Chenggang Wang
Multi-Constraint Safe Reinforcement Learning via Closed-form Solution for Log-Sum-Exp Approximation of Control Barrier Functions
May 01, 2025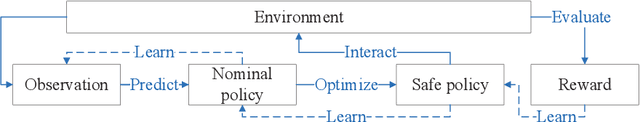
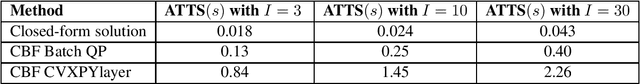
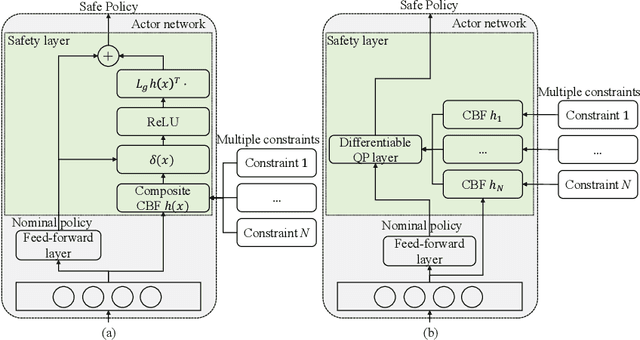
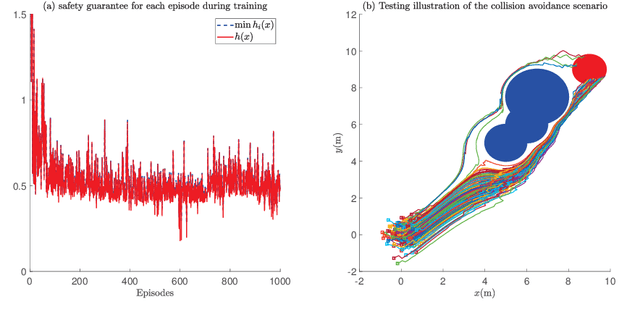
Abstract:The safety of training task policies and their subsequent application using reinforcement learning (RL) methods has become a focal point in the field of safe RL. A central challenge in this area remains the establishment of theoretical guarantees for safety during both the learning and deployment processes. Given the successful implementation of Control Barrier Function (CBF)-based safety strategies in a range of control-affine robotic systems, CBF-based safe RL demonstrates significant promise for practical applications in real-world scenarios. However, integrating these two approaches presents several challenges. First, embedding safety optimization within the RL training pipeline requires that the optimization outputs be differentiable with respect to the input parameters, a condition commonly referred to as differentiable optimization, which is non-trivial to solve. Second, the differentiable optimization framework confronts significant efficiency issues, especially when dealing with multi-constraint problems. To address these challenges, this paper presents a CBF-based safe RL architecture that effectively mitigates the issues outlined above. The proposed approach constructs a continuous AND logic approximation for the multiple constraints using a single composite CBF. By leveraging this approximation, a close-form solution of the quadratic programming is derived for the policy network in RL, thereby circumventing the need for differentiable optimization within the end-to-end safe RL pipeline. This strategy significantly reduces computational complexity because of the closed-form solution while maintaining safety guarantees. Simulation results demonstrate that, in comparison to existing approaches relying on differentiable optimization, the proposed method significantly reduces training computational costs while ensuring provable safety throughout the training process.
Sensor-based Multi-Robot Search and Coverage with Spatial Separation in Unstructured Environments
Mar 04, 2024



Abstract:Multi-robot systems have increasingly become instrumental in tackling search and coverage problems. However, the challenge of optimizing task efficiency without compromising task success still persists, particularly in expansive, unstructured environments with dense obstacles. This paper presents an innovative, decentralized Voronoi-based approach for search and coverage to reactively navigate these complexities while maintaining safety. This approach leverages the active sensing capabilities of multi-robot systems to supplement GIS (Geographic Information System), offering a more comprehensive and real-time understanding of the environment. Based on point cloud data, which is inherently non-convex and unstructured, this method efficiently generates collision-free Voronoi regions using only local sensing information through spatial decomposition and spherical mirroring techniques. Then, deadlock-aware guided map integrated with a gradient-optimized, centroid Voronoi-based coverage control policy, is constructed to improve efficiency by avoiding exhaustive searches and local sensing pitfalls. The effectiveness of our algorithm has been validated through extensive numerical simulations in high-fidelity environments, demonstrating significant improvements in both task success rate, coverage ratio, and task execution time compared with others.
Underwater motions analysis and control of a coupling-tiltable unmanned aerial-aquatic quadrotor
Dec 12, 2023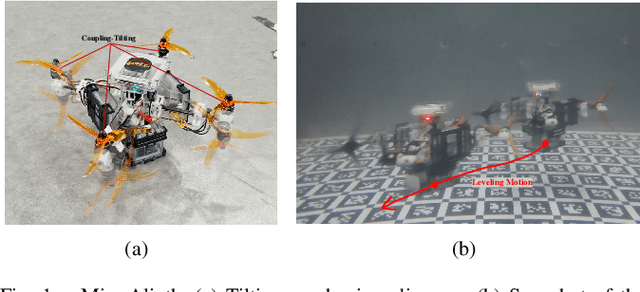
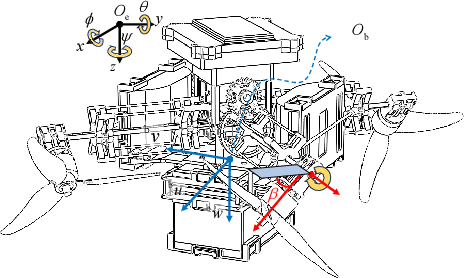
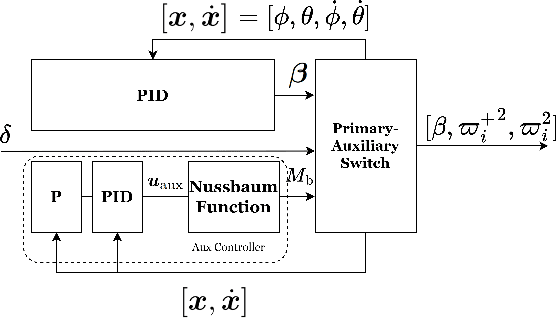
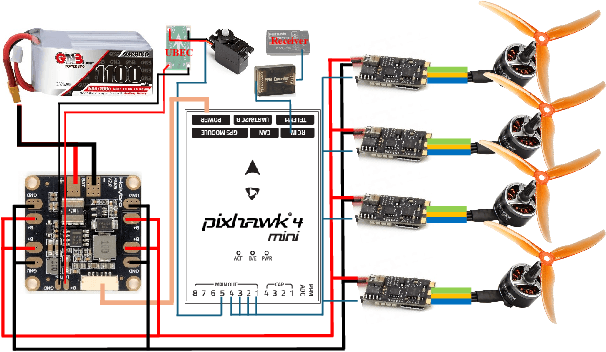
Abstract:This paper proposes a method for analyzing a series of potential motions in a coupling-tiltable aerial-aquatic quadrotor based on its nonlinear dynamics. Some characteristics and constraints derived by this method are specified as Singular Thrust Tilt Angles (STTAs), utilizing to generate motions including planar motions. A switch-based control scheme addresses issues of control direction uncertainty inherent to the mechanical structure by incorporating a saturated Nussbaum function. A high-fidelity simulation environment incorporating a comprehensive hydrodynamic model is built based on a Hardware-In-The-Loop (HITL) setup with Gazebo and a flight control board. The experiments validate the effectiveness of the absolute and quasi planar motions, which cannot be achieved by conventional quadrotors, and demonstrate stable performance when the pitch or roll angle is activated in the auxiliary control channel.
Policy Iteration for Relational MDPs
Jun 20, 2012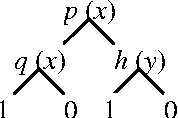
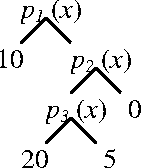
Abstract:Relational Markov Decision Processes are a useful abstraction for complex reinforcement learning problems and stochastic planning problems. Recent work developed representation schemes and algorithms for planning in such problems using the value iteration algorithm. However, exact versions of more complex algorithms, including policy iteration, have not been developed or analyzed. The paper investigates this potential and makes several contributions. First we observe two anomalies for relational representations showing that the value of some policies is not well defined or cannot be calculated for restricted representation schemes used in the literature. On the other hand, we develop a variant of policy iteration that can get around these anomalies. The algorithm includes an aspect of policy improvement in the process of policy evaluation and thus differs from the original algorithm. We show that despite this difference the algorithm converges to the optimal policy.
First Order Decision Diagrams for Relational MDPs
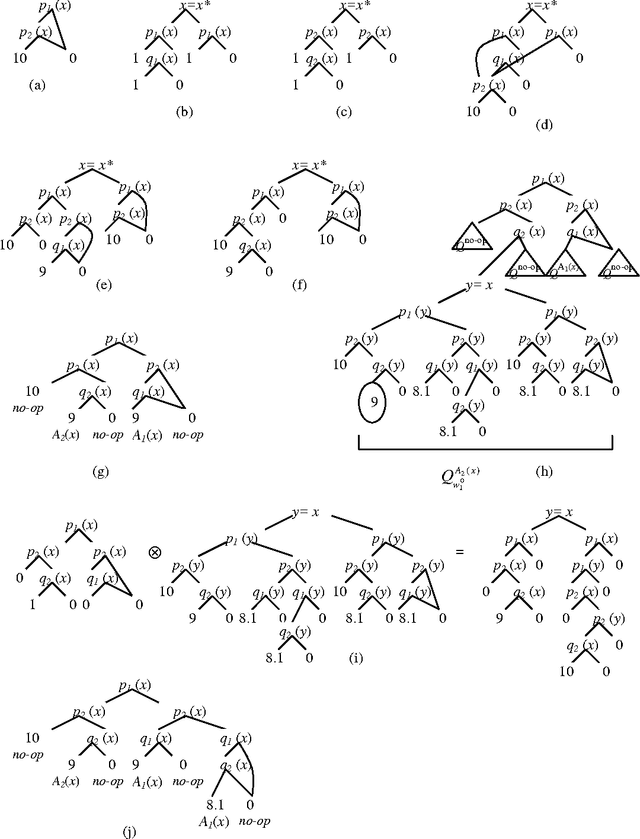
Oct 31, 2011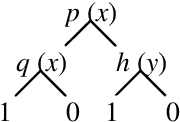

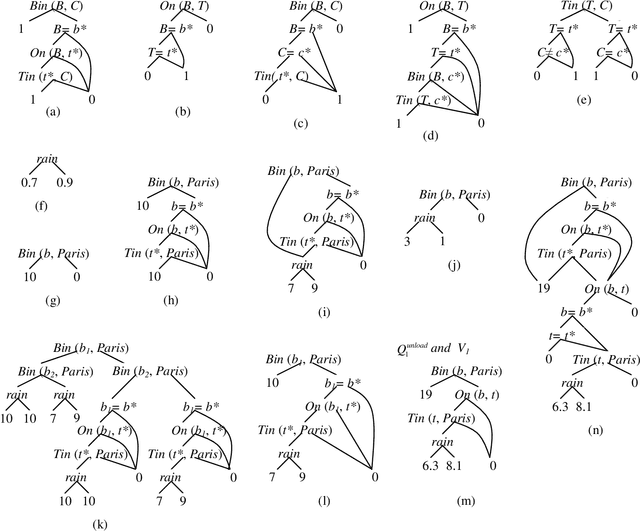
Abstract:Markov decision processes capture sequential decision making under uncertainty, where an agent must choose actions so as to optimize long term reward. The paper studies efficient reasoning mechanisms for Relational Markov Decision Processes (RMDP) where world states have an internal relational structure that can be naturally described in terms of objects and relations among them. Two contributions are presented. First, the paper develops First Order Decision Diagrams (FODD), a new compact representation for functions over relational structures, together with a set of operators to combine FODDs, and novel reduction techniques to keep the representation small. Second, the paper shows how FODDs can be used to develop solutions for RMDPs, where reasoning is performed at the abstract level and the resulting optimal policy is independent of domain size (number of objects) or instantiation. In particular, a variant of the value iteration algorithm is developed by using special operations over FODDs, and the algorithm is shown to converge to the optimal policy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge