Jihan Zhang
One Size doesn't Fit All: A Personalized Conversational Tutoring Agent for Mathematics Instruction
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have been increasingly employed in various intelligent educational systems, simulating human tutors to facilitate effective human-machine interaction. However, previous studies often overlook the significance of recognizing and adapting to individual learner characteristics. Such adaptation is crucial for enhancing student engagement and learning efficiency, particularly in mathematics instruction, where diverse learning styles require personalized strategies to promote comprehension and enthusiasm. In this paper, we propose a \textbf{P}erson\textbf{A}lized \textbf{C}onversational tutoring ag\textbf{E}nt (PACE) for mathematics instruction. PACE simulates students' learning styles based on the Felder and Silverman learning style model, aligning with each student's persona. In this way, our PACE can effectively assess the personality of students, allowing to develop individualized teaching strategies that resonate with their unique learning styles. To further enhance students' comprehension, PACE employs the Socratic teaching method to provide instant feedback and encourage deep thinking. By constructing personalized teaching data and training models, PACE demonstrates the ability to identify and adapt to the unique needs of each student, significantly improving the overall learning experience and outcomes. Moreover, we establish multi-aspect evaluation criteria and conduct extensive analysis to assess the performance of personalized teaching. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our model in personalizing the educational experience and motivating students compared to existing methods.
Sensor-based Multi-Robot Search and Coverage with Spatial Separation in Unstructured Environments
Mar 04, 2024



Abstract:Multi-robot systems have increasingly become instrumental in tackling search and coverage problems. However, the challenge of optimizing task efficiency without compromising task success still persists, particularly in expansive, unstructured environments with dense obstacles. This paper presents an innovative, decentralized Voronoi-based approach for search and coverage to reactively navigate these complexities while maintaining safety. This approach leverages the active sensing capabilities of multi-robot systems to supplement GIS (Geographic Information System), offering a more comprehensive and real-time understanding of the environment. Based on point cloud data, which is inherently non-convex and unstructured, this method efficiently generates collision-free Voronoi regions using only local sensing information through spatial decomposition and spherical mirroring techniques. Then, deadlock-aware guided map integrated with a gradient-optimized, centroid Voronoi-based coverage control policy, is constructed to improve efficiency by avoiding exhaustive searches and local sensing pitfalls. The effectiveness of our algorithm has been validated through extensive numerical simulations in high-fidelity environments, demonstrating significant improvements in both task success rate, coverage ratio, and task execution time compared with others.
Improving Ultrasound Tongue Image Reconstruction from Lip Images Using Self-supervised Learning and Attention Mechanism
Jun 20, 2021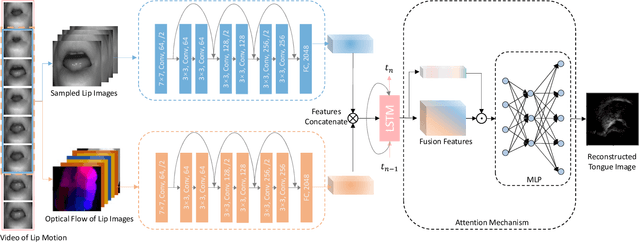
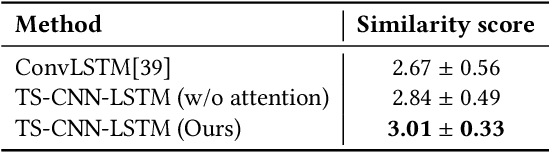

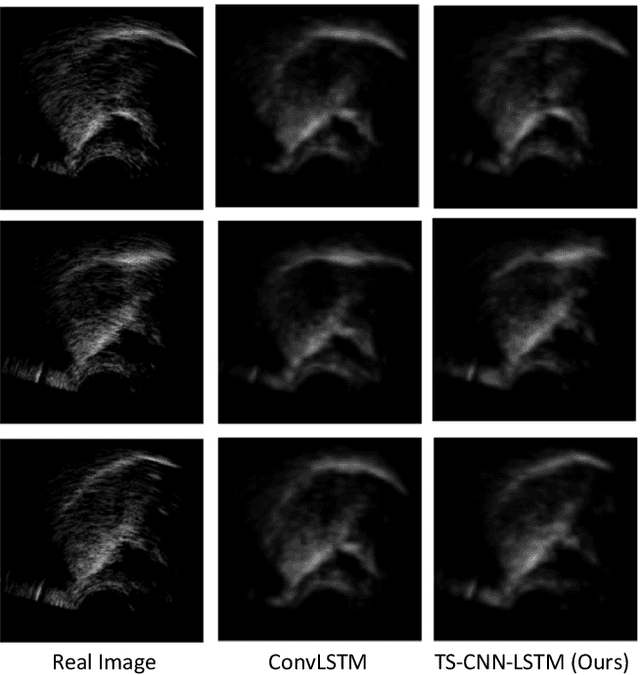
Abstract:Speech production is a dynamic procedure, which involved multi human organs including the tongue, jaw and lips. Modeling the dynamics of the vocal tract deformation is a fundamental problem to understand the speech, which is the most common way for human daily communication. Researchers employ several sensory streams to describe the process simultaneously, which are incontrovertibly statistically related to other streams. In this paper, we address the following question: given an observable image sequences of lips, can we picture the corresponding tongue motion. We formulated this problem as the self-supervised learning problem, and employ the two-stream convolutional network and long-short memory network for the learning task, with the attention mechanism. We evaluate the performance of the proposed method by leveraging the unlabeled lip videos to predict an upcoming ultrasound tongue image sequence. The results show that our model is able to generate images that close to the real ultrasound tongue images, and results in the matching between two imaging modalities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge