to the questions are contained in KGs, neglecting the incompleteness issue of KGs, and 2) they treat the KG as a static repository and overlook the implicit logical reasoning structures inherent in KGs. In this paper, we introduce SymAgent, an innovative neural-symbolic agent framework that achieves collaborative augmentation between KGs and LLMs. We conceptualize KGs as dynamic environments and transform complex reasoning tasks into a multi-step interactive process, enabling KGs to participate deeply in the reasoning process. SymAgent consists of two modules: Agent-Planner and Agent-Executor. The Agent-Planner leverages LLM's inductive reasoning capability to extract symbolic rules from KGs, guiding efficient question decomposition. The Agent-Executor autonomously invokes predefined action tools to integrate information from KGs and external documents, addressing the issues of KG incompleteness. Furthermore, we design a self-learning framework comprising online exploration and offline iterative policy updating phases, enabling the agent to automatically synthesize reasoning trajectories and improve performance. Experimental results demonstrate that SymAgent with weak LLM backbones (i.e., 7B series) yields better or comparable performance compared to various strong baselines. Further analysis reveals that our agent can identify missing triples, facilitating automatic KG updates.
Filter-then-Generate: Large Language Models with Structure-Text Adapter for Knowledge Graph Completion
Dec 12, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) present massive inherent knowledge and superior semantic comprehension capability, which have revolutionized various tasks in natural language processing. Despite their success, a critical gap remains in enabling LLMs to perform knowledge graph completion (KGC). Empirical evidence suggests that LLMs consistently perform worse than conventional KGC approaches, even through sophisticated prompt design or tailored instruction-tuning. Fundamentally, applying LLMs on KGC introduces several critical challenges, including a vast set of entity candidates, hallucination issue of LLMs, and under-exploitation of the graph structure. To address these challenges, we propose a novel instruction-tuning-based method, namely FtG. Specifically, we present a \textit{filter-then-generate} paradigm and formulate the KGC task into a multiple-choice question format. In this way, we can harness the capability of LLMs while mitigating the issue casused by hallucinations. Moreover, we devise a flexible ego-graph serialization prompt and employ a structure-text adapter to couple structure and text information in a contextualized manner. Experimental results demonstrate that FtG achieves substantial performance gain compared to existing state-of-the-art methods. The instruction dataset and code are available at \url{https://github.com/LB0828/FtG}.
Solving General Natural-Language-Description Optimization Problems with Large Language Models
Jul 09, 2024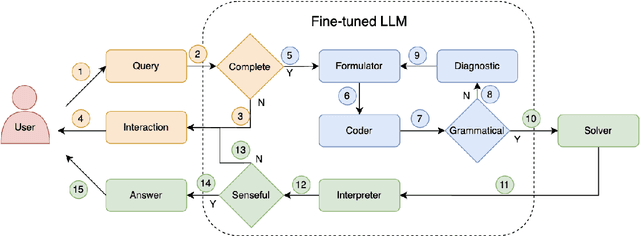
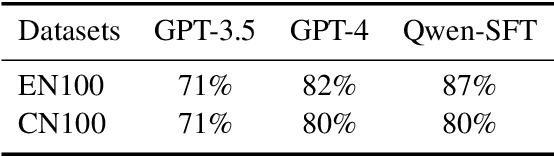

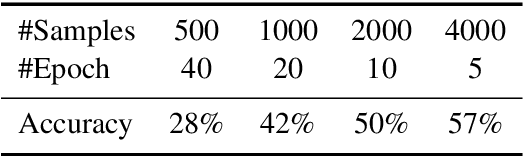
Abstract:Optimization problems seek to find the best solution to an objective under a set of constraints, and have been widely investigated in real-world applications. Modeling and solving optimization problems in a specific domain typically require a combination of domain knowledge, mathematical skills, and programming ability, making it difficult for general users and even domain professionals. In this paper, we propose a novel framework called OptLLM that augments LLMs with external solvers. Specifically, OptLLM accepts user queries in natural language, convert them into mathematical formulations and programming codes, and calls the solvers to calculate the results for decision-making. In addition, OptLLM supports multi-round dialogues to gradually refine the modeling and solving of optimization problems. To illustrate the effectiveness of OptLLM, we provide tutorials on three typical optimization applications and conduct experiments on both prompt-based GPT models and a fine-tuned Qwen model using a large-scale selfdeveloped optimization dataset. Experimental results show that OptLLM works with various LLMs, and the fine-tuned model achieves an accuracy boost compared to the promptbased models. Some features of OptLLM framework have been available for trial since June 2023 (https://opt.alibabacloud.com/chat or https://opt.aliyun.com/chat).
A Stochastic Online Forecast-and-Optimize Framework for Real-Time Energy Dispatch in Virtual Power Plants under Uncertainty
Sep 15, 2023Abstract:Aggregating distributed energy resources in power systems significantly increases uncertainties, in particular caused by the fluctuation of renewable energy generation. This issue has driven the necessity of widely exploiting advanced predictive control techniques under uncertainty to ensure long-term economics and decarbonization. In this paper, we propose a real-time uncertainty-aware energy dispatch framework, which is composed of two key elements: (i) A hybrid forecast-and-optimize sequential task, integrating deep learning-based forecasting and stochastic optimization, where these two stages are connected by the uncertainty estimation at multiple temporal resolutions; (ii) An efficient online data augmentation scheme, jointly involving model pre-training and online fine-tuning stages. In this way, the proposed framework is capable to rapidly adapt to the real-time data distribution, as well as to target on uncertainties caused by data drift, model discrepancy and environment perturbations in the control process, and finally to realize an optimal and robust dispatch solution. The proposed framework won the championship in CityLearn Challenge 2022, which provided an influential opportunity to investigate the potential of AI application in the energy domain. In addition, comprehensive experiments are conducted to interpret its effectiveness in the real-life scenario of smart building energy management.
KDD CUP 2022 Wind Power Forecasting Team 88VIP Solution
Aug 18, 2022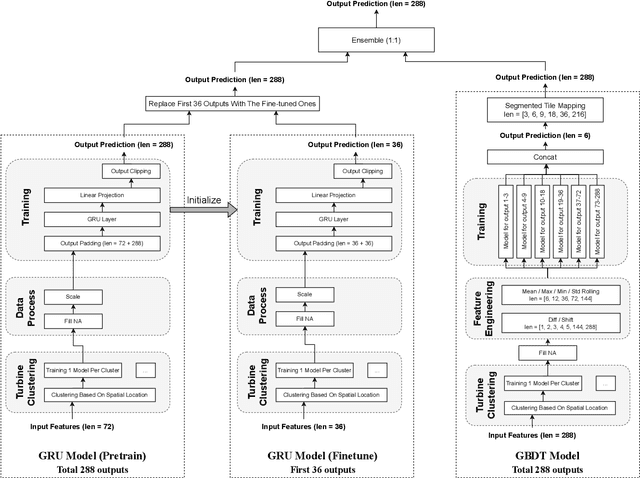
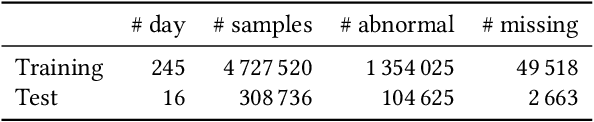
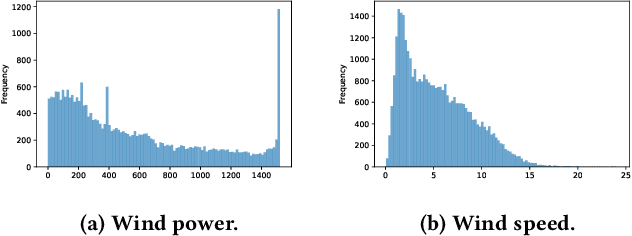
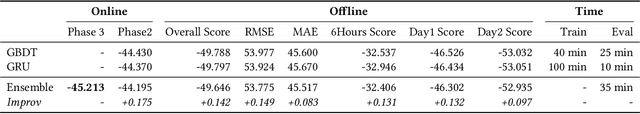
Abstract:KDD CUP 2022 proposes a time-series forecasting task on spatial dynamic wind power dataset, in which the participants are required to predict the future generation given the historical context factors. The evaluation metrics contain RMSE and MAE. This paper describes the solution of Team 88VIP, which mainly comprises two types of models: a gradient boosting decision tree to memorize the basic data patterns and a recurrent neural network to capture the deep and latent probabilistic transitions. Ensembling these models contributes to tackle the fluctuation of wind power, and training submodels targets on the distinguished properties in heterogeneous timescales of forecasting, from minutes to days. In addition, feature engineering, imputation techniques and the design of offline evaluation are also described in details. The proposed solution achieves an overall online score of -45.213 in Phase 3.
GUIM -- General User and Item Embedding with Mixture of Representation in E-commerce
Jul 02, 2022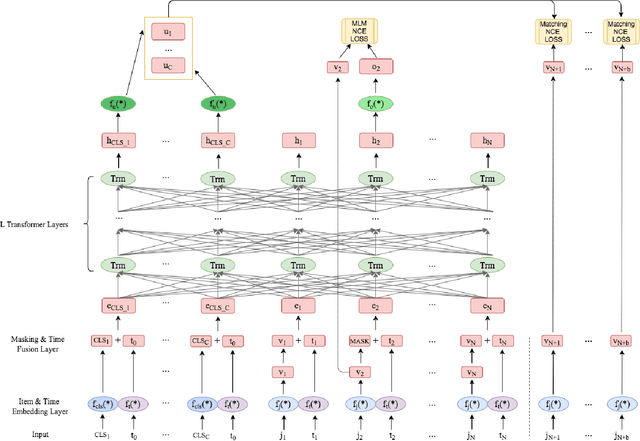

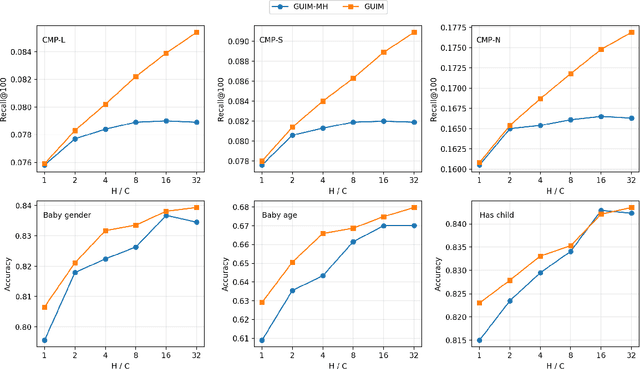
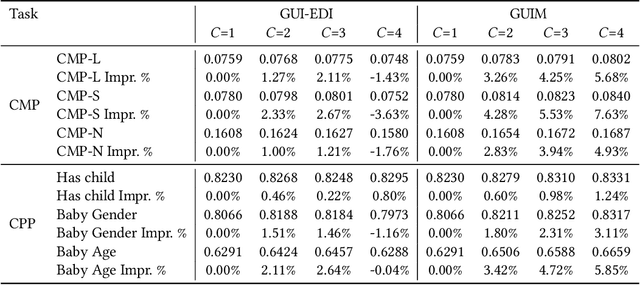
Abstract:Our goal is to build general representation (embedding) for each user and each product item across Alibaba's businesses, including Taobao and Tmall which are among the world's biggest e-commerce websites. The representation of users and items has been playing a critical role in various downstream applications, including recommendation system, search, marketing, demand forecasting and so on. Inspired from the BERT model in natural language processing (NLP) domain, we propose a GUIM (General User Item embedding with Mixture of representation) model to achieve the goal with massive, structured, multi-modal data including the interactions among hundreds of millions of users and items. We utilize mixture of representation (MoR) as a novel representation form to model the diverse interests of each user. In addition, we use the InfoNCE from contrastive learning to avoid intractable computational costs due to the numerous size of item (token) vocabulary. Finally, we propose a set of representative downstream tasks to serve as a standard benchmark to evaluate the quality of the learned user and/or item embeddings, analogous to the GLUE benchmark in NLP domain. Our experimental results in these downstream tasks clearly show the comparative value of embeddings learned from our GUIM model.
CoRe: An Efficient Coarse-refined Training Framework for BERT
Nov 27, 2020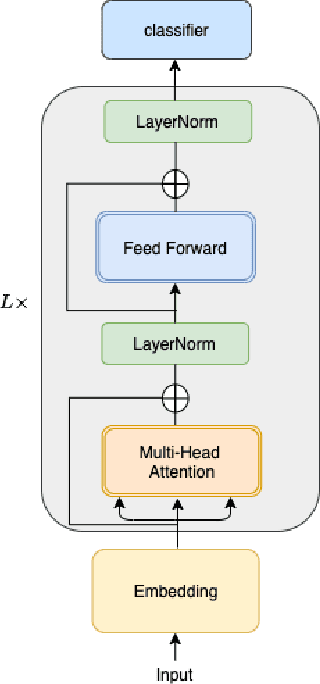
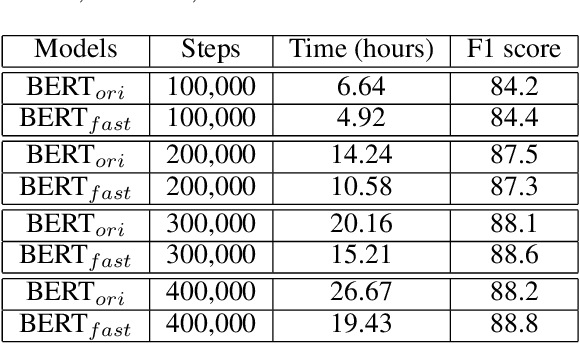
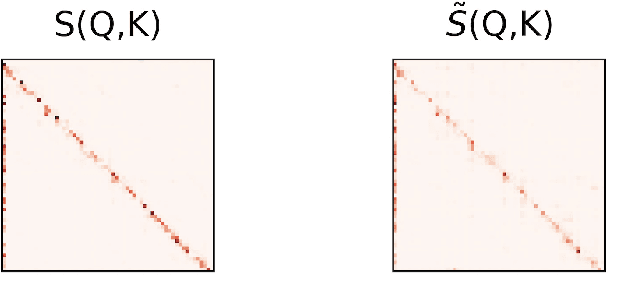
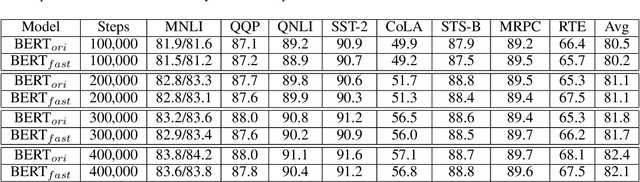
Abstract:In recent years, BERT has made significant breakthroughs on many natural language processing tasks and attracted great attentions. Despite its accuracy gains, the BERT model generally involves a huge number of parameters and needs to be trained on massive datasets, so training such a model is computationally very challenging and time-consuming. Hence, training efficiency should be a critical issue. In this paper, we propose a novel coarse-refined training framework named CoRe to speed up the training of BERT. Specifically, we decompose the training process of BERT into two phases. In the first phase, by introducing fast attention mechanism and decomposing the large parameters in the feed-forward network sub-layer, we construct a relaxed BERT model which has much less parameters and much lower model complexity than the original BERT, so the relaxed model can be quickly trained. In the second phase, we transform the trained relaxed BERT model into the original BERT and further retrain the model. Thanks to the desired initialization provided by the relaxed model, the retraining phase requires much less training steps, compared with training an original BERT model from scratch with a random initialization. Experimental results show that the proposed CoRe framework can greatly reduce the training time without reducing the performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge